Can Hypertension Affect Pregnancy?

Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common medical condition that affects a significant portion of the global population. It is characterized by elevated levels of blood pressure within the arteries, and if left untreated, can lead to various complications and health risks.
One particularly vulnerable population group affected by hypertension is pregnant women. Pregnancy itself places significant physiological demands on the body, and when coupled with the presence of hypertension, can lead to detrimental effects on both the mother and the developing fetus.
This article aims to explore the relationship between hypertension and pregnancy, examining the potential complications that may arise, the impact on the health of both the mother and the baby, and the strategies for managing hypertension during pregnancy. By understanding the implications of hypertension in pregnancy, healthcare professionals can provide appropriate care and support to ensure the best possible outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Key Takeaways
- Hypertension during pregnancy can have detrimental effects on both the mother and the fetus.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity, can help manage blood pressure levels during pregnancy.
- Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy can lead to complications such as preterm birth, placental abruption, and cardiovascular diseases for the mother.
- Regular prenatal care, blood pressure monitoring, and medication management are crucial in effectively managing hypertension during pregnancy.
Understanding Hypertension and Its Causes
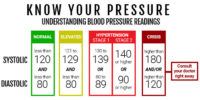
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels. It can be caused by a variety of factors including genetic predisposition, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and excessive salt intake. Understanding risk factors associated with hypertension is crucial in order to effectively manage and prevent complications.
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in controlling blood pressure levels and reducing the risk of developing hypertension-related complications. These modifications include adopting a healthy diet low in sodium and saturated fats, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding tobacco use.
By implementing these lifestyle changes, individuals can better manage their blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of hypertension, thus potentially preventing complications during pregnancy. It is important for healthcare professionals to educate individuals about the significance of lifestyle modifications in preventing and managing hypertension to ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome.
Complications of Hypertension in Pregnancy
Complications arising from high blood pressure during gestation can pose significant risks to both the mother and fetus. Managing hypertension with lifestyle changes is crucial in order to mitigate these risks.
Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, such as preeclampsia and gestational hypertension, can lead to various complications. For the mother, these may include organ damage, such as liver or kidney dysfunction, and an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, the mother may experience preterm birth, placental abruption, or cesarean delivery.
The fetus is also at risk, as hypertension can lead to intrauterine growth restriction, placental insufficiency, and even stillbirth. It is important for pregnant individuals with hypertension to closely monitor their blood pressure levels and follow medical advice to minimize these risks.
Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and a balanced diet, can also play a significant role in managing hypertension during pregnancy, thereby reducing the associated complications.
Impact on the Mother’s Health
The maternal health risks associated with high blood pressure during gestation are significant, including the potential for organ damage, increased cardiovascular disease risk, and complications during childbirth.
Hypertension during pregnancy can have a detrimental impact on maternal wellbeing. It can lead to complications such as preeclampsia, a condition characterized by high blood pressure, protein in the urine, and organ damage. Preeclampsia can result in reduced blood flow to the placenta, affecting the baby’s growth and development.
Additionally, hypertension can increase the risk of placental abruption, where the placenta separates from the uterine wall before delivery. This can lead to severe bleeding and jeopardize both the mother’s and baby’s health.
Other potential complications include preterm birth, gestational diabetes, and an increased likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases later in life.
Therefore, it is crucial to monitor and manage hypertension during pregnancy to safeguard the maternal wellbeing and ensure a safe childbirth.
Impact on the Baby’s Health
Adverse outcomes for the fetus are frequently observed when the mother experiences high blood pressure during gestation. Hypertension during pregnancy can have a significant impact on the baby’s health, particularly on their growth and development.
Some of the key effects include:
- Restricted fetal growth: High blood pressure can impair the flow of nutrients and oxygen to the baby, leading to intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). This can result in a smaller baby and potential long-term health issues.
- Developmental delays: Hypertension can disrupt the normal development of the baby’s organs and systems. It may lead to delays in reaching developmental milestones, both physically and mentally.
- Increased risk of preterm birth: Pregnant women with hypertension are at a higher risk of delivering prematurely. Premature babies may face complications related to their immature organs and may require intensive medical care.
Understanding the impact of hypertension on the baby’s health is crucial for healthcare providers to develop appropriate management strategies and provide necessary support to ensure optimal outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Managing Hypertension during Pregnancy
This paragraph will discuss the management of hypertension during pregnancy, focusing on three key points.
First, regular prenatal care and blood pressure monitoring are essential in managing hypertension during pregnancy. These measures can help identify and address any changes in blood pressure levels promptly.
Second, lifestyle changes and diet modifications may be recommended to help control hypertension during pregnancy. These can include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and following a balanced diet low in sodium.
Lastly, in some cases, medications and medical interventions may be necessary to manage hypertension during pregnancy. These interventions should be carefully considered and monitored by healthcare professionals to ensure the safety of both the mother and the baby.
Regular prenatal care and blood pressure monitoring
Regular prenatal care includes consistent monitoring of blood pressure levels throughout pregnancy. This ensures that any potential hypertension-related complications can be promptly identified and addressed. Blood pressure management is vital during pregnancy to prevent adverse outcomes for both the mother and the fetus. Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to detect any changes in blood pressure and implement appropriate prevention strategies. This may involve lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and regular exercise, or medication if necessary.
Additionally, blood pressure monitoring helps to assess the effectiveness of any interventions and make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal blood pressure control. By closely monitoring blood pressure levels, healthcare providers can identify and address any potential complications early on, reducing the risk of adverse outcomes associated with hypertension during pregnancy.
Lifestyle changes and diet modifications
One effective approach to managing blood pressure during pregnancy involves implementing lifestyle changes and modifications to the diet.
Lifestyle modifications can include engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, which can help to lower blood pressure. Additionally, stress reduction techniques, such as meditation or yoga, may also be beneficial.
In terms of dietary recommendations, it is important for pregnant women with hypertension to follow a balanced diet that is low in sodium and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limiting the intake of processed foods and sugary drinks is also recommended.
Furthermore, healthcare providers may advise pregnant women to monitor their caffeine and alcohol intake, as excessive consumption of these substances can contribute to high blood pressure.
Implementing these lifestyle changes and diet modifications can help to manage hypertension during pregnancy and promote better maternal and fetal outcomes.
Medications and medical interventions
Lifestyle changes and diet modifications are often the first line of defense when managing hypertension in pregnancy. However, in some cases, these modifications may not be sufficient to control blood pressure levels. In such instances, medications and medical interventions become necessary.
It is crucial to consider medication safety during pregnancy, as certain antihypertensive drugs may pose risks to the developing fetus. Therefore, healthcare providers must carefully evaluate the potential benefits and risks before prescribing any medication to pregnant women with hypertension.
Additionally, alternative treatments such as acupuncture, relaxation techniques, and dietary supplements have been explored as potential adjunctive therapies for managing hypertension during pregnancy. However, more research is needed to establish their effectiveness and safety in this specific population.
Overall, a multidisciplinary approach, combining appropriate medication use and alternative treatments, may be necessary to effectively manage hypertension during pregnancy.
Risks and Challenges in Delivery
Delivery poses significant risks and challenges for women with hypertension during pregnancy. It is crucial to carefully monitor these women during labor and delivery to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Some of the potential complications that can arise during delivery for women with hypertension include:
- Preeclampsia: Women with hypertension are at an increased risk of developing preeclampsia, a condition characterized by high blood pressure and organ damage. This can lead to complications such as placental abruption, premature birth, and low birth weight.
- Preterm birth: Hypertension can increase the risk of preterm birth, which can result in health problems for the baby.
- Cesarean section: Women with hypertension may be more likely to require a cesarean section due to concerns about the baby’s well-being or the mother’s health.
Overall, managing hypertension during delivery requires close monitoring and prompt medical intervention to minimize the risks and challenges associated with this condition.
Postpartum Care for Hypertensive Mothers
This paragraph will discuss the postpartum care for hypertensive mothers.
Key points include monitoring blood pressure levels, managing postpartum high blood pressure, and long-term implications and follow-up care.
Monitoring blood pressure levels is crucial in the postpartum period to ensure early detection of any abnormalities and prompt intervention.
Managing postpartum high blood pressure may involve medication, lifestyle modifications, and close monitoring to prevent complications.
Long-term implications of hypertension in pregnancy may include an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, follow-up care is essential to monitor and manage any potential long-term health issues.
Monitoring blood pressure levels
To effectively manage and mitigate the potential risks associated with hypertension during pregnancy, continuous monitoring of blood pressure levels is crucial. Regular blood pressure monitoring allows healthcare providers to closely monitor any fluctuations and promptly intervene if necessary.
Prenatal check-ups serve as an essential platform for this monitoring process. During these appointments, healthcare professionals measure blood pressure using a sphygmomanometer and record the readings. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends using an automated blood pressure device for accuracy.
Monitoring blood pressure levels helps identify hypertensive disorders such as preeclampsia or gestational hypertension early on, enabling timely interventions to prevent complications. Additionally, serial blood pressure measurements help assess the effectiveness of any prescribed medications or lifestyle modifications.
By diligently monitoring blood pressure levels, healthcare providers can closely monitor the well-being of hypertensive mothers and take appropriate steps to ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy.
Managing postpartum high blood pressure
One important aspect of postpartum care involves effectively managing elevated blood pressure levels following childbirth. Managing hypertension postpartum is crucial in preventing postpartum complications.
Postpartum high blood pressure, also known as postpartum hypertension, is defined as elevated blood pressure that occurs within the first 6 weeks after childbirth. It is important to monitor blood pressure levels regularly during this time to identify any potential issues. Women with pre-existing hypertension are at a higher risk of developing postpartum high blood pressure.
To manage postpartum hypertension, lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques can be beneficial. In some cases, medication may be necessary to control blood pressure levels. Close monitoring and regular follow-up visits with healthcare providers are essential for managing postpartum high blood pressure effectively and preventing further complications.
Long-term implications and follow-up care
Long-term implications and follow-up care are crucial aspects of postpartum management, as they ensure the ongoing health and well-being of the mother and help prevent potential complications. Hypertension during pregnancy, or gestational hypertension, can have long-term effects on both the mother and the baby.
Women who experienced high blood pressure during pregnancy are at a higher risk of developing chronic hypertension later in life. Additionally, they may have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and other related health problems. Therefore, it is important for healthcare providers to provide appropriate follow-up care and monitoring for women with a history of hypertension in pregnancy.
This may involve regular blood pressure checks, lifestyle modifications, and possibly medication to manage and prevent further complications. Post-pregnancy care should focus on optimizing overall health and reducing the risk of future cardiovascular issues.
Ensuring a Healthy Outcome
This discussion will focus on the importance of prenatal care and regular check-ups in ensuring a healthy outcome for pregnant women with hypertension.
Collaborative care with healthcare providers is crucial to monitor and manage the condition effectively, ensuring the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Additionally, support systems and resources play a vital role in providing pregnant women with hypertension the necessary assistance and guidance throughout their pregnancy journey.
Importance of prenatal care and regular check-ups
Regular prenatal care and check-ups play a crucial role in ensuring a healthy pregnancy and can significantly impact the management and outcomes of hypertension during this period. Prenatal education, provided during these visits, is essential for women with hypertension as it equips them with knowledge regarding the condition’s potential risks and how to manage them.
Early detection of hypertension during pregnancy allows for timely intervention, reducing the chances of complications for both the mother and the baby. Regular check-ups enable healthcare providers to monitor blood pressure levels, assess the effectiveness of any prescribed medications, and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Through consistent monitoring and support, prenatal care can help mitigate the adverse effects of hypertension on pregnancy and increase the chances of a successful outcome.
Evoke emotion in the audience:
- Peace of mind: Knowing that regular prenatal care helps identify and manage hypertension can alleviate anxiety and provide reassurance for expectant mothers.
- Empowerment: Access to prenatal education empowers women with hypertension to actively participate in their own care and make informed decisions.
- Protection: Early detection and monitoring of hypertension reduce the risk of complications, ensuring the safety and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
- Hope: Regular check-ups offer hope for a healthy pregnancy and delivery by providing ongoing support and interventions to manage hypertension effectively.
Collaborative care with healthcare providers
Collaborative care with healthcare providers involves a coordinated approach, with the involvement of various professionals, to ensure comprehensive management and support for expectant mothers with hypertension. This approach emphasizes the importance of an interdisciplinary team that includes obstetricians, maternal-fetal medicine specialists, nurses, and other healthcare professionals.
By working together, these providers can develop a personalized care plan that addresses the unique needs and risks associated with hypertension during pregnancy.
The collaborative approach begins with regular check-ups and prenatal care, which allow healthcare providers to monitor blood pressure levels, assess the overall health of the mother and baby, and identify any potential complications. Through ongoing communication and collaboration, the interdisciplinary team can make informed decisions regarding medication management, lifestyle modifications, and necessary interventions to optimize maternal and fetal outcomes.
Furthermore, this approach ensures that expectant mothers receive appropriate education and counseling on self-care measures, such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress. By fostering open communication and shared decision-making, collaborative care empowers expectant mothers to actively participate in their own healthcare and make informed choices that promote their well-being.
Ultimately, this comprehensive and interdisciplinary approach plays a crucial role in managing hypertension during pregnancy and optimizing outcomes for both mother and baby.
Support systems and resources for pregnant women with hypertension
Collaborative care with healthcare providers is crucial for pregnant women with hypertension. However, it is equally important for these women to have access to support systems and resources that can provide additional assistance throughout their journey.
Support groups can offer a sense of community and understanding, allowing women to connect with others who are experiencing similar challenges. These groups can provide emotional support, helpful advice, and a safe space to express concerns and fears.
Additionally, educational materials tailored specifically for pregnant women with hypertension can be valuable resources. These materials can provide information on managing blood pressure, dietary recommendations, exercise guidelines, and tips for stress reduction.
By offering support groups and educational materials, healthcare providers can empower pregnant women with hypertension to actively participate in their own care and make informed decisions to promote a healthy pregnancy.
- Joining a support group can alleviate feelings of isolation and provide a sense of belonging.
- Access to educational materials can empower women with knowledge and understanding about their condition.
- Meeting others who are going through the same experience can provide reassurance and emotional support.
- Having access to resources can help women develop effective coping strategies and enhance their overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of hypertension during pregnancy?
Symptoms of hypertension during pregnancy include high blood pressure, protein in the urine, headaches, vision problems, abdominal pain, and swelling. Prevention methods include regular prenatal care, a healthy lifestyle, and managing existing hypertension. Risk factors include obesity, family history, and age.
Can hypertension during pregnancy be prevented?
Prevention strategies for hypertension during pregnancy include maintaining a healthy lifestyle, such as regular exercise, balanced diet, and weight management. Regular check-ups and monitoring blood pressure levels are also important for managing hypertension during pregnancy.
Is it safe to take medication for hypertension during pregnancy?
Safety concerns regarding taking medication for hypertension during pregnancy should be considered. It is advisable to explore alternative treatments to manage hypertension in pregnant women, as certain medications may have potential risks for both the mother and the fetus.
How does hypertension affect the growth of the baby?
Hypertension during pregnancy can negatively impact fetal development, leading to complications. It can restrict blood flow to the placenta, resulting in inadequate oxygen and nutrient supply to the baby, potentially causing growth problems and increasing the risk of preterm birth.
Are there any long-term effects of hypertension on the mother’s health after pregnancy?
Long-term complications of hypertension in mothers after pregnancy include increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, renal dysfunction, and metabolic disorders. Management strategies involve regular follow-up visits, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate medication to control blood pressure levels.