Can Hypertension Be Prevented In Childhood?
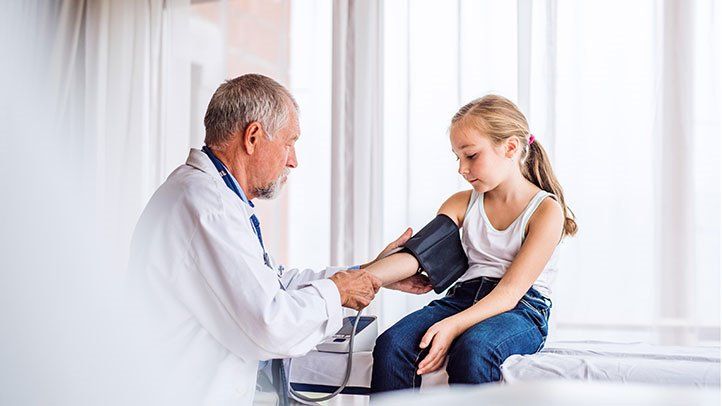
Childhood hypertension is a growing concern due to its association with long-term health consequences. This article aims to explore the question: Can hypertension be prevented in childhood?
To address this question, the article will first discuss the risk factors for childhood hypertension, including genetics, family history, and lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity.
Next, it will examine various preventive strategies that can be implemented to promote a healthy lifestyle and reduce the risk of developing hypertension in childhood. These strategies include promoting a healthy diet and active lifestyle, educating parents and caregivers, addressing childhood obesity, implementing school-based health programs, and monitoring blood pressure in children.
Additionally, the article will emphasize the importance of collaboration with healthcare professionals in implementing preventive measures and promoting overall wellness.
By adopting these preventive strategies, it is possible to reduce the incidence of childhood hypertension and promote lifelong habits of healthy living.
Key Takeaways
- Implementing school-based health programs can prevent hypertension in childhood.
- Regular blood pressure checks are essential for assessing cardiovascular health in children.
- Collaborating with healthcare professionals improves the prevention and early detection of hypertension in childhood.
- Promoting overall wellness and lifelong habits, such as mental health promotion and healthy sleep habits, can prevent hypertension in childhood.
Understanding the Risk Factors for Childhood Hypertension
Understanding the risk factors associated with childhood hypertension is crucial for effectively preventing this condition. Early detection plays a vital role in identifying children who are at risk of developing hypertension. Several risk factors have been identified, including genetic predisposition. Family history of hypertension is a significant predictor of the condition in children. Studies have shown that children with one or both parents having hypertension are more likely to develop the condition themselves.
Other factors, such as obesity, sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet, and exposure to secondhand smoke, also contribute to the development of hypertension in childhood. Identifying these risk factors allows healthcare professionals to implement preventive measures and interventions to reduce the likelihood of hypertension in children.
Early intervention and lifestyle modifications can play a crucial role in preventing the onset of hypertension and its associated complications in childhood.
Promoting a Healthy Diet and Active Lifestyle
This paragraph discusses the importance of promoting a healthy diet and active lifestyle in preventing childhood hypertension.
It specifically focuses on two key points: encouraging regular physical activity and limiting sodium and sugar intake.
Regular physical activity is crucial in maintaining cardiovascular health and can help prevent hypertension.
Similarly, limiting sodium and sugar intake can contribute to a healthy diet and reduce the risk of hypertension in children.
Encouraging Regular Physical Activity
Promoting and incorporating regular physical activity into a child’s daily routine can serve as an effective strategy in preventing hypertension. Encouraging social interaction and incorporating fun activities can motivate children to engage in regular exercise, thus reducing their risk of developing hypertension. Physical activity not only strengthens the cardiovascular system, but also helps to maintain a healthy weight and improve overall well-being. By providing opportunities for children to participate in sports, dance, or other active games, they are more likely to enjoy physical activity and continue engaging in it as they grow older. Additionally, promoting physical activity within a social context can foster a sense of community and support among children, further enhancing their motivation to lead an active lifestyle.
| Encouraging Social Interaction | Incorporating Fun Activities |
|---|---|
| Group sports and games | Dance classes |
| Team-based physical activities | Outdoor adventures |
| Physical education classes | Active video games |
| Community fitness events | Scavenger hunts |
| Active playdates | Water sports |
Limiting Sodium and Sugar Intake
Limiting sodium and sugar intake can be a key factor in maintaining a healthy diet and reducing the risk of health complications. Reducing processed foods and promoting home-cooked meals are effective strategies in achieving this goal.
Processed foods are often high in sodium and added sugars, which contribute to the development of hypertension. By limiting the consumption of processed foods, individuals can reduce their overall sodium and sugar intake.
Instead, promoting home-cooked meals allows individuals to have better control over the ingredients they use, making it easier to avoid excessive sodium and sugar. Home-cooked meals also tend to be healthier overall, as they are often made with fresh ingredients and can be tailored to individual dietary needs.
By adopting these strategies, individuals can make significant progress in preventing hypertension in childhood.
Educating Parents and Caregivers
Educating parents and caregivers about healthy lifestyle choices and early detection of risk factors can significantly contribute to the prevention of hypertension in childhood, instilling a sense of responsibility and empowerment in the audience. Effective communication strategies play a crucial role in conveying important information to parents and caregivers.
Engaging the community through workshops, seminars, and informational campaigns can create awareness and provide practical tips on promoting a healthy lifestyle for children. Providing accessible and accurate information regarding the risks associated with high sodium and sugar intake can help parents make informed choices about their child’s diet.
Additionally, educating parents about the importance of regular physical activity and stress management techniques can further reduce the risk of hypertension. By equipping parents and caregivers with the necessary knowledge and tools, hypertension in childhood can be prevented, leading to improved health outcomes for children.
Addressing Childhood Obesity
This discussion will focus on two key points in addressing childhood obesity: promoting a balanced and nutritious diet and encouraging regular exercise.
These strategies are essential in preventing and managing childhood obesity, as they help to establish healthy habits and promote overall well-being.
By promoting a balanced and nutritious diet, children can consume the necessary nutrients while avoiding excessive intake of unhealthy foods.
Regular exercise can help them maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of obesity-related health issues.
Promoting a Balanced and Nutritious Diet
Promoting a balanced and nutritious diet is crucial in the prevention of hypertension in childhood, as it fosters healthy eating habits and provides essential nutrients that support cardiovascular health. By encouraging children to consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, their risk of developing hypertension can be significantly reduced. Additionally, limiting the intake of processed foods high in sodium, saturated fats, and added sugars is essential in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. A balanced diet rich in nutrients such as potassium, magnesium, and fiber can help regulate blood pressure and promote overall cardiovascular health. Educating parents and caregivers about the importance of proper childhood nutrition and providing resources for meal planning can play a key role in preventing hypertension and establishing lifelong healthy eating habits.
| Nutrient | Function |
|---|---|
| Potassium | Helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels |
| Magnesium | Supports smooth muscle relaxation and blood vessel dilation |
| Fiber | Assists in regulating blood cholesterol levels |
| Fruits | Provide vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants |
| Vegetables | Offer essential nutrients and promote satiety |
Encouraging Regular Exercise
Regular exercise plays a vital role in fostering healthy cardiovascular function and promoting overall well-being, as it strengthens the heart, improves blood circulation, and enhances the body’s ability to regulate blood pressure.
Preventing sedentary behavior and incorporating physical activity into daily routines are essential strategies for preventing hypertension in childhood.
Encouraging children to engage in regular exercise can help prevent the development of hypertension by reducing the risk factors associated with the condition, such as obesity and high cholesterol levels.
Incorporating activities that children enjoy, such as sports, dancing, or outdoor play, can make exercise more enjoyable and sustainable.
Additionally, promoting active transportation, such as walking or cycling to school, can further increase physical activity levels.
By prioritizing regular exercise, we can instill healthy habits in children that can help prevent hypertension and promote lifelong cardiovascular health.
Implementing School-Based Health Programs
Implementing school-based health programs offers a promising approach to preventing hypertension in childhood. These programs utilize school settings to deliver interventions that promote healthy behaviors and educate students about the importance of maintaining cardiovascular health.
School-based interventions have the advantage of reaching a large number of children and adolescents and can provide a platform for community engagement. By involving parents, teachers, and healthcare professionals, these programs can create a supportive environment that promotes healthy lifestyle choices.
The interventions may include physical activity programs, nutrition education, and stress management techniques. By targeting multiple risk factors for hypertension, such as sedentary behavior and unhealthy diet, school-based health programs can help children develop lifelong habits that reduce their risk of developing hypertension later in life.
Monitoring Blood Pressure in Children
Monitoring blood pressure in children is an essential component of assessing their cardiovascular health and identifying early signs of potential hypertension. It is crucial to implement regular blood pressure checks in order to detect hypertension in children, as it can have long-term effects on their health. According to pediatric hypertension guidelines, blood pressure should be measured at least once a year in children aged 3 years and older. However, more frequent monitoring may be necessary for children with certain risk factors, such as obesity or a family history of hypertension. Early detection of hypertension allows for timely intervention and management, which can help prevent the progression of the condition and reduce the risk of associated cardiovascular complications in adulthood.
To engage the audience, a table can be used to display the pediatric hypertension guidelines and the potential long-term effects of childhood hypertension.
| Pediatric Hypertension Guidelines | Long-Term Effects of Childhood Hypertension |
|---|---|
| Blood pressure should be measured at least once a year in children aged 3 years and older | Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases in adulthood |
| More frequent monitoring may be necessary for children with certain risk factors | Higher likelihood of developing chronic kidney disease |
| Early detection allows for timely intervention and management | Potential impact on cognitive function and academic performance |
| Intervention can prevent progression of hypertension | Increased risk of stroke and heart attack in adulthood |
| Management can reduce the risk of associated cardiovascular complications in adulthood | Higher healthcare costs and burden on the healthcare system |
Collaborating with Healthcare Professionals
Collaboration with healthcare professionals is vital for ensuring comprehensive and effective management of pediatric cardiovascular health. By employing collaborative strategies and forming healthcare partnerships, the prevention and early detection of hypertension in childhood can be significantly improved.
Healthcare professionals, including pediatricians, nurses, and other specialists, play a crucial role in monitoring blood pressure and identifying potential risk factors in children. They can provide valuable guidance and education to both parents and children regarding healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress.
Additionally, healthcare professionals can work closely with schools and community organizations to implement preventive measures and promote awareness about the importance of cardiovascular health in children.
Through a collaborative approach, healthcare professionals can contribute to the prevention and management of hypertension in childhood, ultimately reducing the risk of long-term cardiovascular complications.
Promoting Overall Wellness and Lifelong Habits
Collaborating with healthcare professionals is crucial in preventing hypertension in childhood. However, it is equally important to promote overall wellness and instill lifelong habits from a young age. By focusing on promoting mental health and instilling healthy sleep habits, we can further reduce the risk of hypertension in children.
To engage the audience and maintain their interest, a 2 column and 4 row table can be used to highlight the benefits of promoting mental health and healthy sleep habits. This table could include information such as the positive effects of physical activity on mental health, the importance of adequate sleep in preventing hypertension, the correlation between mental well-being and overall health, and the role of stress management techniques in maintaining a healthy blood pressure.
By prioritizing mental health and healthy sleep habits in childhood, we can lay a strong foundation for preventing hypertension and promoting lifelong well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the specific risk factors for childhood hypertension?
Specific risk factors for childhood hypertension include obesity, family history of hypertension, sedentary lifestyle, high sodium intake, and certain medical conditions. Prevention strategies include promoting healthy diet and physical activity, regular blood pressure screenings, and early intervention.
How can parents and caregivers be educated about the importance of managing childhood hypertension?
Parents and caregivers can be educated about the importance of managing childhood hypertension through parental involvement and community awareness programs. These programs can provide information, resources, and support to help parents understand the risks and take appropriate actions to manage their child’s hypertension.
What are the main strategies to address childhood obesity and its impact on hypertension?
Prevention strategies for childhood obesity and its impact on hypertension include promoting healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, reducing sedentary behavior, and implementing policies to create healthier environments. These strategies can improve overall health outcomes.
How can school-based health programs effectively contribute to the prevention of childhood hypertension?
School-based health programs can effectively contribute to the prevention of childhood hypertension through various interventions, such as promoting healthy eating and physical activity, providing health education, and engaging the community in supporting healthy behaviors.
What role do healthcare professionals play in preventing and managing childhood hypertension?
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in preventing and managing childhood hypertension through early intervention. By providing regular check-ups, screenings, and promoting healthy lifestyle choices, they can identify and address hypertension risk factors in children.







