Can Hypertension Lead To Kidney Damage?
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a prevalent medical condition that affects a significant portion of the global population. It is characterized by sustained elevated blood pressure levels, which can lead to various health complications.
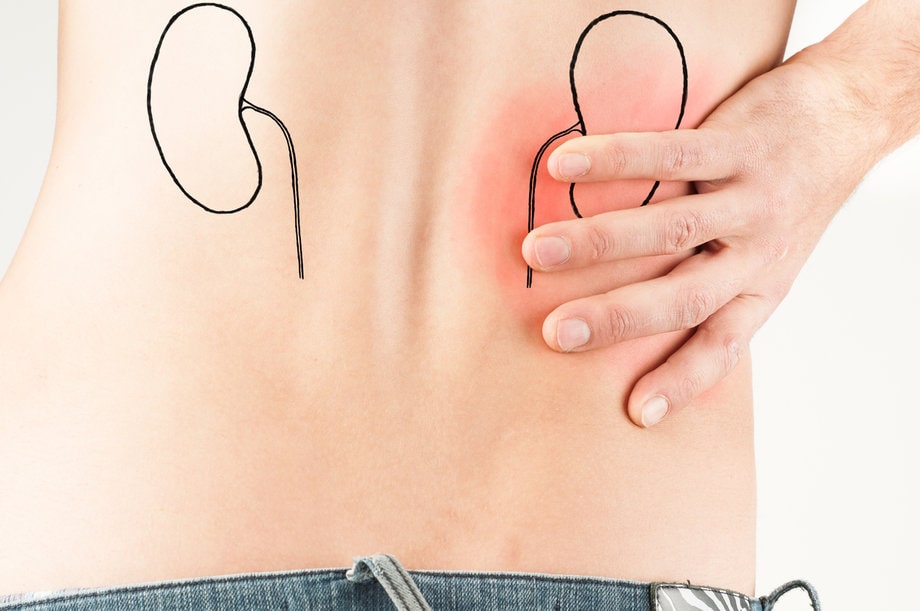
One potential consequence of hypertension is kidney damage, a condition that can have serious implications for an individual’s overall health and well-being. Understanding the relationship between hypertension and kidney damage is crucial for effective prevention and management of these conditions.
This article aims to explore the link between hypertension and kidney damage, examining the mechanisms through which high blood pressure can cause harm to the kidneys. Additionally, it will discuss the potential development of chronic kidney disease as a result of uncontrolled hypertension.
The article will also provide insights into strategies for managing hypertension to prevent kidney damage, including lifestyle modifications and medication options. Regular monitoring and screening for hypertension-related kidney damage will also be considered as essential components of effective management.
Key Takeaways
- Hypertension can lead to kidney damage.
- Regular blood pressure checks are necessary for identifying kidney damage.
- Urine tests can detect protein or blood in the urine, indicating kidney damage.
- Renal function tests, such as BUN and creatinine levels, can assess kidney function and detect impairment.
Understanding Hypertension and Its Effects on the Kidneys
Hypertension has been shown to have detrimental effects on kidney function, potentially leading to kidney damage. Preventing hypertension is crucial in maintaining kidney health.
One important aspect in preventing hypertension is maintaining a healthy diet. Certain dietary factors have been found to have an impact on kidney health. For example, a high intake of sodium has been associated with an increased risk of hypertension and subsequent kidney damage. Similarly, a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, which are low in sodium and high in potassium, has been shown to have a protective effect on kidney function.
Therefore, adopting a diet that is low in sodium and high in fruits and vegetables can play a significant role in preventing hypertension and reducing the risk of kidney damage.
The Role of High Blood Pressure in Kidney Damage
High blood pressure has been identified as a significant contributing factor in the development of renal impairment. Hypertension, if left uncontrolled, can lead to kidney damage and various complications.
The impact of hypertension on renal health is well-documented and understood. The sustained high pressure in the blood vessels can damage the delicate blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to impaired kidney function. The damage may progress over time, resulting in chronic kidney disease or even end-stage renal disease, necessitating dialysis or kidney transplantation.
Additionally, hypertension can also cause narrowing of the renal arteries, reducing blood flow to the kidneys and further compromising their function. Therefore, it is crucial to manage and control high blood pressure effectively to prevent long-term kidney damage and related complications.
How Hypertension Causes Damage to the Kidneys
The sustained elevated pressure within the blood vessels can have detrimental effects on the delicate structures of the kidneys, resulting in compromised renal function and potential long-term consequences.
Hypertension causes kidney damage through various mechanisms, such as:
- Increased pressure: High blood pressure puts strain on the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to damage and impairment of their filtering function.
- Reduced blood flow: Hypertension narrows and damages the blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the kidneys. This inadequate blood supply can cause further damage to the renal tissues.
- Protein leakage: High blood pressure damages the filtering units of the kidneys, leading to the leakage of proteins into the urine.
Preventing hypertension-related kidney damage involves lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and reducing sodium intake. Dietary recommendations for kidney health include consuming a balanced diet with adequate fluid intake, limiting protein intake, and avoiding excessive salt and processed foods.
The Link Between Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease
One important aspect to consider regarding the relationship between elevated blood pressure and chronic kidney disease is the impact that sustained hypertension can have on renal function and long-term health outcomes. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a leading cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and can lead to kidney damage over time. Early detection of kidney damage due to hypertension is crucial in preventing further complications. It is essential to manage hypertension effectively through lifestyle modifications and medication to minimize the risk of kidney damage. Regular blood pressure monitoring and routine kidney function tests can aid in the early detection of kidney damage and allow for timely interventions. By controlling blood pressure and detecting kidney damage early, individuals can prevent or slow down the progression of hypertension-related kidney damage, ultimately improving long-term health outcomes.
| Preventing Hypertension-Related Kidney Damage | Early Detection of Kidney Damage due to Hypertension |
|---|---|
| Manage blood pressure through lifestyle changes | Regular blood pressure monitoring |
| Take prescribed medications as directed | Routine kidney function tests |
| Reduce salt intake | Timely interventions for kidney damage |
Managing Hypertension to Prevent Kidney Damage
Managing blood pressure effectively through lifestyle modifications and medication is crucial in preventing further complications and improving long-term health outcomes. Hypertension, if left uncontrolled, can lead to kidney damage. Therefore, managing hypertension through diet and exercise is essential.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products, combined with reduced sodium intake, can help lower blood pressure. Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, can also contribute to blood pressure reduction.
Additionally, it is important to detect hypertension early to prevent kidney damage. Regular blood pressure screenings and monitoring can help identify high blood pressure and initiate timely interventions. Early detection enables healthcare professionals to implement lifestyle modifications and prescribe appropriate medications to manage hypertension effectively and prevent kidney damage.
Overall, managing hypertension through diet, exercise, and early detection plays a crucial role in preventing kidney damage and promoting better long-term health outcomes.
Lifestyle Changes to Control Blood Pressure and Protect the Kidneys
Implementing lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity, can effectively control blood pressure and safeguard renal health.
A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products can help reduce blood pressure. Limiting sodium intake is also crucial, as excessive sodium can contribute to high blood pressure.
Regular exercise is another essential aspect of managing hypertension and protecting the kidneys. Engaging in aerobic exercises such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling for at least 150 minutes per week can help lower blood pressure.
Additionally, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption can further promote renal health.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes, individuals can take proactive steps to control their blood pressure and mitigate the risk of kidney damage.
Medications for Hypertension and Kidney Health
To effectively control blood pressure and protect renal health, the use of medication is often recommended.
Medications for hypertension and kidney health play a crucial role in managing high blood pressure and preventing kidney damage. These medications aim to lower blood pressure and reduce the strain on the kidneys, thereby minimizing the risk of kidney disease.
Commonly prescribed antihypertensive medications include angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), diuretics, and calcium channel blockers. These medications work by dilating blood vessels, reducing fluid volume, or blocking certain hormones that contribute to high blood pressure.
However, it is important to note that medication alone is not sufficient for optimal kidney health. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, following a balanced diet low in sodium, and reducing alcohol consumption, are also crucial for managing hypertension and protecting the kidneys.
Regular Monitoring and Screening for Hypertension-Related Kidney Damage
Regular monitoring and screening for the potential consequences of elevated blood pressure on renal function is essential in order to effectively address the impact of hypertension on overall health. Early detection plays a crucial role in preventing complications and managing hypertension-related kidney damage. To ensure regular monitoring and screening, the following steps should be taken:
- Blood pressure measurement: Regular blood pressure checks are necessary to identify any fluctuations or abnormalities that may indicate kidney damage. This can be done using a sphygmomanometer or an automated blood pressure monitor.
- Urine analysis: Urine tests can help detect the presence of protein or blood in the urine, which may indicate kidney damage. This can be done through a simple dipstick test or a more comprehensive urinalysis.
- Renal function tests: These tests assess the kidney’s ability to filter waste products from the blood. Common tests include blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels, which can indicate impaired kidney function.
By implementing regular monitoring and screening protocols, healthcare professionals can detect hypertension-related kidney damage early on, allowing for timely intervention and management to prevent further complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can hypertension be completely cured?
Hypertension reversal is possible through various lifestyle changes and natural remedies for hypertension. However, it is important to note that complete cure of hypertension may not be achievable for everyone.
Are there any alternative treatments for hypertension other than medication?
Alternative therapies and lifestyle modifications can be effective in managing hypertension. These may include regular exercise, a healthy diet, stress reduction techniques, weight loss, and limiting alcohol and sodium intake.
How long does it take for hypertension to cause kidney damage?
The timeline for hypertension to cause kidney damage varies depending on individual factors. However, it is important to implement prevention strategies such as maintaining a healthy blood pressure, managing stress, and adopting a balanced diet to reduce the risk of kidney damage.
Is kidney damage reversible once it has occurred due to hypertension?
Reversible kidney damage caused by hypertension can occur over a long-term period. It is crucial to manage hypertension effectively to prevent further damage and reduce the risk of irreversible complications in the future.
Are there any specific dietary recommendations for managing hypertension and protecting the kidneys?
Dietary restrictions and lifestyle changes are recommended to manage hypertension and protect the kidneys. These recommendations may include reducing sodium intake, following a DASH diet, limiting alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight.