Glands And Hormonal Regulation Explained
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands and hormones that work together to regulate various bodily functions, including growth and development, metabolism, and reproduction. These hormones are responsible for maintaining a delicate balance in the body, and any disruption to this balance can lead to a range of health problems.
Understanding the role of glands and hormones in the body is crucial for maintaining optimal health and wellbeing. In this article, we will provide an overview of the endocrine system, explore the various types of glands and their functions, and discuss the importance of hormonal regulation in the body.
We will also explore common hormonal imbalances and their associated health conditions, as well as diagnostic tests and treatment options for these imbalances.
Finally, we will provide tips for maintaining hormonal balance through lifestyle changes and other supportive measures.
Key Takeaways
- The endocrine system regulates bodily functions through glands and hormones.
- Hormones maintain balance in the body and disruption can lead to health problems.
- Hormonal imbalances can lead to health conditions such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, PCOS, diabetes, and adrenal insufficiency.
- Treatment options for hormonal imbalances include lifestyle changes, medication, and hormone therapy.
The Endocrine System: An Overview
The endocrine system, which is a complex network of glands and organs, plays a crucial role in the regulation of various physiological processes in the human body through the secretion of hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers that are produced by the endocrine glands and are released into the bloodstream to communicate with target cells throughout the body.
These hormones are responsible for regulating a wide range of bodily functions, including growth and development, metabolism, reproduction, and the body’s response to stress.
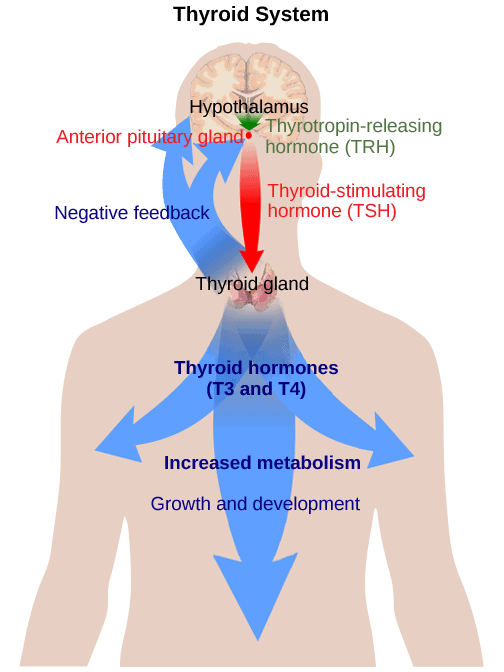
The endocrine system consists of a number of glands, including the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, pancreas, and ovaries or testes. Each gland produces specific hormones that are responsible for regulating different physiological processes in the body.
For example, the pituitary gland produces growth hormone, which is responsible for the growth and development of bones and muscles, while the thyroid gland produces thyroid hormone, which regulates metabolism.
Overall, the endocrine system is a complex and highly regulated system that plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the human body.
Types of Glands and Their Functions
One way to categorize the various types of glands is by their mode of secretion. There are two main types of glands: exocrine glands and endocrine glands.
Exocrine glands secrete their products into ducts that lead to the outside of the body or to a body cavity. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat glands, salivary glands, and mammary glands.
In contrast, endocrine glands secrete their products, called hormones, directly into the bloodstream. Hormones are transported throughout the body and affect various organs and tissues. Examples of endocrine glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, and adrenal gland.
Each type of gland has a unique function in maintaining homeostasis in the body. Exocrine glands play a role in regulating body temperature, digestion, and lubrication of body surfaces. Endocrine glands are involved in a wide range of processes such as growth and development, metabolism, and reproduction.
Proper functioning of both types of glands is essential for maintaining overall health and wellbeing. Dysfunction of glands can lead to various disorders such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and hormonal imbalances.
Understanding the different types of glands and their functions is crucial for diagnosing and treating these disorders.
The Role of Hormones in the Body
Hormones act as chemical messengers in the body, transmitting signals from one organ or tissue to another, and playing a crucial role in maintaining physiological balance. Hormones are produced by endocrine glands and secreted into the bloodstream. Once they reach their target cells, hormones bind to specific receptors on the surface or inside the cell, triggering a series of biochemical reactions that ultimately result in a physiological response.
The role of hormones in the body is diverse and complex. Hormones regulate a wide range of physiological processes, including growth and development, metabolism, reproduction, and stress responses. For example, growth hormone stimulates the growth of bone and muscle tissue, while insulin regulates glucose metabolism.
In addition, hormones play a significant role in the regulation of the body’s internal environment, such as the regulation of body temperature, pH balance, and electrolyte balance. Overall, hormones are essential for the proper functioning of the body and maintaining homeostasis.
Hormonal Imbalances and Health Conditions
Hormonal imbalances can lead to a variety of health conditions and disruptions in physiological processes. Here are some examples:
- Hypothyroidism: A condition that occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. Symptoms may include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, and cold intolerance.
- Hyperthyroidism: A condition that occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. Symptoms may include weight loss, anxiety, heart palpitations, and heat intolerance.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): A hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by high levels of androgens (male hormones) and can lead to irregular periods, acne, and excess hair growth.
- Diabetes: A chronic condition that affects how the body processes glucose (sugar) in the blood. It is caused by a deficiency in insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, or by the body’s inability to use insulin effectively.
- Adrenal insufficiency: A condition that occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones. Symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, and weight loss.
It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of hormonal imbalances and seek medical attention if necessary. Treatment may include medication, hormone replacement therapy, or lifestyle changes.
Diagnostic Tests for Hormonal Imbalances
Diagnostic tests are essential in identifying hormonal imbalances and determining appropriate treatment options. These tests help to measure the levels of hormones in the bloodstream, urine, or saliva.
Some of the commonly used diagnostic tests include blood tests, imaging tests, and stimulation tests. Blood tests are the most common and widely used diagnostic tests for hormonal imbalances. They involve drawing blood samples from the patient and analyzing them in the laboratory. The tests can measure the levels of various hormones in the blood, such as thyroid hormones, sex hormones, and adrenal hormones.
Imaging tests, such as ultrasounds, MRIs, and CT scans, are also used in diagnosing hormonal imbalances. These tests help to visualize the glands that produce hormones and detect any abnormalities or tumors.
Stimulation tests are used to measure the response of the glands to certain stimuli. For instance, the insulin tolerance test is used to measure the response of the pituitary gland to insulin.
The results of these diagnostic tests help doctors to determine the cause of hormonal imbalances and develop appropriate treatment plans.
Treatment Options for Hormonal Imbalances
There are a variety of treatment options available for individuals with hormonal imbalances, including lifestyle changes, medications, and hormone therapy.
Lifestyle changes may include a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management techniques, and getting enough sleep. These changes may help regulate hormone levels and improve overall health.
Medications may also be prescribed to help regulate hormone levels. For example, birth control pills may be used to regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce symptoms of hormonal imbalances, such as acne and excessive hair growth. Other medications, such as thyroid hormone replacement therapy, may be prescribed to treat specific hormonal imbalances.
Hormone therapy may also be an option for some individuals, particularly those experiencing menopause or andropause. This may involve the use of estrogen, progesterone, or testosterone to alleviate symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
It is important to discuss all treatment options with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for individual needs and circumstances.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Hormonal Health
One effective approach to support hormonal health is through implementing lifestyle changes. The first step is to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise. Excess body fat can lead to increased levels of estrogen, which can disrupt hormonal balance.
Incorporating whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can provide the necessary nutrients to support hormonal health. In addition, regular exercise can help regulate insulin levels, which can affect hormone production.
Other lifestyle changes that can support hormonal health include reducing stress levels, getting enough sleep, and avoiding toxins. Chronic stress can lead to increased cortisol levels, which can disrupt the balance of other hormones. Adequate sleep is also important for hormonal regulation, as lack of sleep can disrupt the production of hormones such as cortisol, growth hormone, and melatonin.
Finally, avoiding exposure to toxins such as chemicals in plastics, pesticides, and other environmental pollutants can help maintain hormonal balance. By implementing these lifestyle changes, individuals can support their hormonal health and potentially reduce the risk of hormonal imbalances and related health conditions.
Maintaining Hormonal Balance for Optimal Health and Wellbeing
Maintaining hormonal balance is crucial for achieving optimal health and wellbeing, as hormones play a vital role in regulating various bodily functions and processes. Hormones are chemical messengers that are produced by the endocrine glands and released into the bloodstream to travel to various parts of the body. These hormones are responsible for controlling various bodily functions, including growth and development, metabolism, mood, and reproduction.
When the hormonal balance in the body is disrupted, it can lead to various health problems, including weight gain, mood swings, and fertility issues.
To maintain hormonal balance, it is essential to lead a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep. Exercise helps to regulate the production of hormones, including insulin and cortisol, which play a crucial role in metabolism and stress response.
A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains, can help to support hormonal health.
Additionally, getting enough sleep is critical for hormonal regulation, as the body produces hormones during sleep that help to regulate various bodily functions. By making these lifestyle changes, individuals can maintain hormonal balance and promote optimal health and wellbeing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the endocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions through the production and secretion of hormones by different glands.
Hormones are responsible for maintaining homeostasis and coordinating different physiological processes throughout the body.
However, hormonal imbalances can lead to various health conditions and affect overall wellbeing.
Diagnostic tests such as blood tests, imaging, and physical examinations can help identify hormonal imbalances, and treatment options such as medication, surgery, and lifestyle changes can help restore hormonal balance.
It is essential to prioritize hormonal health and make necessary lifestyle changes to maintain optimal health and wellbeing.
With proper management and care, individuals can achieve hormonal balance and lead a healthy life.









