Heart Function And Circulation Explained
The heart is an essential organ that plays a critical role in maintaining the body’s overall health and well-being. It is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to various tissues and organs. Understanding the heart’s function and circulation is fundamental in preventing and managing cardiovascular diseases, which are among the leading causes of death worldwide.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the anatomy and physiology of the heart, including its chambers, blood circulation, electrical system, and cardiac cycle. Additionally, the article will discuss the importance of heart rate and blood pressure in maintaining heart health, common cardiovascular diseases, and their impact on heart function, and lifestyle changes and medical treatments that can help manage heart conditions.
By the end of this article, readers will have a better understanding of how the heart works and how to take care of it to prevent or manage heart disease.
Key Takeaways
- The heart has four chambers with unique functions in blood circulation.
- The cardiac cycle involves the coordinated contraction and relaxation of the heart’s chambers.
- Hypertension, coronary artery disease, and heart failure are common cardiovascular diseases.
- A healthy diet, regular physical activity, not smoking, limiting alcohol intake, managing stress, and getting enough sleep are important for heart health.
The Anatomy of the Heart: Four Chambers and Their Functions
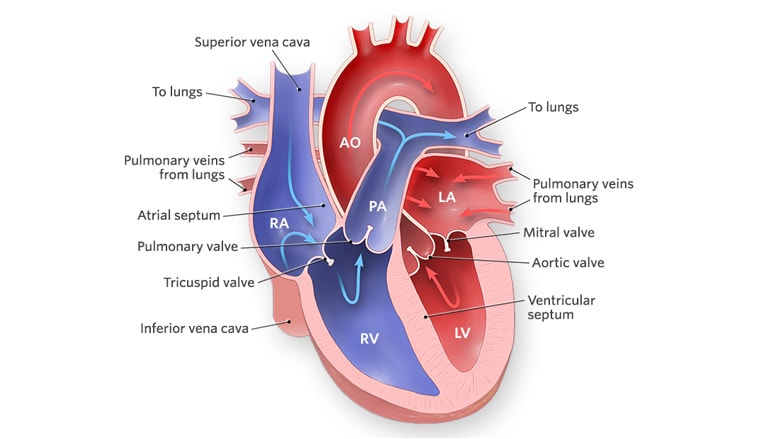
The heart consists of four chambers, each with a unique function in the circulation of blood throughout the body.
The two upper chambers are called the atria and they receive blood returning to the heart from the body and lungs. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body, while the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
The atria then contract to push the blood into the two lower chambers, called the ventricles. The ventricles are the two larger chambers of the heart and are responsible for pumping blood out of the heart.
The right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation, while the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. The left ventricle is the most powerful chamber because it pumps blood to the body against the force of gravity.
The coordinated contraction and relaxation of the four chambers ensure that blood is efficiently circulated throughout the body.
The Role of Blood in Circulation
Blood is a vital component of the circulatory system, responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products from the body. Blood is composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Plasma is the liquid component of blood that carries nutrients, hormones, and waste products. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds oxygen and carries it to the body’s tissues. White blood cells are part of the body’s immune system and help fight infections. Platelets are involved in blood clotting and help prevent excessive bleeding.
The heart pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products. Blood circulates through two types of blood vessels: arteries and veins. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body’s tissues. Veins return deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Blood flow is regulated by the contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles in the walls of blood vessels. The circulatory system is a complex network that works together to ensure the body’s tissues receive the necessary oxygen and nutrients to function properly.
Understanding the Heart’s Electrical System
Understanding the electrical impulses that regulate cardiac rhythm is essential for comprehending the intricate workings of the circulatory system. The heart’s electrical system is a complex network of specialized cells responsible for controlling the heartbeat and maintaining the appropriate rhythm.
The following list of four key components of the heart’s electrical system can help clarify its role in the cardiovascular system:
- Sinoatrial (SA) Node: This specialized group of cells located in the right atrium of the heart serves as the natural pacemaker of the heart. The SA node generates the electrical impulses that control the heartbeat and set the heart rate.
- Atrioventricular (AV) Node: Located between the atria and the ventricles, this node receives the electrical impulses from the SA node and regulates their transmission to the ventricles.
- Bundle of His: This is a group of specialized muscle fibers that transmit the electrical impulses from the AV node to the ventricles.
- Purkinje Fibers: These fibers extend from the bundle of His and spread throughout the ventricles, distributing the electrical impulses and coordinating the contraction of the heart muscle.
By understanding the function of each component of the heart’s electrical system, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and treat cardiac arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats. Additionally, advancements in medical technology have allowed for the development of devices such as pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) that can help regulate the heart’s electrical system and ensure proper cardiac function.
The Cardiac Cycle: How the Heart Contracts and Relaxes
One critical aspect of cardiovascular physiology is the mechanism of the cardiac cycle, which involves the coordinated contraction and relaxation of the heart’s chambers.
The cardiac cycle is a complex process that involves multiple phases, including atrial and ventricular diastole (relaxation) and systole (contraction).
During the diastolic phase, the heart’s chambers fill with blood as the atria and ventricles relax. This is followed by the systolic phase, during which the atria and ventricles contract to propel blood out of the heart and into the circulation.
The cardiac cycle is regulated by a complex interplay of electrical and mechanical signals that originate from the heart’s intrinsic electrical system. This system is responsible for generating the electrical impulses that coordinate the contraction and relaxation of the heart’s chambers.
Additionally, various hormones and neurotransmitters can influence the cardiac cycle by affecting the heart’s electrical and mechanical properties.
Understanding the cardiac cycle is crucial for diagnosing and treating cardiovascular diseases, as abnormalities in this process can lead to a range of disorders, including arrhythmias, heart failure, and valvular diseases.
The Importance of Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
The regulation of heart rate and blood pressure is a crucial aspect of cardiovascular physiology that plays a significant role in maintaining homeostasis and preventing cardiovascular diseases. Heart rate refers to the number of times the heart beats per minute, while blood pressure refers to the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the blood vessels. The heart rate and blood pressure are regulated by a complex interplay of various factors, including the autonomic nervous system, hormones, and physical activity. Any disruption in this regulation can lead to a variety of cardiovascular disorders, including hypertension, coronary artery disease, and heart failure.
Heart rate and blood pressure are closely related and are often used together to assess the overall cardiovascular health of an individual. The following table provides a brief overview of the normal range for heart rate and blood pressure in adults:
| Parameter | Normal Range |
|---|---|
| Heart Rate | 60-100 bpm |
| Systolic BP | 90-119 mmHg |
| Diastolic BP | 60-79 mmHg |
It is essential to maintain a healthy heart rate and blood pressure to prevent the development of cardiovascular diseases. Lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management, can help regulate heart rate and blood pressure and reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disorders. In some cases, medications may be required to maintain normal heart rate and blood pressure levels.
Common Cardiovascular Diseases and Their Impact on Heart Function
Cardiovascular diseases are a major concern worldwide, affecting millions of individuals annually. Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a common cardiovascular disease that can lead to serious health complications. It occurs when the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently high, causing the heart to work harder to pump blood throughout the body. This can lead to damage to the heart, kidneys, and other organs. Additionally, hypertension is a major risk factor for stroke, heart attack, and other cardiovascular diseases.
Coronary artery disease is another common cardiovascular disease that occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart, become narrowed or blocked. This can lead to chest pain, shortness of breath, and even heart attack.
Heart failure, on the other hand, occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This can result in fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling in the legs and ankles.
It is important to seek medical attention if any symptoms of cardiovascular disease are present, as early detection and treatment can prevent further damage to the heart and improve overall health outcomes.
Lifestyle Changes for a Healthy Heart
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for reducing the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and improving overall health outcomes.
One of the most important lifestyle changes that one can make is adopting a healthy diet. A diet that is high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help to reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, high cholesterol, and diabetes. It is also important to limit the intake of saturated and trans fats, as well as salt and sugar.
In addition to a healthy diet, regular physical activity is also essential for a healthy heart. Engaging in regular exercise can help to improve heart function and circulation, reduce blood pressure, and lower the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. It is recommended that adults engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, as well as muscle-strengthening activities at least twice a week.
Other healthy lifestyle habits include not smoking, limiting alcohol intake, managing stress, and getting enough sleep. These lifestyle changes can all work together to improve heart function and overall health outcomes.
Medical Treatments for Heart Conditions
Medical treatments for heart conditions include various options such as medications, procedures, and surgeries to improve heart health.
Medications such as beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and statins are commonly used to manage heart conditions like high blood pressure, heart failure, and high cholesterol levels. Beta-blockers work by reducing heart rate and blood pressure, while ACE inhibitors help to dilate blood vessels and reduce the workload on the heart. Statins are used to lower cholesterol levels and prevent the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can lead to heart disease.
Procedures like angioplasty and stenting are used to clear blocked arteries and improve blood flow to the heart. During angioplasty, a small balloon is inflated inside the blocked artery to widen it, while a stent is a small mesh tube that is inserted into the artery to keep it open.
In more severe cases, surgeries like bypass surgery and heart valve replacement may be necessary to restore proper heart function. Bypass surgery involves using a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body to reroute blood around a blocked artery, while heart valve replacement involves replacing a damaged or diseased heart valve with a prosthetic valve.
Overall, the choice of medical treatment depends on the specific heart condition and the patient’s overall health status.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the heart is a vital organ responsible for the circulation of blood throughout the body. It consists of four chambers that work together to pump blood and maintain proper circulation.
Understanding the heart’s electrical system and the cardiac cycle is crucial in comprehending heart function. Maintaining a healthy heart rate and blood pressure is important to prevent cardiovascular diseases, which can severely impact heart function.
Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can promote heart health. Medical treatments, including medications and surgical procedures, can also help manage heart conditions.
Further research and advancements in medical technology are crucial in improving heart function and treating cardiovascular diseases. It is essential to prioritize heart health and take steps towards maintaining a healthy heart for optimal overall health and well-being.