How Skin Protection And Sensation Work
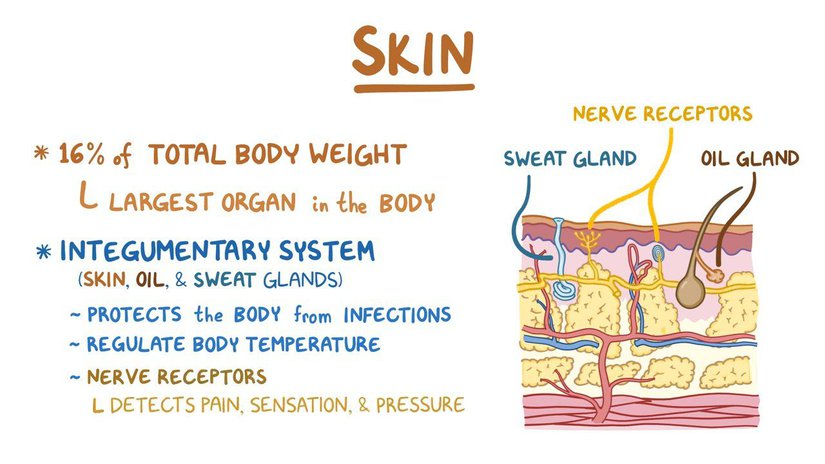
Skin is the largest organ in the human body, serving a number of important functions. Apart from its role in regulating body temperature, skin also provides protection from the external environment, acts as a barrier against harmful toxins, and allows us to experience different sensations. Understanding how skin protection and sensation work is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and preventing skin-related health issues.
The anatomy of skin is complex, with multiple layers and structures that play different roles in skin function. The outermost layer, called the epidermis, provides a protective barrier against external factors such as UV radiation, pollution, and microorganisms.
The dermis, located beneath the epidermis, contains nerve receptors that allow us to experience different sensations such as touch, pressure, heat, and cold. Additionally, the presence of melanin in the skin helps to protect against UV radiation and prevent skin damage.
By understanding the anatomy and function of skin, we can learn how to protect and maintain our skin health.
Key Takeaways
- Skin is the largest organ in the human body and provides protection against external factors, but environmental factors can impact skin health.
- Sunscreens can prevent skin damage and irritations, as well as skin cancer and premature aging by absorbing or reflecting UV rays.
- Nerve receptors in the skin detect different types of stimuli and are connected to the nervous system, with different types responsible for different sensations.
- Positive touch can create feelings of happiness and relaxation, while negative touch can induce feelings of fear and anxiety, with neural pathways and processes involved.
The Anatomy of Skin: Layers and Functions
The anatomy of skin consists of three main layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue.
The epidermis is the outermost layer of skin and serves as a protective barrier against the external environment. It is composed of several layers of cells, including keratinocytes, which produce the protein keratin that helps to strengthen the skin, and melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin that helps to protect the skin from harmful UV rays.
The dermis is the middle layer of skin and is responsible for providing structural support to the skin. It contains various types of connective tissue, including collagen and elastin, that help to give the skin its elasticity and firmness. It also contains numerous sensory receptors that allow us to perceive touch, pressure, temperature, and pain.
The subcutaneous tissue is the deepest layer of skin and is primarily composed of adipose (fat) tissue that helps to cushion and insulate the body.
Together, these three layers of skin work in concert to provide both protective and sensory functions that are essential for our survival.
The Role of Melanin in Skin Protection
Melanin, a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes, plays a crucial role in shielding the skin from harmful UV radiation. Melanin is a natural sunscreen that absorbs and scatters UV rays, preventing them from penetrating the skin’s deeper layers. It is responsible for the skin’s color and is produced in response to UV exposure, which is why people tan when they spend time in the sun. The more melanin in the skin, the better protected it is from UV damage.
Melanin also plays a role in skin sensation. Melanocytes are closely connected to nerve cells, which allows them to communicate and regulate the skin’s response to external stimuli. The melanocytes can signal the nervous system to release neurotransmitters that affect the skin’s sensitivity to touch, pressure, and pain. This interaction between melanin and the nervous system is crucial for maintaining the skin’s protective function and ensuring a healthy response to external stimuli.
Environmental Factors and Their Effects on Skin
Exposure to environmental factors such as pollution, extreme temperatures, and dry air can significantly impact the health and appearance of our skin. Pollution, for example, can lead to the formation of free radicals which cause oxidative stress and damage to the skin’s cells. This can result in premature aging, hyperpigmentation, and an increased risk of skin cancer.
Extreme temperatures, on the other hand, can cause dehydration and a breakdown of the skin’s natural barrier function, leading to dryness, redness, and inflammation. Finally, dry air can also strip the skin of its natural oils, leaving it feeling tight, itchy, and prone to cracking.
To protect our skin from these environmental stressors, it is important to take certain preventative measures. One of the most effective ways to protect the skin from pollution is to use products that contain antioxidants such as vitamin C and E. These antioxidants work to neutralize free radicals and prevent them from causing damage.
Additionally, using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least an SPF of 30 can help to protect the skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays. To combat the effects of extreme temperatures and dry air, it is important to use a moisturizer that contains hydrating ingredients such as hyaluronic acid and ceramides. This will help to restore moisture to the skin and strengthen its natural barrier function, keeping it healthy and resilient.
The Benefits of Using Sunscreen
Using sunscreen is an effective way to prevent damage caused by the sun’s harmful UV rays. Sunscreen works by absorbing or reflecting UV rays, which helps to prevent damage to the skin. This can help to prevent skin cancer, premature aging, and other skin conditions caused by UV exposure. In addition to this, using sunscreen can also help to improve the overall appearance of the skin, as it can prevent sunburn, dryness, and other skin irritations caused by UV exposure.
To better understand the benefits of using sunscreen, the following table outlines the various ways in which it can help to protect the skin:
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Prevents skin cancer | Sunscreen can help to prevent damage to the skin caused by UV radiation, which can lead to the development of skin cancer. |
| Prevents premature aging | UV radiation can cause premature aging, including wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots. Using sunscreen can help to prevent these signs of aging from developing. |
| Prevents sunburn | Sunburn is a common skin condition caused by UV radiation. Using sunscreen can help to prevent sunburn, which can cause pain, redness, and discomfort. |
| Prevents dryness and irritation | UV radiation can cause the skin to become dry and irritated. Using sunscreen can help to prevent this from happening, which can help to improve the overall appearance of the skin. |
| Improves overall skin health | Using sunscreen can help to protect the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation, which can help to improve the overall health of the skin. |
Overall, using sunscreen is an important part of protecting the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. By understanding the benefits of using sunscreen, individuals can make informed decisions about how to best protect their skin from the damaging effects of the sun.
How Skin Sensation Works: Nerve Receptors and Signals
The process of skin sensation relies on the interaction between nerve receptors and signals. Nerve receptors are specialized cells that are responsible for detecting different types of stimuli such as temperature, pressure, and pain. These receptors are located in the skin, as well as other parts of the body, and are connected to the nervous system.
When a stimulus is detected, the receptor sends a signal to the brain through the nervous system. The brain then processes the information and generates a response, such as moving away from a source of pain.
There are different types of nerve receptors that are responsible for different types of sensations. For example, thermoreceptors are sensitive to changes in temperature, while mechanoreceptors respond to pressure and touch. Nociceptors, on the other hand, are specialized receptors that are responsible for detecting pain.
Understanding how these receptors work and interact with each other is essential for developing treatments for conditions related to skin sensation, such as chronic pain or neuropathy.
Different Types of Sensations: Touch, Pressure, Heat, and Cold
Different stimuli such as touch, pressure, heat, and cold elicit a variety of sensations that are detected by specialized nerve receptors in the body. These sensations are crucial for the survival of humans and other animals, as they provide information about the environment and enable individuals to respond appropriately to different situations.
For instance, the sensation of touch can help individuals detect the presence of objects in their environment, while the sensation of heat or cold can help individuals regulate their body temperature.
The different types of sensations are detected by different types of nerve receptors that are located throughout the body. For example, the sensation of touch is detected by mechanoreceptors, which are found in the skin and respond to changes in pressure or movement. Heat and cold sensations, on the other hand, are detected by thermoreceptors, which are also found in the skin and respond to changes in temperature.
The ability to detect these different types of sensations is an important aspect of skin protection and sensation, as it enables individuals to respond appropriately to different environmental conditions and stimuli.
The Connection Between Skin Sensation and Emotions
The experience of emotions and the sensation of touch are closely linked, with studies suggesting that touch can have a significant impact on an individual’s emotional state. Touch is a powerful communication tool that can convey a wide range of emotions and is often used to express affection, comfort, and support. Positive touch, such as a hug or a pat on the back, can create feelings of happiness, relaxation, and security. In contrast, negative touch, such as a slap or a punch, can induce feelings of fear, anger, and anxiety.
The connection between skin sensation and emotions is complex and involves a variety of neural pathways and processes. For example, the activation of mechanoreceptors in the skin can trigger the release of endorphins and oxytocin, which are neurotransmitters associated with pleasure and social bonding. Additionally, the insula, a brain region involved in processing emotions, is activated by both physical touch and emotional experiences. This suggests that the way we experience touch is not only influenced by our physical senses but also by our emotions and social context. The following table summarizes the different types of touch and their associated emotional states:
| Type of Touch | Emotional State | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hug | Happiness, comfort, security | |||
| Pat on the back | Approval, recognition | |||
| Handshake | Respect, trust | |||
| Slap, punch | Fear, anger, anxiety | Caress | Affection, love, intimacy |
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Skin: Protection and Sensation
Effective maintenance of healthy skin involves implementing practices that shield the delicate tissue from external factors and promote tactile sensitivity. Here are some tips for maintaining healthy skin:
- Protect your skin from the sun by wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen, and limiting your exposure during peak hours.
- Overexposure to the sun can lead to premature aging, sunburn, and skin cancer.
- Keep your skin hydrated by drinking plenty of water and using moisturizers.
- Dry skin can lead to itching, cracking, and an increased risk of infection.
- Avoid harsh chemicals and irritants by using gentle cleansers and avoiding products with fragrances, dyes, and alcohol.
- These substances can strip the skin of its natural oils and cause irritation and inflammation.
By following these simple guidelines, you can help maintain healthy skin that is protected and sensitive to touch. Remember, healthy skin not only looks better, but it also plays a critical role in protecting your body from harmful external factors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the skin serves as the first line of defense against environmental stressors and harmful agents. The different layers and functions of the skin ensure that the body is protected from injury, infection, and dehydration. Melanin, in particular, is an essential pigment that helps shield the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. However, with the constant exposure to various environmental factors, the skin is prone to damage, which can lead to health problems. The use of sunscreen and other protective measures can help prevent skin damage and maintain its health.
Moreover, the skin’s ability to sense touch, pressure, heat, and cold is crucial in our daily lives. The nerve receptors and signals that relay these sensations to the brain are responsible for our emotional and physical responses.
Maintaining healthy skin sensation is equally important in ensuring overall well-being. Proper hydration, a balanced diet, and regular exercise are just a few ways to promote healthy skin sensation. By taking care of our skin, we can protect ourselves from harm and maintain a healthy and happy life.