How to Improve Gut Microbiome for Brain & Overall Health – Revolutionary Insights
The gut microbiome holds incredible potential for optimizing our health and well-being.
Discover the revolutionary insights and practical steps to unlock the power of your gut microbiome and embark on a path towards optimal health and vitality.
Key Takeaways
- The gut microbiome consists of trillions of microorganisms in the digestive tract and plays a crucial role in our overall health.
- Crypts and niches within the digestive tract provide specific locations for microbiota to reside and support our health.
- Supporting a healthy gut microbiome can be achieved through the consumption of fermented foods and a high-fiber diet.
- The gut microbiome has a direct impact on brain health and function, influencing mood, metabolism, hunger, and immune system function.
The Gut Microbiome and Its Importance
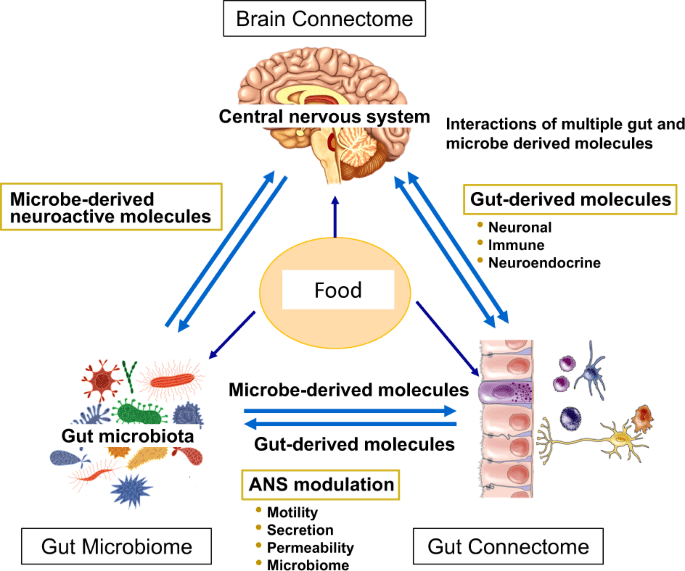
The gut microbiome plays a critical role in maintaining overall health and well-being through its intricate interactions with the human body. Extensive gut microbiome research has revealed the existence of a gut-brain connection, highlighting the impact of the microbiome on brain health and function.
The gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters that influence mood and brain function. Additionally, it affects metabolism, hunger, and immune system function. This connection underscores the importance of optimizing the gut microbiome for overall brain-body health.
Understanding the mechanisms by which the gut microbiome influences the brain and body is crucial for developing strategies to support and enhance its function. Ongoing research in this field aims to uncover the intricate relationship between the gut microbiome and brain health, paving the way for potential therapeutic interventions and personalized approaches to improve overall well-being.
Dr. Justin Sonnenburg’s Expertise
Dr. Justin Sonnenburg’s extensive knowledge and expertise in the gut microbiome make him a leading authority in the field. His research on microbial diversity has provided valuable insights into the intricate relationship between the gut microbiome and hormonal health.
Through his studies, Dr. Sonnenburg has discovered that the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating hormonal balance and optimizing overall health. The microbial diversity within the gut has been found to influence the production and metabolism of hormones, affecting various aspects of our well-being, including metabolism, mood, and reproductive health.
Dr. Sonnenburg’s groundbreaking research has shed light on the importance of maintaining a healthy gut microbiome for hormonal health and has paved the way for further exploration in this field. His expertise is invaluable in understanding and harnessing the power of the gut microbiome to promote optimal hormonal balance and overall wellness.
Understanding Crypts and Niches
Crypts and niches within the digestive tract are specialized microenvironments that harbor specific microbiota and play a crucial role in maintaining the optimal functioning of the gut microbiome. These microenvironments provide a unique habitat for different types of bacteria, allowing them to thrive and contribute to the overall health of the gut. Understanding the organization and dynamics of these crypts and niches is essential for comprehending microbial symbiosis and gut ecosystem dynamics.
To illustrate the diversity and distribution of microbiota within the gut, the following table provides an overview of some key microbiota species and their respective locations within the digestive tract:
| Microbiota Species | Location in the Gut |
|---|---|
| Bacteroidetes | Large Intestine |
| Firmicutes | Small Intestine |
| Actinobacteria | Stomach |
| Proteobacteria | Colon |
| Verrucomicrobia | Ileum |
Optimizing the Microbiome Organization
To optimize the organization of the gut microbiome, a comprehensive understanding of the spatial distribution and interactions of different microbiota is essential. The microbiome composition refers to the collection of microorganisms that reside in the gut, while spatial organization refers to their arrangement within the digestive tract. Research has shown that specific microbiota inhabit distinct locations within the gut, such as crypts and niches.
These microenvironments provide optimal conditions for the microbiota to carry out their functions and support our health. Understanding the organization of these microenvironments is crucial for optimizing the gut microbiome. By studying the spatial distribution and interactions of different microbiota, we can gain insights into how they contribute to overall gut health and identify strategies to promote a balanced and diverse microbiome composition.
This knowledge can ultimately help us develop interventions and practices that serve to enhance our well-being.
Supporting a Healthy Gut Microbiome
What are the key factors for supporting a healthy gut microbiome?
One crucial factor is maintaining microbiome diversity. A diverse gut microbiome is associated with better overall health and resilience to diseases. To promote diversity, it is essential to consume a variety of plant-based foods rich in fiber. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, nourishing beneficial gut bacteria and promoting their growth.
Another factor to consider is the gut-brain connection. The gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters that influence mood and brain function, highlighting the importance of a healthy microbiome for mental well-being.
Additionally, behaviors and interactions with the outside world can impact the gut microbiome. Interactions with animals, personal hygiene, and even mood can influence its composition.
The Role of Fermented Foods and Fiber
Fermented foods and fiber play pivotal roles in supporting a healthy gut microbiome and optimizing overall well-being.
The benefits of fermented foods include:
- Increased diversity of beneficial bacteria: Fermented foods contain live bacteria that can help populate the gut with a diverse range of beneficial microbes.
- Improved digestion: Fermented foods such as yogurt, sauerkraut, and kimchi can enhance digestion by providing enzymes that break down food.
- Enhanced nutrient absorption: Fermentation can increase the bioavailability of nutrients in foods, making them easier for the body to absorb.
- Strengthened immune system: The probiotics found in fermented foods can support a healthy immune response and reduce the risk of infections.
In addition to fermented foods, fiber also plays a significant role in gut health. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. It helps promote regular bowel movements, prevents constipation, and can reduce the risk of certain digestive disorders.
Including a variety of fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, in your diet can support a healthy gut microbiome and overall well-being.
Behaviors and Interactions Impacting the Microbiome
Various behaviors and interactions with the outside world have been shown to have a significant impact on the microbiome, shaping its composition and function. Interactions with animals, personal hygiene, and mood have all been found to influence the microbiome. Let’s take a closer look at how these behaviors can modify the microbiome:
| Behaviors and Interactions | Impact on Microbiome |
|---|---|
| Interactions with animals | Animals can introduce different microorganisms to the gut, diversifying the microbiome. Additionally, exposure to animals has been associated with a reduced risk of allergies and asthma. |
| Personal hygiene | Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, can help prevent the spread of harmful bacteria and maintain a balanced microbiome. However, excessive use of antimicrobial products may disrupt the natural microbial ecosystem. |
| Mood | Psychological stress and mood disorders have been linked to alterations in the gut microbiome. Stress can lead to changes in gut motility and increased inflammation, impacting the microbial composition. |
| Dietary habits | Diet plays a crucial role in shaping the microbiome. Consuming a diverse range of plant-based foods rich in fiber can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. On the other hand, diets high in processed foods and low in fiber can negatively impact the microbiome. |
Understanding the impact of these behaviors and interactions on the microbiome allows us to make informed choices to support a healthy gut ecosystem. By adopting practices that promote a diverse and balanced microbiome, we can optimize our overall health and well-being.
The Gut Microbiome’s Influence on Brain Health
Psychological stress and mood disorders have been found to have a profound impact on the gut microbiome, influencing its composition and function. This connection between the gut microbiome and the brain is known as the microbiome-brain connection or the gut-brain axis.
The gut microbiome can influence brain health in several ways. First, it can affect neurotransmitter production. The microbiome produces neurotransmitters that play a crucial role in regulating mood and brain function.
Second, the gut microbiome can impact metabolism and hunger. Changes in the microbiome can affect metabolism and hunger, which in turn can impact brain health.
Third, the gut microbiome plays a critical role in regulating immune system function. The immune system is closely linked to brain health, and the gut microbiome helps to maintain a healthy immune system.
Finally, imbalances in the gut microbiome can lead to chronic inflammation, which has been associated with various brain disorders.
Understanding the microbiome-brain connection is essential for optimizing brain-body health and finding strategies to support both gut and brain health.
Neurotransmitters and Brain-Body Function
The production of neurotransmitters by the gut microbiome is a critical factor in regulating brain-body function. The gut microbiome, composed of trillions of microorganisms in the digestive tract, plays a significant role in mental health and overall well-being. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells in the brain and the rest of the body. They are essential for various brain functions, including mood regulation, cognition, and behavior. The gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which have a profound impact on our mental health. This gut-brain connection highlights the importance of a healthy gut microbiome for maintaining optimal brain-body function.
To better understand the role of neurotransmitters in brain-body function, let’s take a closer look at some key neurotransmitters and their functions:
| Neurotransmitter | Function |
|---|---|
| Serotonin | Regulates mood, sleep, and appetite. Low levels are associated with depression and anxiety. |
| Dopamine | Involved in reward and pleasure pathways, motivation, and motor control. Imbalances can lead to conditions such as Parkinson’s disease and addiction. |
| GABA | Inhibitory neurotransmitter that calms the nervous system and reduces anxiety. Low levels are associated with anxiety disorders. |
The gut microbiome influences the production and availability of these neurotransmitters through its interactions with the body and the food we consume. Imbalances in the gut microbiome can disrupt neurotransmitter production, leading to mental health issues. Therefore, nurturing a healthy gut microbiome is crucial for mental well-being and overall brain-body health.
The Impact on Metabolism and Immune System
The gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in regulating metabolism and immune system function through its intricate interactions with the body’s physiological processes. This complex ecosystem of microorganisms has a profound impact on hormonal health and the gut-brain axis.
Here are some key insights into how the gut microbiome influences metabolism and immune system function:
- Hormonal Health: The gut microbiome influences the production and regulation of hormones that are involved in various metabolic processes, including energy balance, appetite regulation, and fat storage. Imbalances in the gut microbiome can disrupt hormonal signaling and contribute to metabolic disorders.
- Gut-Brain Axis: The gut and the brain communicate bidirectionally through a complex network of nerves, hormones, and immune cells. The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in this communication by producing neurotransmitters and modulating immune responses. Dysbiosis in the gut microbiome can lead to inflammation and dysfunction in the immune system, impacting overall health and well-being.
- Immune System Function: The gut microbiome plays a vital role in training and regulating the immune system. It helps distinguish between harmless substances and potential threats, ensuring an appropriate immune response. Imbalances in the gut microbiome can disrupt immune tolerance and contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases and allergies.
Understanding the impact of the gut microbiome on metabolism and immune system function is essential for optimizing overall health and well-being. By supporting a healthy gut microbiome, individuals can promote hormonal balance, enhance the gut-brain axis, and strengthen immune system function.
Live Events and Sponsors
Continuing our exploration of the gut microbiome’s impact on metabolism and immune system function, our focus now shifts to live events and sponsors. In May 2022, Andrew Huberman, in collaboration with Stanford, will be hosting two live events as part of ‘The Brain-Body Contract’ series. These events will delve into various topics related to science, health, and performance. To show appreciation for podcast listeners, pre-sale tickets are exclusively available using the code ‘Huberman’. The podcast, separate from Andrew Huberman’s roles at Stanford, aims to provide science-related information to the public. It is sponsored by Athletic Greens and ROKA, two brands that offer products supporting health and performance.
| Event Date | Event Location | Topics Covered |
|---|---|---|
| May 14, 2022 | San Francisco, CA | Gut microbiome, brain health, metabolism |
| May 21, 2022 | New York City, NY | Immune system function, hormonal health, performance |
These live events provide an opportunity for individuals to gain valuable insights from experts in the field and learn about the latest research on the gut microbiome’s impact on overall health. By offering pre-sale tickets and podcast sponsorship, Andrew Huberman and his sponsors are dedicated to serving others by making this information accessible to a wider audience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Specific Microorganisms That Make up the Gut Microbiome?
The gut microbiome consists of a diverse array of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and archaea. These microorganisms play a crucial role in gut microbiome research and contribute to overall health and well-being.
How Does the Gut Microbiome Impact Hormonal Health?
The gut microbiome has a profound impact on hormonal health. It plays a crucial role in regulating hormone production and metabolism, which can affect fertility and weight management. Understanding and optimizing the gut microbiome is essential for maintaining hormonal balance.
Can the Gut Microbiome Affect Our Mood and Mental Health?
The gut-brain connection is a fascinating area of research that explores how the gut microbiome can influence mood and mental health. Emerging evidence suggests that imbalances in the gut microbiome may contribute to anxiety and other mental health disorders.
What Are Some Practical Ways to Modify and Optimize the Gut Microbiome?
To modify and optimize the gut microbiome, practical strategies include incorporating fermented foods and fiber-rich diet, practicing good personal hygiene, managing stress levels, and establishing a healthy lifestyle. These interventions can have a significant impact on gut health.
Are There Any Specific Fermented Foods or Types of Fiber That Are Particularly Beneficial for the Gut Microbiome?
Fermented foods, such as yogurt, sauerkraut, and kefir, are beneficial for the gut microbiome due to their high levels of beneficial bacteria. Types of fiber, like soluble fiber found in fruits and vegetables, also support a healthy gut microbiome.







