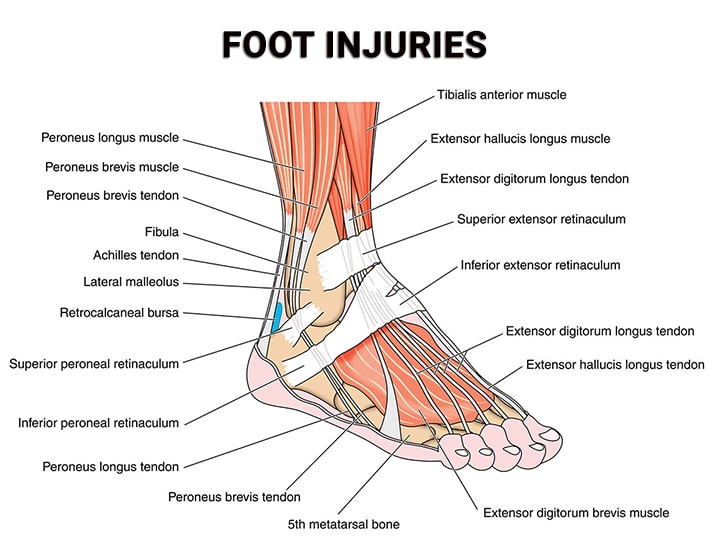
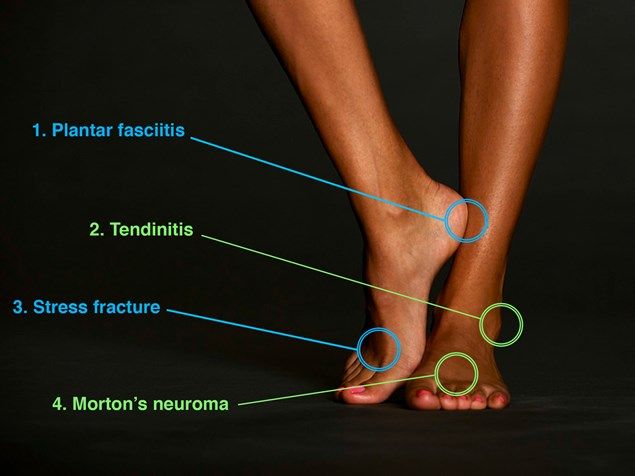
How To Recognize And Treat Common Foot Injuries
Foot injuries are a common occurrence, especially in athletes. While many foot injuries can be treated with home remedies such as rest and elevation, some may require medical attention or even surgery. It is important to recognize the signs of common foot injuries so that proper treatment can be obtained. This article will provide information on how to identify and treat common foot injuries.
The first step in recognizing and treating common foot injuries is being aware of the different types of injury that exist. Common types include sprains, strains, fractures, tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, bursitis, Achilles tendinopathy and stress fractures. Each type has its own set of symptoms which should be monitored for if an injury occurs. For example, strains usually cause pain when stretching or contracting the affected muscle while fractures often result in swelling and bruising around the area of impact.
Finally, once a diagnosis has been made it is important to determine what kind of treatment is needed for each particular injury. Treatment options range from rest and ice to physical therapy exercises depending on the severity of the injury. Proper care must always be taken to ensure full recovery without any long-term effects such as chronic joint instability or weakened muscles due to scarring from surgery or other treatments.
Definition Of Foot Injury
According to the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons, an estimated 4 million people suffer from foot injuries each year. A foot injury is defined as any type of damage that affects the bones, ligaments, or tendons in the foot. This can range from minor scrapes and bruises to serious fractures and dislocations.
The most common types of foot injuries include sprains, strains, Achilles tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, stress fractures, turf toe, bunion deformities, and heel pain syndrome. Sprains are caused by overstretching or tearing a ligament while strains involve stretching or tearing a muscle or tendon. Achilles tendonitis occurs when the large Achilles tendon at the back of the ankle becomes inflamed due to overuse. P
lantar fasciitis is inflammation of thick tissue on the bottom of one’s foot that connects your heel bone to your toes and causes severe radiating heel pain. Stress fractures occur when small cracks form due to repeated physical stress on a single area such as running long distances every day without proper footwear support.
Turf toe is another repetitive strain injury which involves excessive force placed on big toe joint causing it to bend too far forward resulting in swelling and pain around the area. Bunions are bony lumps typically found near base of great toe where bones become misaligned leading to redness and discomfort whereas Heel Pain Syndrome mostly results from overpronation (when feet roll inward excessively) leading to uneven distribution of weight across heels making them vulnerable for pain and soreness.
Given these potential sources of injury it is important to pay attention to signs that may indicate you have injured your foot so treatment can begin quickly before further complications arise.
Signs And Symptoms
The most common signs and symptoms of a foot injury are pain, swelling, bruising, tenderness or deformity. Pain is usually the first symptom to appear when an injury occurs. It may be localized in one area or spread throughout the entire foot. Swelling can occur right away, but it may also take several hours for it to become noticeable. Bruising may not show up until days after the initial trauma, so keep an eye out for any discoloration that might indicate internal bleeding.
Tenderness around the affected area should also be monitored as this could suggest deeper tissue damage such as fractures and ligament tears. Deformity of the injured part of the foot is another sign of significant harm and requires medical attention immediately. In some cases, even mild discomfort can signify severe underlying issues with tendons, bones or nerves that require professional diagnosis and treatment. Transition: To identify possible risk factors associated with foot injuries, understanding how certain activities put individuals at greater risk is essential.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for foot injuries can vary from person to person. For example, a professional athlete may be more prone to sprained ankles due to the intensity of their sport versus someone who is mostly inactive and not regularly exercising. An individual with poor circulation or existing medical conditions such as diabetes may have increased risk for developing ulcers on their feet that could lead to infection if left untreated. Poor footwear choices can also increase the chance of suffering an injury due to lack of support or improper fit.
Wearing shoes that are too small or do not provide adequate cushioning can contribute to instability in the foot, leading to pain and potential damage over time. Structural abnormalities within the foot itself, such as flat arches or bunions, can increase one’s odds of sustaining an injury while walking or running as well. To reduce risk, it is important for people across all ages and activity levels to take proper care of their feet by selecting appropriate shoes, stretching before exercise, and elevating the legs when possible. Transitioning into diagnosis methods, there are various tests available for detecting and assessing a wide range of common foot injuries.
Diagnosis Methods
Having discussed risk factors for foot injuries, the subsequent section will focus on diagnosis methods that can help to identify and treat these common ailments. Diagnosis of a foot injury is typically based upon an individual’s reported symptoms, as well as physical tests done by a licensed medical professional. A thorough evaluation should include visual inspection of the affected area, palpation or feeling the area or structure with the hands, and possibly range-of-motion testing to ensure there are no structural problems such as ligament damage.
Additional assessment techniques may involve imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasound scans, MRI scans, and CT scans. These tests provide further insight into any underlying conditions that could be causing pain or other symptoms in the feet.
If an injury is determined to be present due to any of the tests described above, treatment options will depend upon what type of injury has been identified. Treatment plans usually consist of rest, immobilization using splints or casts if necessary, over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain relief and inflammation reduction, icing the injured area several times per day for up to 20 minutes at a time initially followed by heat therapy after 48 hours have passed since initial onset of pain in order to promote healing process; stretching exercises recommended by a doctor or physical therapist; orthoses or custom shoe inserts for arch support; and possible surgical intervention depending on severity of condition.
The next section will discuss home care for minor injuries which do not require medical attention but still need proper management in order to heal properly.
Home Care For Minor Injuries
Home care is a viable option for minor foot injuries. After an injury, it is important to rest the affected area and reduce activities that lead to further pain or discomfort. Simple measures such as elevation of the feet above heart level, using crutches if available and wearing supportive shoes can also help in managing pain levels during recovery. In addition, over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be used to relieve pain and swelling.
It is essential to protect injured tissue from additional trauma while allowing appropriate healing time. Protection can involve bandaging, taping techniques or even splinting with commercially available products designed for home use. Analgesic creams containing capsaicin or topical lidocaine are often helpful when applied on areas where there is localized tenderness or inflammation.
Compression stockings may also aid in reducing swelling by providing a gradual pressure gradient around the ankle region that promotes venous return circulation. Additionally, some people find relief through alternative therapies such as acupuncture and yoga which are believed to relax muscles, reduce stress and promote better posture. Transition sentence: Ice or heat therapy may also be beneficial depending on the type of injury sustained.
Ice Or Heat Therapy
The power of heat and cold to relieve pain has been known since antiquity. In today’s world, ice or heat therapy is a most common method for treating foot injuries. Utilization of both can:
- Reduce swelling
- Decrease inflammation
- Ease muscle spasms
- Diminish pain
By applying an appropriate temperature source, the body will draw blood to the injured area which helps in restoring tissue damage and promoting healing. Cold sources such as gels and packs numb the area while hot sources like baths and wraps relax it. Depending on the severity and type of injury, either one may be applied up to three times per day for 20 minutes at a time. It is advised that if there is any redness or swelling associated with using these treatments then they should cease immediately.
Furthermore, over-the-counter medications are also available to provide relief from common foot pains.
Over-The-Counter Medications
Different over-the-counter medications are available to treat foot injuries. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation, such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium. They should be taken with meals to minimize side effects. If a patient has an allergy to NSAIDs, acetaminophen is a good alternative for relieving pain without increasing the risk of adverse reactions. Topical analgesics such as mentholated creams and gels may also provide temporary relief by numbing the affected area.
Cold therapy using ice packs applied several times a day helps decrease swelling and discomfort from mild soft tissue injury. Heat therapy using warm compresses can promote relaxation in sore muscles but should not be used if there is any sign of infection present at the site of injury; otherwise it could lead to further complications. Transitions between treatments should occur slowly so that skin does not become irritated due to rapid temperature changes. Physiotherapy is another option for treating common foot injuries…
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is a common treatment for foot injuries. It involves targeted exercises and stretching to reduce pain, improve mobility, and strengthen the area around the injury. For instance, if an individual sprained their ankle due to overuse or incorrect form during physical activity, physiotherapy could help restore range of motion in the joint by using manual manipulation techniques as well as specific exercises that target muscles used when walking. Additionally, appropriate stretches can be prescribed to ensure proper flexibility and strength are maintained while healing from the injury. Finally, special braces may also be recommended to support weakened joints or tissues until they have healed completely. Orthotics and braces provide extra protection against further damage and assist with rehabilitation efforts.
Orthotics And Braces
Orthotics and braces are another form of treatment for common foot injuries. Orthotics are devices that provide support to the feet, reduce pain and improve function. They can be used in cases of flatfoot or high arch collapse, plantar fasciitis, heel spurs, bunions and hammertoes. Braces also provide stability, but they are designed to limit movement in order to protect a weakened area or prevent further injury.
Common types of braces include ankle supports such as stirrups or lace-up style braces; heel pads which help relieve pressure from Achilles tendonitis; compression socks which increase circulation; and shoe inserts which add cushioning and shock absorption. Both orthotics and braces should be prescribed by a medical professional who will assess an individual’s needs based on their diagnosis.
When using these treatments it is important to follow instructions carefully in order to maximize results. These may include wearing them only when needed, keeping them clean and dry after use, replacing them regularly if necessary and avoiding activities that could result in further injury while using them. Additionally, there may be certain lifestyle modifications required depending on the severity of the condition being treated with orthotics or bracing.
Properly fitted orthotics or bracing can play a significant role in restoring proper alignment during healing from a foot injury as well as helping to prevent future problems if worn for long enough periods of time. With careful consideration given to appropriate usage guidelines, this type of treatment can often yield positive outcomes without the need for more invasive procedures such as steroid injections.
Steroid Injections
Stepping up to the plate, steroid injections can be a powerful tool in treating common foot injuries. These injections aim to reduce inflammation and pain while also promoting healing of soft tissue. They are most effective when used with proper rest and activity modification. However, it is important to note that they do not change the underlying cause of an injury, so they should only be used after other conservative treatment methods have been exhausted.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Reduces Pain & Inflammation | Does Not Change Underlying Cause |
| Promotes Healing Of Soft Tissue | Temporary Solution Only |
| Can Be Used With Activity Modification | Can Have Side Effects (i.e Numbness) |
When considering steroid injections for any foot injury, one must weigh both the benefits and risks associated with them. It is always advised to seek professional medical advice from a doctor or sport medicine specialist before deciding on this form of treatment. Furthermore, it is essential to follow post-treatment recommendations such as wearing appropriate shoes and avoiding activities that may aggravate the condition until fully healed.
Steroid injections offer many potential benefits but their use should be carefully considered on a case by case basis due to associated risks involved. Taking all these factors into account will help ensure successful outcomes and improved quality of life for those suffering from common foot injuries. Moving forward, surgery offers another option for those looking to treat more serious conditions affecting their feet.
Foot Surgery
When the injury is severe, surgery may be necessary. It can help repair damage to bones and tendons, address infection or remove a foreign body from the foot. Surgery will depend on the type of injury and its severity. Common procedures include tendon repairs, wound closures, bone fractures or joint fusions. Depending on the procedure, it could take anywhere from one hour for minor surgeries to multiple hours for complex ones. During this time, general anesthesia may be used to ensure that no pain is felt during surgery.
Post-operative care is essential in order to reduce risks of complications such as infections and blood clots. This includes regularly changing dressings and taking medications as prescribed by healthcare professionals. Patients must also keep their feet elevated above heart level when possible and avoid putting too much weight on them while healing takes place. Adhering to these post-operative instructions is critical for successful healing after surgical intervention for common foot injuries.
The next step in treating common foot injuries is focusing on recovery tips.
Recovery Tips after Foot Injuries
Having discussed the various surgical approaches to dealing with common foot injuries, it is time now to turn attention towards recovery. To begin this journey, we must first understand what steps need to be taken in order to ensure a safe and speedy healing process. Like shining a light on a dark path, knowledge of proper care can help guide us toward successful rehabilitation.
The initial phase after surgery should involve rest and elevation. Keeping weight off of the injured area and allowing gravity to do its work will help reduce swelling, promote circulation, and encourage the body’s natural healing capabilities. Compression may also be beneficial at times when reducing inflammation or providing support; however caution should be exercised as too much pressure could cause further injury. Additionally, icing the affected area for 10-15 minutes every two hours can help relieve pain and minimize tissue damage.
Rehabilitation exercises are an important part of any postoperative treatment plan as they allow for gradual return of strength and range of motion around the joint. It is essential that these activities are done slowly and with precise technique in order to avoid exacerbating existing conditions or causing new ones. Physical therapy can be very helpful in designing individualized programs tailored specifically for each patient so as to maximize healing outcomes while minimizing potential complications from overdoing it.
As we look ahead towards our next destination – prevention strategies – let us remember all that has been learned about recovering from common foot injuries: rest, elevation, compression when necessary, icing regularly, physical therapy if possible; all tools which enable us achieve long term success through smart short term decisions.
Foot Injuries Prevention Strategies
In order to prevent common foot injuries, it is important to take certain precautions. The following are a few preventive strategies:
- Wear appropriate footwear that fits properly and provides adequate cushioning and support for the feet.
- Increase physical activity gradually so as not to overexert the muscles and tendons in the feet.
- Strengthen the muscles in your feet with exercises such as toe curls or ankle circles.
- Stretch before any strenuous activities to help reduce muscle tension and improve flexibility in the feet.
It is also important to recognize signs of potential injury early on, when treatment can be more effective and recovery time shorter. Understanding how to prevent these injuries is key for maintaining healthy feet over time, but even those who practice prevention can experience an unexpected sprain, fracture, or strain due to accidents or intense sports activities. In such cases, professional care considerations become necessary in order to ensure proper healing and full rehabilitation from an injury.
Professional Care Considerations
After establishing a prevention strategy, it is important to recognize and treat common foot injuries. The most effective way to do this is by understanding the signs and symptoms of various ailments so that one can seek professional care sooner rather than later.
An effective metaphor for recognizing and treating foot injuries is like driving a car: if you pay attention to warning signals before they become major problems, then expensive repairs are sometimes avoidable. This means keeping an eye out for any red flags such as swelling, pain, or difficulty in mobility. For example, if you have been running more frequently than usual and experience sudden pain while doing so, it could be indicative of a stress fracture which requires medical intervention.
| Injury | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Stress Fracture | Pain during activity Swelling around bone Tenderness on bone surface |
Rest from activity Medication/physical therapy Casting or bracing as needed |
| Plantar Fasciitis | Heel pain when standing Pain worsened with exercise Sharp stabbing sensation in arch area |
Ice massage and stretching exercises Anti-inflammatory medications Custom orthotics or night splints |
| Achilles Tendonitis | Reduced flexibility in calf muscles Pain behind anklebone after activities Popping sound during movement at back of heel |
RICE (rest, ice, compression & elevation) Stretching & strengthening exercises Night splints or custom orthotics as needed |
When seeking professional help, there are several options available depending on the severity of the injury. A primary care physician may perform basic exams and refer patients to specialists if necessary. Orthopedic doctors specialize in musculoskeletal issues along with sports medicine physicians who focus on athletes’ health concerns. Physical therapists provide therapeutic measures like ultrasound therapy and taping techniques for relief of inflammation and pain associated with foot conditions. Lastly, podiatrists deal specifically with feet related disorders ranging from fungal infections to serious deformities requiring surgery.
Although treatment strategies vary based on the type of injury incurred, prompt recognition is key to managing any issue effectively over time. Long-term outlook involves continued preventive practices such as rest periods between strenuous activities coupled with regular physical maintenance programs that address strength training specific areas of weakness within the body’s biomechanics.
Long-Term Outlook
In most cases, foot injuries can be treated with rest and proper care. However, if an injury is more severe or occurs repeatedly, long-term outlook should be taken into consideration. The overall prognosis of a foot injury depends on the type and severity of the injury:
- For fractures, recovery times vary depending on the severity of the fracture as well as how quickly treatment was sought out
- Minor ligament sprains may heal in one to two weeks; however, more serious ligament tears require longer periods for healing
- Plantar fasciitis usually responds well to conservative treatments but may take several months before full pain relief is achieved
The outcomes for those who experience recurrent foot injuries are typically not good. Without properly addressing the underlying cause of these issues, such as improper footwear or poor body mechanics, re-injury is likely. It is important to seek medical advice from a professional to ensure that any necessary adjustments are made prior to returning to activity. With appropriate measures in place, individuals can reduce their future risk of further injury while also improving their quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Most Effective Treatment For A Severe Foot Injury?
Navigating an injury to the foot can be a delicate process that requires proper care and treatment. Severe injuries demand specialized attention from medical professionals, who can provide effective treatments for those suffering from these issues. This article will explore what is considered the most effective approach when treating severe foot injuries.
The first step in addressing a significant foot injury is seeking out professional medical help. Consulting with trained personnel allows for an accurate diagnosis of the condition at hand; this may involve X-rays or other imaging tests to determine the severity and any underlying factors present. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to ensure optimal healing; however, further analysis by experienced physicians should always come before making such decisions. Furthermore, physical therapy or rehabilitation programs may also be recommended so as to strengthen muscles and restore range of motion around the affected area.
Finally, appropriate medications are often prescribed following an examination performed by healthcare providers. Pain relief drugs such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may offer temporary respite while more powerful opioids could be administered depending on the level of discomfort being experienced. Moreover, topical ointments can reduce swelling and inflammation caused by a serious foot injury if recommended by a doctor after evaluation of symptoms and possible risks associated with their use.
In sum, it is essential to find guidance from qualified medical professionals when dealing with a severe foot injury due to its complexity and potential consequences if ignored or not treated correctly. Proper diagnosis followed up with suitable medication and/or rehabilitative exercises are commonly used strategies that have been found beneficial in many similar cases over time.
Are There Any Exercises That Can Help Strengthen My Foot Muscles?
Exercises to strengthen foot muscles are an important element of any injury prevention and recovery program. Strength training can help reduce the risk of injuries, as well as improve overall performance in everyday activities. There is a wide range of exercises that can be used to target different areas of the foot, including strengthening the ankle joint, improving balance and stability, and increasing flexibility.
Dynamic stretching has been found to be effective at targeting all muscle groups connected to the feet. Examples include heel raises, toe pulls, shin stretches, calf raises, side lunge steps and single-leg hops. Isometric exercises such as wall sits or planks may also help build strength in certain parts of the foot while working other muscles simultaneously. Additionally, resistance bands or free weights can provide additional benefits when it comes to building strength throughout the entire lower body area.
Injury rehabilitation should always follow advice from a medical professional but pursuing appropriate exercise programs for strengthening your feet is likely to have positive effects on both preventing further injury and aiding with existing ones. It will also benefit you by enhancing physical activity performance if practiced correctly with guidance from specialists such as physiotherapists or personal trainers who specialize in this field.
How Long Is The Recovery Period For A Foot Injury?
Recovery from a foot injury can vary greatly depending on the severity of the injury and the type of treatment used. When it comes to recovery times, one size does not fit all; as with many things in life, each individual case is unique. Despite this complexity, there are some general guidelines that may be useful when considering how long a period of time will be needed for full healing. As the old saying goes: patience is a virtue – especially when it comes to treating an injured foot.
The initial stages of any foot injury typically involve rest, compression, elevation and ice therapy (RICE). Depending on the specifics of the injury and recommended treatments by medical professionals, these steps may take anywhere from two days up to three weeks or more to complete. In cases where surgical intervention is necessary, additional weeks should be factored into expected length of total recovery time.
In addition to following RICE protocol closely during initial treatment phases, physical therapy exercises have been found to improve blood flow and help in restoring strength and range-of-motion faster than traditional methods alone. While progress may appear slow at first glance – much like watching paint dry – steady rehabilitation over time often yields positive results in terms of pain relief and full restoration of function. Allowing ample time for recovery helps ensure proper healing takes place before resuming regular activities such as running or playing sports again.
For those who suffer from serious injuries involving fractures or torn ligaments/tendons in their feet, taking measured steps towards regaining pre-injury levels can lead to better overall outcomes. By implementing an appropriate plan designed by healthcare providers based on individual needs combined with self-discipline through patient adherence to prescribed protocols, recovering from a foot injury can become less daunting and ultimately rewarding experience in the end.
Are There Lifestyle Changes I Should Make To Prevent Future Foot Injuries?
Foot injuries are common, and often result in debilitating pain. As such, it is important to consider lifestyle changes that can be made to help prevent future foot injuries. In order to understand what these changes may entail, one should first look at the potential causes of foot injury. Commonly, improper footwear or physical activities with high levels of impact cause most cases of foot injury.
To reduce risk of further injury, individuals should make sure they have proper fitting shoes for any activity they plan on participating in. This means wearing shoes designed specifically for the activity – running shoes for running, basketball shoes for playing basketball, etc. Additionally, those who participate in sports or exercise regularly should incorporate rest periods into their routine so as not to overwork the muscles and ligaments in their feet. It is also beneficial to stretch before any strenuous physical activity as this allows muscles time to warm up and become more flexible prior to use; likewise cooling down stretches after a workout can help reduce inflammation and soreness.
Finally, if an individual suspects they may already have a minor injury developing due to prolonged standing or repetitive movements like jogging or dancing then it is recommended that they take some time off from whatever task brought them the discomfort initially and seek medical advice if needed. Taking preventive measures such as these can go a long way toward avoiding serious foot injuries in the future.
What Are The Side Effects Of Steroid Injections For Foot Injuries?
As the use of steroids for foot injuries becomes increasingly common, it is important to understand the potential side effects of steroid injections. Steroid injections are commonly used to reduce inflammation and pain associated with a variety of conditions, including plantar fasciitis and Achilles tendinopathy. While these treatments may offer short-term relief from symptoms, they can also have lasting consequences if not monitored closely.
The most significant risk associated with steroid injections is that of infection. As any foreign substance injected into the body carries an increased risk of bacterial contamination, patients should be sure to follow their doctor’s instructions precisely when administering the injection. Additionally, long-term use or overuse of steroids can lead to weakened bones and soft tissue damage due to atrophy of surrounding muscles and connective tissues. Other possible risks include elevated blood sugar levels and changes in hormone production which could lead to development issues such as Cushing’s Syndrome or adrenal suppression.
For those who choose steroid injections as a treatment option, careful monitoring by both patient and physician will be required throughout the process. This includes regular checkups, laboratory tests, and imaging scans to ensure that no serious complications arise from continued usage. It is also essential that individuals maintain an appropriate level of activity following an injection so as not to aggravate underlying conditions further. Taking all these steps helps ensure safe administration of this powerful medication while minimizing its potential harmful effects on one’s health over time.
Conclusion
Foot injuries can cause a great deal of pain and discomfort, but fortunately there are treatment options available. The most effective approach to treating a severe foot injury is to seek medical assistance as soon as possible. This will help to prevent further damage and reduce the risk of complications. Exercise may also be beneficial in strengthening weakened muscles around the area of injury, whilst lifestyle changes such as wearing appropriate footwear and avoiding activities that could worsen the injury should also be considered.
Steroid injections for severe cases have been found to provide relief from inflammation and swelling, however this method carries with it potential side effects which must be taken into account when making any decisions about treatment. Although steroid injection therapy is often successful, it has been suggested that other treatments such as cold compresses or physical therapy may prove more beneficial in relieving symptoms without introducing the risks associated with medication-based solutions.
In conclusion, although foot injuries can present moderate to severe levels of pain and discomfort, swift diagnosis and early intervention are key elements in achieving an optimal recovery outcome. A combination of professional medical advice combined with supportive home care measures including exercise regimens specifically tailored to individual needs offer hope for a complete return to pre-injury mobility and function.