Menstrual Cycle And Fertilization Explained
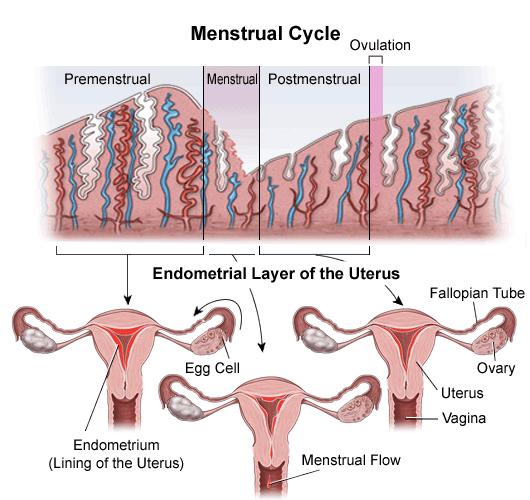
The menstrual cycle is a complex physiological process that occurs in the female reproductive system, consisting of multiple phases that are regulated by a complex interplay of hormones.
The primary purpose of the menstrual cycle is to prepare the female body for potential fertilization and pregnancy.
Understanding the menstrual cycle and the factors that affect fertility is crucial for individuals who are trying to conceive and for healthcare providers who specialize in reproductive health.
Fertilization, the process by which a sperm cell merges with an egg cell to form a zygote, is dependent on a variety of factors, including the timing of ovulation, the quality of the sperm and egg cells, and the overall health of the reproductive system.
In this article, we will explore the phases of the menstrual cycle, the role of hormones in regulating the cycle, the process of ovulation, factors that affect fertility, and common issues that can impact the menstrual cycle and fertility.
We will also discuss strategies for timing intercourse for conception and when to seek medical help for fertility concerns.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the menstrual cycle and factors affecting fertility is crucial for conception and reproductive health.
- Hormones play a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle and maintaining optimal conditions for ovulation.
- Age, health conditions, lifestyle choices, and medical conditions can impact fertility.
- Optimizing timing of sexual intercourse is crucial for couples trying to conceive.
The Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle consists of four distinct phases, each characterized by hormonal changes that regulate the physiological processes involved in ovulation and menstruation.
The first phase is the follicular phase, which begins on the first day of menstruation and lasts for approximately 14 days. During this phase, the pituitary gland releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the growth of several follicles in the ovaries. These follicles contain immature eggs, and as they grow, they produce estrogen, which thickens the lining of the uterus in preparation for a potential pregnancy.
The second phase is ovulation, which occurs around day 14 of the menstrual cycle. The surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary gland triggers the release of a mature egg from one of the follicles in the ovaries. The egg then travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus, where it may be fertilized by sperm.
If the egg is not fertilized, it will disintegrate, and the cycle will continue into the next phase, the luteal phase. During this phase, the empty follicle from which the egg was released becomes the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone to maintain the thickened uterine lining.
The Role of Hormones in the Menstrual Cycle
Hormonal regulation in the female reproductive system plays a crucial role in the maintenance of optimal conditions for ovulation. The hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and ovaries work together to ensure a successful menstrual cycle.
The hypothalamus produces gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which signals the pituitary gland to release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). These hormones, in turn, stimulate the growth and development of follicles in the ovaries, leading to the release of an egg during ovulation.
The role of hormones in the menstrual cycle is complex, and any imbalance can result in irregular periods or infertility. As such, women may experience a range of emotions throughout their menstrual cycle, including anxiety, stress, and frustration.
The uncertainty of when ovulation will occur, coupled with the physical and emotional symptoms of menstruation, can be overwhelming. Nevertheless, understanding the role of hormones in the menstrual cycle can help women make informed decisions about their reproductive health and seek appropriate medical attention if necessary.
How Ovulation Occurs
In the female reproductive system, ovulation occurs through a complex interplay of signals between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and ovaries.
The hypothalamus, a small region in the brain, secretes gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) which stimulates the pituitary gland to release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
FSH stimulates the development of follicles in the ovaries, which contain immature egg cells. As the follicles grow, they produce estrogen, which helps to thicken the uterine lining in preparation for pregnancy.
As estrogen levels rise, they trigger a surge in LH, which causes the dominant follicle to rupture, releasing a mature egg cell into the fallopian tube.
This process is known as ovulation and typically occurs around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle. The released egg cell is then available for fertilization by sperm, which can occur in the fallopian tube before the fertilized egg travels to the uterus for implantation.
If fertilization does not occur, the egg cell disintegrates and is absorbed by the body, and the menstrual cycle begins again.
Factors Affecting Fertility
Various factors can impact a person’s ability to conceive a child, which can be overwhelming and distressing for those hoping to start a family. These factors include age, overall health, lifestyle choices, and medical conditions. Age is perhaps the most significant factor affecting fertility, as a woman’s egg quality and quantity decline as she ages. Women over the age of 35 are at higher risk of infertility, miscarriage, and complications during pregnancy.
Overall health is also important for fertility, as conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and thyroid disorders can negatively impact reproductive function. Lifestyle choices, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use, can also reduce fertility. Medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can also affect fertility. However, it is important to note that infertility is not always caused by the female partner, as male factors such as low sperm count or poor sperm quality can also contribute to difficulty conceiving. Understanding these factors and seeking medical advice can help individuals make informed decisions about their fertility and family planning.
| Factor | Impact on Fertility | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Egg quality and quantity decline with age, increasing risk of infertility, miscarriage, and complications during pregnancy | ||
| Health Conditions | Obesity, diabetes, thyroid disorders, and other medical conditions can negatively impact reproductive function | ||
| Lifestyle Choices | Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use can reduce fertility | ||
| Medical Conditions | Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and other conditions can affect fertility | as well as certain chronic illnesses such as diabetes and autoimmune disorders. It is important to address and manage these conditions in order to optimize fertility. |
Timing Intercourse for Conception
Optimizing the timing of sexual intercourse is crucial for couples trying to conceive, as it increases the chances of successful fertilization. There are several factors that need to be taken into consideration when timing intercourse, such as the menstrual cycle of the female partner, the lifespan of sperm and the timing of ovulation.
Here are four important things to keep in mind when trying to conceive:
- Understanding the menstrual cycle: The menstrual cycle typically lasts for 28 days, with ovulation occurring around day 14. However, this can vary from woman to woman, with some having cycles that last between 21-35 days. It is important to track the menstrual cycle to determine the most fertile days.
- Monitoring basal body temperature: Basal body temperature (BBT) is the body temperature taken immediately upon waking up in the morning. A rise in BBT indicates ovulation has occurred, and the most fertile days are the 3 days leading up to this rise in temperature.
- Using ovulation prediction kits: Ovulation prediction kits detect the luteinizing hormone (LH) surge that occurs 24-48 hours before ovulation. These kits can help determine the most fertile days.
- Timing intercourse: Timing intercourse to coincide with the most fertile days can increase the chances of successful fertilization. It is recommended to have intercourse every other day during the fertile period.
By keeping these factors in mind, couples can increase their chances of successful fertilization and increase their chances of conceiving. It is important to remember that every woman is different and may require different methods for determining the most fertile days. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help couples determine the best approach for their individual situation.
Timing intercourse for conception is an important aspect of fertility. By understanding the menstrual cycle, monitoring basal body temperature, using ovulation prediction kits and timing intercourse, couples can increase their chances of successful fertilization and conceive. It is important to remember that patience and consistency are key when trying to conceive, and that every couples journey is unique.
Signs of Ovulation and Fertility
Identifying the signs of ovulation and fertility can be a hopeful and exciting moment for couples trying to conceive. Ovulation is the process when the ovary releases a mature egg into the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm. The menstrual cycle provides clues to help identify when ovulation is likely to occur. On average, the menstrual cycle lasts 28 days, with ovulation occurring on day 14. However, cycles can vary from 21 to 35 days, and some women may not ovulate every cycle.
There are several signs of ovulation and fertility that couples can look out for. One of the most reliable indicators is a change in cervical mucus. During ovulation, cervical mucus becomes clear, slippery and stretchy, similar to raw egg whites. This type of mucus helps sperm travel up to the fallopian tube to fertilize the egg.
Another sign of ovulation is a slight increase in basal body temperature, which is the bodys resting temperature. This increase can be detected by taking the temperature every morning before getting out of bed.
Additionally, some women may experience mild cramping or pain on one side of their lower abdomen around the time of ovulation.
Common Issues with Menstrual Cycles and Fertility
Irregularities in the menstrual cycle and fertility can present challenges for couples trying to conceive. One common issue is anovulation, which is the absence of ovulation or the failure of the ovaries to release an egg. This can be caused by hormonal imbalances, stress, weight fluctuations, or conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Another issue is irregular menstrual cycles, which can make it difficult to predict ovulation and time intercourse correctly. Irregular cycles can be caused by various factors, including thyroid disorders, stress, excessive exercise, and certain medications.
In addition, some women may experience pain or discomfort during ovulation, a condition known as mittelschmerz. This can be a sign of a more serious condition such as endometriosis, in which tissue that is supposed to grow inside the uterus grows outside it.
Finally, age can also affect fertility, as a woman’s ovarian reserve declines over time. While there are various treatments available for these issues, it is important for couples to seek medical advice if they are having difficulty conceiving.
Seeking Medical Help for Fertility Concerns
One effective approach for addressing fertility concerns is to seek medical guidance from a qualified professional who can provide personalized recommendations and treatment options. When individuals or couples have been trying to conceive for a year or more without success, it may be time to consult with a fertility specialist. These medical professionals have specialized training and expertise in diagnosing and treating fertility issues, and they can help identify potential causes of infertility, such as hormonal imbalances, structural abnormalities, or genetic disorders.
During a fertility consultation, the doctor will typically ask about the individual’s medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order various tests to assess the individual’s reproductive health. Based on the findings, the doctor may recommend a range of treatment options, which can include medication, surgery, assisted reproductive technologies, or lifestyle changes. Seeking medical help for fertility concerns can be a difficult and emotional decision, but it can also be the first step towards achieving a successful pregnancy.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive evaluation of reproductive health | Costly treatments |
| Personalized treatment options | Time-consuming appointments |
| Access to specialized expertise | Emotional stress and uncertainty |
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the menstrual cycle and fertilization process is crucial for those trying to conceive. The menstrual cycle has four distinct phases, each regulated by hormones that prepare the body for pregnancy.
Ovulation is the pivotal point in the cycle, where an egg is released and can be fertilized by sperm.
Several factors can affect fertility, including age, health, and lifestyle habits. Timing intercourse during the fertile window can increase the chances of conception. Signs of ovulation and fertility can also aid in identifying the best time to try for a baby.
Additionally, monitoring menstrual cycles and seeking medical help for fertility concerns can provide valuable insight into potential issues. Overall, a thorough understanding of the menstrual cycle and fertilization process can help individuals take control of their fertility journey.