The Impact Of High Cholesterol On Blood Health
Cholesterol is a fatty substance found in the blood that is essential for the proper functioning of the body. However, when levels of cholesterol become too high, it can have a negative impact on overall blood health.
High cholesterol levels are a common health concern and can lead to a variety of health problems, including heart disease and stroke. Understanding the connection between high cholesterol and blood health is important for individuals to take proactive steps to manage their cholesterol levels and maintain overall health.
Research has shown that high cholesterol levels can increase the risk of plaque buildup in arteries, which can lead to a range of health problems. Plaque buildup occurs when cholesterol and other substances accumulate on the walls of the arteries, causing them to narrow and harden. This can restrict blood flow to vital organs, including the heart and brain, and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Additionally, high cholesterol levels can also increase the risk of blood clots, which can be life-threatening if they occur in critical areas of the body, such as the lungs or brain. Understanding the impact of high cholesterol on blood health is crucial for individuals to take proactive steps to manage their cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of developing serious health problems.
Key Takeaways
- High cholesterol levels can negatively impact blood health and increase the risk of various health issues, including heart disease, stroke, and aneurysms.
- LDL cholesterol is considered ‘bad’ and can build up in arteries, while HDL cholesterol is ‘good’ and helps remove LDL from the bloodstream.
- Lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet and regular exercise, can help improve cholesterol levels.
- Medications such as statins can also be effective in reducing LDL cholesterol levels and the risk of cardiovascular events, but potential side effects should be closely monitored by healthcare professionals.
Understanding Cholesterol and Its Role in the Body
The understanding of cholesterol and its physiological role in the body is crucial in comprehending the impact of high cholesterol on blood health, evoking a sense of urgency in addressing the issue.
Cholesterol is a type of lipid, or fat, that is produced by the liver and found in certain foods. It plays a crucial role in the body, as it is essential for the formation of cell membranes, the production of hormones, and the digestion of fats.
There are two types of cholesterol: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL cholesterol is often referred to as ‘bad’ cholesterol, as it can build up in the walls of the arteries and lead to atherosclerosis, a condition in which the arteries become narrowed and hardened.
HDL cholesterol, on the other hand, is often referred to as ‘good’ cholesterol, as it helps to remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. It is important to maintain a healthy balance of these two types of cholesterol to ensure optimal blood health.
The Connection Between High Cholesterol and Blood Health
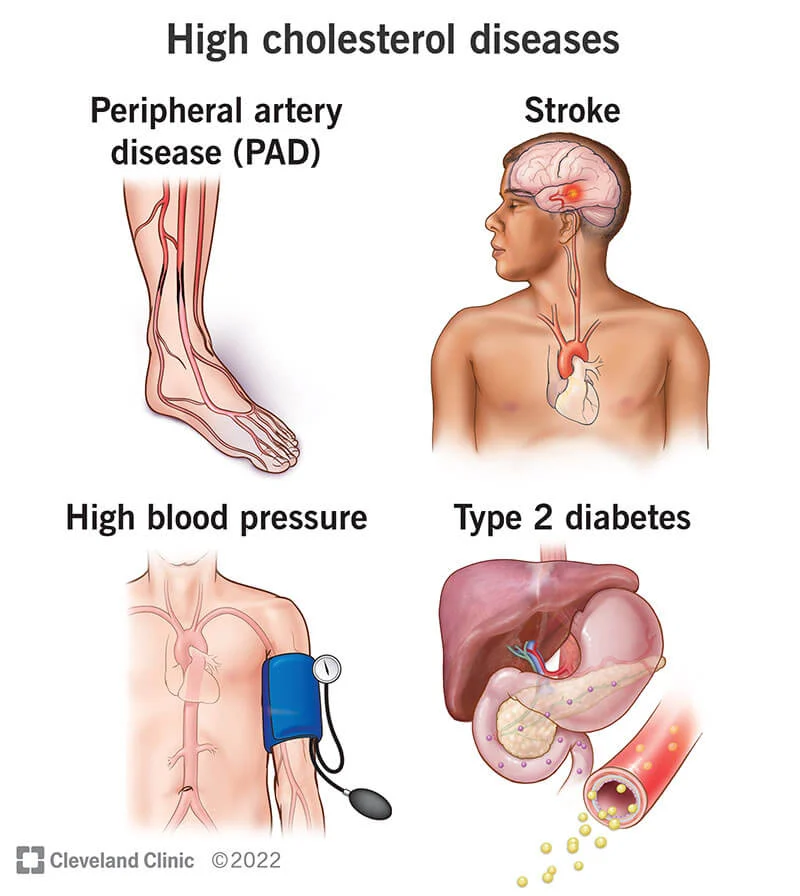
One of the factors that can have negative effects on the circulatory system is the accumulation of lipids in the blood vessels. This is commonly known as high cholesterol and is a major risk factor for developing cardiovascular disease. High levels of cholesterol can lead to the formation of plaque in the arteries, which can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of blood clots. As a result, this can lead to serious health complications such as heart attack and stroke.
High cholesterol can also increase the risk of other blood-related health issues, including peripheral artery disease, which is a condition where the arteries in the legs and feet narrow, leading to pain and numbness in the affected areas. Additionally, high cholesterol levels can contribute to the development of aneurysms, which are bulges in the walls of the blood vessels that can burst, causing internal bleeding.
Overall, having high cholesterol levels can have a significant impact on blood health and can increase the risk of developing serious health complications.
The Dangers of Plaque Buildup in Arteries
Accumulation of lipids in the blood vessels can lead to the formation of plaque, a potentially life-threatening condition that restricts blood flow and increases the risk of serious health complications such as heart attack and stroke.
Plaque buildup in arteries is a gradual process that occurs over time and is usually asymptomatic until it reaches a critical point.
Once the plaque ruptures or breaks off, it can cause a blood clot that blocks the artery, leading to a heart attack or stroke.
The risk of plaque buildup can be influenced by several factors, including high levels of cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes.
The dangers of plaque buildup in arteries are significant, and it is crucial to manage cholesterol levels to prevent the formation and progression of plaque.
Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of plaque buildup and improve overall blood health.
In some cases, medication may also be necessary to lower cholesterol levels and prevent plaque buildup.
Early detection and treatment of high cholesterol can prevent the development of plaque and reduce the risk of serious health complications.
Therefore, it is essential to monitor cholesterol levels regularly and take appropriate measures to maintain a healthy cholesterol level.
The Risk of Blood Clots and Their Effects on Health
Blood clots pose a significant threat to overall wellbeing and can cause severe health complications. When blood clots form in veins or arteries, they can obstruct blood flow, causing tissue damage or even death. These clots can form due to various factors, including high cholesterol levels, smoking, obesity, and prolonged periods of inactivity.
When a blood clot forms, it can travel through the bloodstream, causing blockages in critical organs such as the lungs or heart. This can lead to potentially life-threatening conditions such as pulmonary embolism or heart attack.
The effects of blood clots can be emotionally and physically devastating. Patients who suffer from blood clots may experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, and swelling in the affected area. They may also require long-term medication or even invasive procedures to manage the condition.
Furthermore, the fear of developing another blood clot can cause significant anxiety and stress. As such, it is crucial to take preventative measures such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing cholesterol levels, and seeking medical attention promptly if symptoms arise.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing High Cholesterol
Implementing lifestyle changes, such as adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, can effectively manage and improve cholesterol levels. A balanced diet includes foods that are low in saturated and trans fats, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products. Additionally, limiting the consumption of processed foods, red meat, and sugary drinks can also improve cholesterol levels. On the other hand, engaging in physical activity for at least 30 minutes a day, five times a week can help increase the levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) or “good”cholesterol, while reducing the levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or “bad”cholesterol.
To better understand the impact of lifestyle changes on cholesterol management, below is a table summarizing some of the recommended dietary guidelines and types of physical activity that can help improve cholesterol levels.
| Dietary Guidelines | Physical Activity |
|---|---|
| Consume a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products. | Engage in moderate-intensity aerobic exercises such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 30 minutes a day, five times a week. |
| Limit the consumption of processed foods, red meat, and sugary drinks. | Incorporate strength training exercises such as weight lifting or resistance band workouts at least twice a week. |
| Choose foods that are low in saturated and trans fats. | Incorporate high-intensity interval training (HIIT) workouts once or twice a week to increase cardiovascular fitness. |
Overall, adopting healthy dietary habits and regular physical activity can effectively manage and improve cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of developing various cardiovascular diseases.
Diet and Exercise Strategies for Lowering Cholesterol
Adopting appropriate dietary and physical activity strategies can effectively manage and improve cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Consuming a diet that is low in saturated and trans fats, and high in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help lower cholesterol levels. Foods such as fatty meats, full-fat dairy products, fried foods, and processed snacks should be limited or avoided altogether. Instead, individuals should opt for lean meats, fish, and plant-based protein sources such as legumes and nuts.
Regular physical activity can also help lower cholesterol levels. Exercise helps increase the levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), the ‘good’cholesterol, which helps remove low-density lipoprotein (LDL), the ‘bad’cholesterol, from the blood. Even moderate-intensity exercise such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming can provide significant benefits.
Experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise. Incorporating strength training exercises can also help improve overall health and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases.
By incorporating these dietary and physical activity strategies, individuals can effectively manage and improve their cholesterol levels and reduce their risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Medications for Managing Cholesterol Levels
One approach to managing high levels of LDL cholesterol is through the use of medications prescribed by healthcare professionals. These medications work by blocking or reducing the production of cholesterol in the liver, or by increasing the removal of LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
There are several types of medications available, including statins, bile acid sequestrants, niacin, fibrates, and PCSK9 inhibitors.
Statins are the most commonly prescribed medication for managing high cholesterol levels. They work by inhibiting an enzyme in the liver that is responsible for producing cholesterol. Statins have been shown to significantly reduce LDL cholesterol levels and the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular events.
However, like all medications, statins have potential side effects, including muscle pain and liver damage. It is important for healthcare professionals to closely monitor patients taking statins and to adjust the dosage or switch to a different medication if necessary.
Monitoring Cholesterol Levels and Working with Healthcare Providers
Monitoring cholesterol levels is crucial to preventing the negative impact it can have on blood health. By regularly checking cholesterol levels, individuals can gain a better understanding of their condition and work with their healthcare providers to establish an effective treatment plan. This can include making lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, as well as potentially adjusting medication dosages or trying different medications altogether.
Working closely with healthcare providers is also important in ensuring effective management of high cholesterol levels. Healthcare providers can help individuals understand their test results and provide guidance on how to make lifestyle changes that can improve their overall health. They can also monitor any potential side effects of medications and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
By taking an active role in their own health and seeking guidance from healthcare providers, individuals can effectively manage high cholesterol levels and prevent the negative impact it can have on their blood health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, high cholesterol levels can have a significant impact on blood health, leading to various health complications. The accumulation of plaque in arteries can cause blockages, leading to heart attacks and strokes.
Additionally, high cholesterol levels increase the risk of blood clots, which can cause further damage to blood vessels.
Fortunately, lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and exercise, can help manage high cholesterol levels. Healthcare providers can also prescribe medications to help control cholesterol levels.
It is crucial to monitor cholesterol levels regularly and work with healthcare providers to develop an appropriate plan to manage high cholesterol levels.
By taking proactive steps to manage cholesterol levels, individuals can improve their overall blood health and potentially avoid the serious health complications associated with high cholesterol levels.