Top Sports Injuries And Rehabilitation
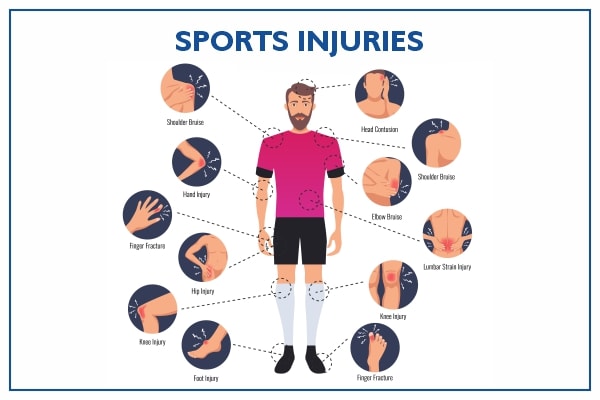
Sports injuries are a common occurrence among athletes, regardless of the level of competition or the sport they play. These injuries can range from minor sprains to severe fractures and can have a significant impact on an athlete’s physical and mental well-being. Proper rehabilitation is crucial to ensuring a full recovery and returning to the sport as quickly as possible.
In this article, we will discuss the top sports injuries experienced by athletes and the rehabilitation process associated with each of them. We will cover a range of sports, including football, basketball, tennis, golf, long-distance running, weightlifting, and sprinting. Understanding these injuries and the proper rehabilitation techniques can help athletes prevent future injuries and improve their overall performance.
Key Takeaways
- Sports injuries range from minor sprains to severe fractures and can impact physical and mental well-being, making proper rehabilitation crucial for full recovery and return to sport.
- Specific injuries like ACL tears in football players, ankle sprains in basketball players, head injuries in contact sports, tennis elbow in tennis players, golfer’s elbow in golfers, runner’s knee in long-distance runners, and rotator cuff injuries in weightlifters require different treatments and rehabilitation methods.
- Prevention measures like proper warm-up and stretching, appropriate protective equipment, safe playing techniques, and education for coaches, athletes, and parents can help reduce the likelihood of sports injuries.
- Rehabilitation can take 6 months to a year, and there is no guarantee of returning to pre-injury performance level, making injury prevention important for a healthier and more productive athletic career.
ACL Tears in Football Players
ACL tears are a common and potentially career-ending injury among football players. The ACL, or anterior cruciate ligament, is a vital component of the knee joint that provides stability and support during high-impact activities such as running, jumping, and pivoting. When the ACL is torn, the knee becomes unstable and can cause significant pain, swelling, and inability to bear weight. The injury typically occurs when a player changes direction suddenly or lands awkwardly from a jump, causing the knee to twist unnaturally.
Rehabilitation is crucial for football players who suffer from ACL tears as it is a long and arduous process. The first step in rehabilitation is to reduce pain and swelling through rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Once the swelling has subsided, the focus shifts to strengthening and stabilizing the knee joint through a combination of physical therapy and strength training exercises.
The rehabilitation process can take anywhere from six months to a year, and even then, there is no guarantee that the player will be able to return to their pre-injury level of performance.
Ankle Sprains in Basketball Players
Basketball players commonly experience ankle sprains, which can significantly impact their ability to perform on the court. Ankle sprains occur when the ligaments that connect the bones in the ankle joint are stretched or torn due to sudden twisting or rolling of the foot.
This injury is particularly common in basketball players due to the frequent jumping, quick changes of direction, and landing on uneven surfaces. Ankle sprains can cause pain, swelling, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected foot, which can lead to a decrease in performance and even time off the court for recovery.
Rehabilitation for ankle sprains typically involves a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevation to reduce pain and swelling. Physical therapy exercises are also commonly prescribed to improve range of motion, strength, and balance in the affected ankle.
In more severe cases, immobilization with a cast or brace may be necessary to allow the ligaments to heal properly. Preventative measures such as proper warm-up and stretching before games and practices, wearing supportive shoes, and taping or bracing the ankle can also help reduce the risk of ankle sprains in basketball players.
Concussions in Contact Sports
Head injuries are a common occurrence in contact sports, with concussions being a significant concern due to the potential for long-term cognitive damage. A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury that results from a blow to the head or body that causes the brain to move rapidly back and forth. This movement can cause the brain to bounce or twist within the skull, damaging brain cells and causing chemical changes in the brain.
Symptoms of a concussion can include headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, and sensitivity to light or noise. Recovery from a concussion typically involves rest and a gradual return to physical activity. Athletes who have sustained a concussion should be evaluated by a healthcare provider and should not return to play until they have fully recovered.
In some cases, more serious concussions may require hospitalization or surgery. Prevention is key, and athletes can reduce their risk of concussion by wearing appropriate protective equipment, following safe playing techniques, and avoiding high-risk activities. Education for coaches, athletes, and parents can also play an important role in preventing and managing concussions.
Tennis Elbow in Tennis Players
Tennis players are at risk of developing tennis elbow, a common overuse injury that affects the muscles and tendons in the forearm. This condition is caused by repetitive gripping and twisting motions, which can cause tiny tears in the tendons that attach to the lateral epicondyle of the elbow. Over time, these tears can become inflamed and painful, making it difficult for athletes to continue playing and performing at their best.
To diagnose tennis elbow, doctors will typically perform a physical examination and may also order imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans. Treatment options for tennis elbow include rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and swelling. Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises may also be recommended to help strengthen the muscles and tendons in the forearm and improve flexibility. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove damaged tissue.
| Pros of Rehabilitation for Tennis Elbow | Cons of Rehabilitation for Tennis Elbow |
|---|---|
| Helps to improve strength and flexibility of the forearm muscles and tendons | Treatment may not work for everyone |
| Can help to reduce pain and inflammation in the affected area | Rehabilitation may take time and require patience |
| Non-invasive approach that does not require surgery | May require multiple sessions for optimal results |
Golfer’s Elbow in Golfers
Golfer’s elbow, also known as medial epicondylitis, is a common overuse injury among golfers that affects the tendons in the inner side of the elbow. This condition is caused by repetitive gripping and twisting motions of the wrist and forearm, which can lead to inflammation and pain in the affected area.
The symptoms of golfer’s elbow include pain and tenderness on the inner side of the elbow, stiffness in the elbow joint, weakness in the affected arm, and numbness or tingling in the fingers.
To properly diagnose golfer’s elbow, a physical examination and medical history review is required. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI, may also be necessary to rule out other potential causes of pain in the elbow.
Treatment for golfer’s elbow typically involves rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medications to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy and exercises may also be recommended to help strengthen the affected muscles and improve flexibility. In severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery may be necessary.
To prevent golfer’s elbow, golfers should practice proper technique and use appropriate equipment, such as properly fitting clubs with grips that provide adequate support and cushioning.
Runner’s Knee in Long-Distance Runners
Long-distance runners often experience a common overuse injury called runner’s knee, which can cause pain and discomfort in the kneecap area during and after running. This injury is caused by repetitive stress on the knee joint, which can lead to irritation and inflammation of the cartilage under the kneecap. It is also known as patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS), and it affects mostly women and young adults who engage in high-impact activities such as running, jumping, and squatting.
Here are three important things to know about runner’s knee and its rehabilitation:
- Rest and ice: The first step in rehabilitating runner’s knee is to rest the affected knee and apply ice to reduce the swelling. This can help alleviate the pain and promote healing.
- Strengthening exercises: Strengthening exercises that focus on the hip, knee, and ankle can help improve the stability and alignment of the leg, which can reduce the stress on the knee joint. These exercises can include leg raises, squats, and lunges.
- Proper footwear and running technique: Wearing proper shoes and using good running technique can also prevent and rehabilitate runner’s knee. It is important to choose shoes with good cushioning and support, and to avoid overstriding and landing on the heel. This can help reduce the impact on the knee joint and prevent further injury.
Rotator Cuff Injuries in Weightlifters
Weightlifters are prone to rotator cuff injuries, a common overuse injury caused by repetitive overhead lifting that can lead to pain and weakness in the shoulder. The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that attach to the shoulder blade and help to stabilize the shoulder joint. When these muscles and tendons are overused, they can become inflamed, leading to pain and discomfort.
Weightlifters who frequently perform overhead lifts, such as the snatch and overhead press, are at increased risk of developing rotator cuff injuries. Factors that contribute to the development of these injuries include poor technique, inadequate warm-up, and overtraining.
Treatment for rotator cuff injuries typically involves rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medication. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged tendons and muscles.
To prevent rotator cuff injuries, weightlifters should focus on proper form and technique during overhead lifts, as well as incorporating exercises to strengthen the rotator cuff muscles into their training routines.
Hamstring Strains in Sprinters
Sprinters who frequently engage in high-intensity running are susceptible to hamstring strains, a common injury caused by sudden, forceful movements that can result in pain and swelling in the back of the thigh. This type of injury is particularly prevalent in sprinters due to the intense demands placed on the hamstring muscles during sprinting.
Hamstring strains can range from minor injuries that only require rest and rehabilitation to more severe injuries that may require surgery. To prevent hamstring strains, sprinters can take several measures, including proper warm-up and stretching.
Stretching exercises that target the hamstring muscles, such as the seated hamstring stretch and the standing hamstring stretch, can help increase flexibility and reduce the risk of injury. Adequate rest and recovery between workouts is also essential to prevent overuse injuries.
Additionally, proper technique and form while sprinting can help reduce the risk of injury and improve performance. By following these measures, sprinters can reduce the risk of hamstring strains and enjoy a healthier, more productive athletic career.
Conclusion
Various sports have their unique challenges and injuries that athletes face.
ACL tears are common among football players, while ankle sprains are prevalent in basketball players. Concussions are a significant concern in contact sports, whereas tennis elbow and golfer’s elbow are common conditions in tennis and golf players, respectively. Long-distance runners often experience runner’s knee, while weightlifters are susceptible to rotator cuff injuries. Sprinters are prone to hamstring strains, which can be severe and debilitating.
Rehabilitation is an essential aspect of sports injury management. Treatment plans typically include physical therapy, medication, and rest, among other interventions. Athletes must follow their rehabilitation plans closely to ensure optimal recovery and prevent further injury.
Proper rehabilitation can also help athletes regain their strength, mobility, and overall physical fitness. Furthermore, preventive measures such as wearing protective gear and undergoing regular checkups can help reduce the risk of sports injuries.
In conclusion, sports injuries are a significant concern for athletes, but with proper management and rehabilitation, they can overcome these challenges and continue to excel in their chosen sport.