Understanding The Heart And Blood Vessels
The human heart and blood vessels are essential components of the cardiovascular system, responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues and organs. Understanding the anatomy, function, and circulation of the heart and blood vessels is crucial to maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system and preventing cardiovascular diseases. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the heart and blood vessels, including their structure, function, and common conditions, as well as lifestyle changes that can promote cardiovascular health.
Anatomy of the Heart: A Closer Look
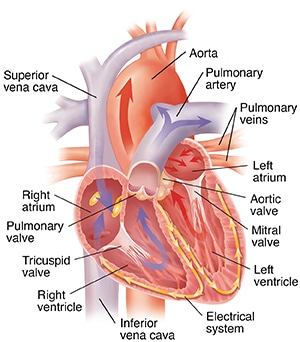
The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest, between the lungs. It is approximately the size of a fist and is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. The heart is composed of four chambers: the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
Blood enters the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena cava, then flows into the right ventricle, which pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation. Oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins, enters the left atrium, and then flows into the left ventricle, which pumps it out to the rest of the body through the aorta.
Understanding the anatomy of the heart is crucial to understanding its function in the cardiovascular system.
Key Takeaways
- The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood and is composed of four chambers, valves, and blood vessels.
- The cardiovascular system maintains oxygen and nutrient delivery and removes waste products through blood circulation.
- Maintaining appropriate blood pressure levels and understanding the process of blood circulation is crucial for optimal heart health and preventing cardiovascular diseases.
- Engaging in healthy habits such as physical activity, balanced diet, avoiding smoking, and managing stress can greatly impact the health of the cardiovascular system and promote overall heart health.
Anatomy of the Heart: A Closer Look
The intricate structure of the heart, including its four chambers, valves, and blood vessels, reveals the remarkable complexity of this vital organ, inspiring awe and appreciation for the intricacies of the human body.
The heart is a muscular organ that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It is located in the chest cavity and is roughly the size of a fist.
The heart is divided into four chambers: the right atrium, the left atrium, the right ventricle, and the left ventricle. The atria are the upper chambers of the heart and receive blood from the body and lungs, respectively. The ventricles are the lower chambers of the heart and are responsible for pumping blood to the body and lungs, respectively.
The heart is surrounded by a sac called the pericardium, which helps protect it from injury and infection. The heart is also supplied with blood vessels, including the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle itself.
The valves of the heart are responsible for ensuring that blood flows in the correct direction. There are four valves in the heart: the tricuspid valve, the pulmonary valve, the mitral valve, and the aortic valve. Each valve has flaps that open and close to allow blood to flow through the heart in the correct direction.
Understanding the anatomy of the heart is essential to understanding how it functions and how to maintain its health.
The Function of the Heart in the Cardiovascular System
One of the most crucial components of the circulatory network is the organ responsible for pumping oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. This organ is the heart, which is a muscular organ located in the chest cavity and is roughly the size of a fist.
The heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. Blood enters the atria and is then pumped out of the heart through the ventricles. The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs, where it receives oxygen, while the left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
The heart works in conjunction with blood vessels to form the cardiovascular system. Blood vessels include arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while veins carry deoxygenated blood towards the heart. Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that connect arteries and veins and allow for the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the blood and tissues.
The cardiovascular system is responsible for maintaining oxygen and nutrient delivery to all parts of the body, as well as removing waste products. The heart plays a vital role in this process, ensuring that blood is constantly circulating through the body to meet the needs of the cells.
Understanding Blood Vessels: Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries
Arteries, veins, and capillaries are vital components of the circulatory system, working together to ensure the constant delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body.
Arteries are responsible for carrying oxygenated blood away from the heart and towards the rest of the body. They are thick-walled and have a muscular layer that contracts and relaxes, allowing for the regulation of blood flow. The largest artery in the body is the aorta, which originates from the left ventricle of the heart and branches out into smaller arteries throughout the body.
Veins, on the other hand, are responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood back to the heart. They have thinner walls than arteries and are equipped with one-way valves that prevent backflow of blood. The largest vein in the body is the vena cava, which carries blood from the lower part of the body to the heart. Veins also have a role in regulating blood pressure, as they can expand and contract to accommodate changes in blood volume.
Capillaries, the smallest blood vessels, connect arteries and veins and are responsible for the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and the body’s tissues. They have thin walls that allow for the diffusion of molecules and are found in large numbers throughout the body, providing a vast network for the exchange of substances.
The Importance of Blood Pressure
Maintaining appropriate blood pressure levels is crucial for optimal bodily function and overall health. Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by blood against the walls of the blood vessels. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is expressed as systolic pressure and diastolic pressure.
Systolic pressure is the pressure exerted on the walls of the arteries when the heart contracts, while diastolic pressure is the pressure exerted on the walls of the arteries when the heart is at rest. Normal blood pressure ranges from 90/60 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a condition where the force of blood against the walls of the blood vessels is consistently too high. This can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Hypertension is often called a ‘silent killer’because it usually has no symptoms and can go unnoticed for years.
It is important to get regular blood pressure checks and to take steps to maintain healthy blood pressure levels through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques. In addition, medication may be necessary to control blood pressure in some individuals.
How Blood Circulates Through the Body
The process of blood circulation involves the movement of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood through a complex network of interconnected pathways within the body. The heart plays a vital role in this process by pumping blood through the circulatory system.
Blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries, serve as conduits for blood flow. The circulatory system is responsible for delivering nutrients and oxygen to the body’s organs and tissues, collecting waste products, and maintaining homeostasis.
To better understand the process of blood circulation, consider the following key points:
- Blood flows from the heart through arteries and arterioles, which carry oxygenated blood to the body’s organs and tissues.
- Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that connect arterioles to venules and allow for the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and the body’s cells.
- Blood returns to the heart through venules and veins, which carry deoxygenated blood back to the lungs to be re-oxygenated.
The circulatory system is regulated by a complex network of hormones, enzymes, and neural signals that help to maintain blood pressure, blood volume, and other aspects of homeostasis.
Understanding the process of blood circulation is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing cardiovascular disease. By learning more about how the heart and blood vessels work together to circulate blood throughout the body, we can make informed decisions about our lifestyle choices and seek medical attention when necessary.
Common Heart and Blood Vessel Conditions
Common conditions affecting the cardiovascular system can have significant impacts on overall health and well-being. One such condition is coronary artery disease (CAD), which is caused by the buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. This buildup can narrow the arteries and reduce blood flow, leading to chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, and even heart attack.
Risk factors for CAD include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and diabetes, among others. Treatment for CAD may include lifestyle changes, such as exercise and diet modifications, as well as medication and possibly surgery in more severe cases.
Another common heart condition is arrhythmia, which is an irregular heartbeat that can cause dizziness, fainting, and even sudden cardiac arrest. There are several types of arrhythmia, including atrial fibrillation, which is the most common type, and ventricular tachycardia, which is a more serious condition.
Risk factors for arrhythmia include age, family history, heart disease, and certain medications. Treatment may include medication, electrical cardioversion, or implantation of a pacemaker or defibrillator. It is important for individuals with arrhythmia to receive proper medical care and management to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Maintaining a Healthy Cardiovascular System
One’s lifestyle choices greatly impact the health of their cardiovascular system, emphasizing the importance of making healthy decisions.
Maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system involves adopting habits that promote heart health. These include:
- Eating a balanced diet consisting of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises, strength training, and stretching
- Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises
By making these healthy lifestyle choices, individuals can help prevent the onset of cardiovascular diseases and promote overall heart health.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before making significant changes in diet and exercise routines. Additionally, regular check-ups and screenings can help detect early signs of heart conditions, allowing for prompt treatment and management.
Maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system is critical for overall health and well-being. By adopting healthy habits, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques, individuals can promote heart health and reduce their risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Remember, small changes in lifestyle choices can have a significant positive impact on heart health, so start making healthy decisions today!
Lifestyle Changes for a Healthier Heart
Adopting healthy lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, can significantly improve cardiovascular health. Engaging in physical activity for at least 30 minutes a day, five times a week, can help reduce the risk of developing heart disease. Exercise helps to strengthen the heart muscle, improve blood flow, and reduce inflammation, all of which contribute to maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
Furthermore, a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help lower blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and the risk of developing obesity and diabetes, all of which are risk factors for heart disease.
In addition to exercise and a healthy diet, there are other lifestyle changes that can improve cardiovascular health. For instance, quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing heart disease. Smoking damages the blood vessels and increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, leading to heart attack or stroke.
Additionally, managing stress through activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce blood pressure and improve heart health. By adopting these healthy lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly improve their cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of developing heart disease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the anatomy and function of the heart and blood vessels is crucial in maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood throughout the body, while the blood vessels transport blood to and from the heart.
The three types of blood vessels arteries, veins, and capillaries play a vital role in regulating blood pressure and ensuring proper circulation.
Maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system involves making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding tobacco use.
Additionally, managing stress levels and regularly monitoring blood pressure are essential in preventing heart and blood vessel conditions.
Early detection and treatment of these conditions can also help prevent further complications.
By understanding the complexities of the cardiovascular system and taking proactive measures to maintain its health, individuals can improve their overall well-being and quality of life.