What Are Antifungal Medications And How Do They Treat Yeast Infections?
Yeast infections, also known as candidiasis, are a common medical condition caused by an overgrowth of the Candida fungus. This condition can affect various parts of the body, including the mouth, throat, genital areas, and skin folds.
Antifungal medications have been widely used to treat yeast infections by targeting and eliminating the underlying fungal infection. This article aims to provide an overview of antifungal medications and their role in the treatment of yeast infections. It will discuss the different types of antifungal medications available, such as topical creams and ointments, as well as oral medications.
Additionally, the article will explore natural remedies and alternative treatments that can be used alongside or instead of traditional antifungal medications. Furthermore, it will offer prevention tips for yeast infections and guidance on when to seek medical attention.
Understanding the mechanisms and effectiveness of antifungal medications is crucial in effectively managing yeast infections and improving patient outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Antifungal medications target yeast cells and inhibit their growth, providing relief from yeast infection symptoms.
- Antifungal medications are available in various forms such as creams, suppositories, and oral tablets.
- Seeking medical attention is important for proper diagnosis and treatment of yeast infections.
- Prompt treatment with antifungal medications leads to quicker resolution of yeast infections.
Understanding Yeast Infections
Yeast infections, also known as candidiasis, are a common type of fungal infection that affect various parts of the body, such as the mouth, skin, and genital areas. They are caused by an overgrowth of a type of fungus called Candida, specifically Candida albicans.
This fungus is normally present in small amounts in the body, but certain factors can disrupt the natural balance, leading to an overgrowth and subsequent infection. Common causes of yeast infections include a weakened immune system, hormonal changes, antibiotic use, and poor hygiene.
Symptoms of yeast infections can vary depending on the affected area but commonly include itching, redness, swelling, and a thick, white discharge. It is important to seek medical treatment for yeast infections to relieve symptoms and prevent complications.
Introduction to Antifungal Medications
Antifungal medications are a crucial part of treating yeast infections.
There are various types of antifungal medications available, including topical creams, oral medications, and suppositories.
These medications work by targeting the fungal cells and inhibiting their growth, ultimately eliminating the infection.
Types of Antifungal Medications
There are various classes of antifungal medications available for the treatment of yeast infections. These medications work by targeting the fungal cells and inhibiting their growth or killing them altogether. Some common types of antifungal medications include azoles, allylamines, polyenes, and echinocandins. Azoles, such as fluconazole, are commonly used as the first-line treatment for yeast infections due to their effectiveness and low risk of side effects. Allylamines, like terbinafine, are often used to treat fungal skin infections. Polyenes, such as amphotericin B, are typically reserved for more severe or resistant infections. Echinocandins, like caspofungin, are newer antifungal agents that target the cell wall of the fungus. Although antifungal medications are generally safe and well-tolerated, they may have potential side effects such as gastrointestinal upset, skin rash, or liver toxicity. It is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any antifungal treatment and to discuss alternative remedies and potential side effects.
| Class of Antifungal Medication | Examples |
|---|---|
| Azoles | Fluconazole, itraconazole |
| Allylamines | Terbinafine, naftifine |
| Polyenes | Amphotericin B, nystatin |
| Echinocandins | Caspofungin, micafungin |
How They Work to Treat Yeast Infections
One way antifungal medications work is by specifically targeting fungal cells and either inhibiting their growth or killing them altogether. These medications have different mechanisms of action to achieve their antifungal effects.
Some commonly used antifungal medications work by disrupting the synthesis of ergosterol, a vital component of the fungal cell membrane. This disruption weakens the cell membrane, leading to leakage of cellular contents and ultimately cell death.
Other antifungal medications inhibit the enzyme responsible for converting lanosterol to ergosterol, further compromising the integrity of the fungal cell membrane.
Additionally, antifungal medications may interfere with the synthesis of nucleic acids or proteins, crucial for fungal cell replication and survival.
While these medications are effective in treating yeast infections, they may also have potential side effects such as gastrointestinal disturbances, liver toxicity, and allergic reactions.
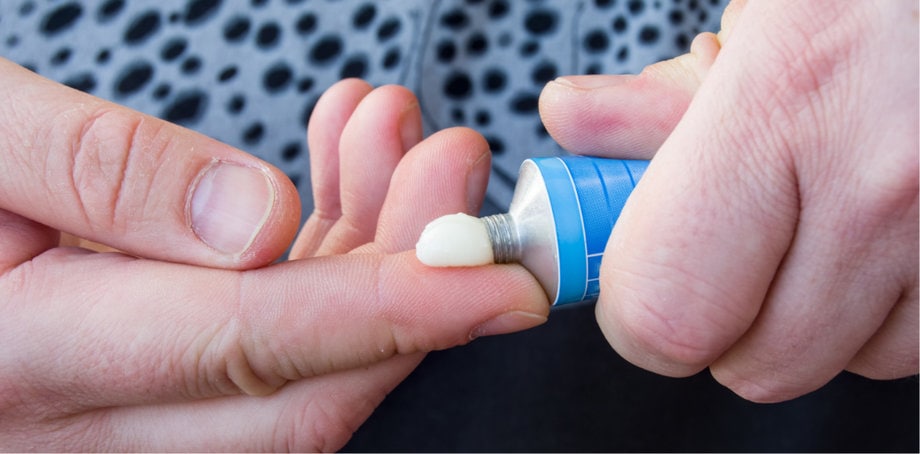
Topical Antifungal Creams and Ointments
Topical antifungal creams and ointments offer a convenient and effective treatment option for yeast infections, providing relief from symptoms and promoting the eradication of the fungal overgrowth. These medications are commonly used as alternatives to oral antifungal drugs, particularly for mild to moderate cases of yeast infections.
One of the key advantages of topical antifungal creams and ointments is their direct application to the affected area, allowing for targeted treatment. This ensures that the active ingredients in the medication are concentrated on the site of infection, maximizing their effectiveness. Furthermore, topical antifungal medications are easily absorbed by the skin, allowing for rapid and localized action.
Commonly used antifungal agents in topical creams and ointments include clotrimazole, miconazole, and terbinafine. These medications work by inhibiting the growth and replication of the fungi responsible for yeast infections, ultimately leading to their elimination.
Overall, topical antifungal creams and ointments are a valuable treatment option for yeast infections due to their convenience and effectiveness.
Oral Antifungal Medications
Oral antifungal drugs are frequently prescribed for more severe cases of fungal overgrowth and can effectively target the root causes of yeast infections. These medications work by inhibiting the growth and reproduction of fungi, ultimately eliminating the infection.
While oral antifungal drugs are highly effective, they are also associated with potential side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. In rare cases, more serious side effects such as liver damage may occur.
It is important for individuals taking oral antifungal medications to closely follow their healthcare provider’s instructions and report any adverse reactions.
In some cases, alternative oral treatments may be considered, such as natural remedies or probiotics. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before considering any alternative treatment options to ensure their safety and efficacy.
Natural Remedies and Alternative Treatments
This paragraph introduces a discussion on natural remedies and alternative treatments for yeast infections.
The focus is on three key points: probiotics and yogurt, tea tree oil, and garlic.
These natural remedies are commonly used as alternative treatments for yeast infections and may provide relief by promoting the growth of healthy bacteria, reducing inflammation, and inhibiting the growth of yeast.
However, it is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand their effectiveness and potential side effects.
Probiotics and Yogurt
Probiotics, such as yogurt, are often considered as a potential adjunct therapy for yeast infections. Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer health benefits to the host. Yogurt, a popular probiotic food, contains Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains, which are believed to promote gut health and support the immune system. These beneficial bacteria may help prevent the overgrowth of Candida, the fungus responsible for yeast infections, by competing for resources and producing antimicrobial substances. However, the effectiveness of probiotics in treating yeast infections remains uncertain, as studies have yielded mixed results. Additionally, the specific strains and dosages required for optimal therapeutic effects are still under investigation. It is important to note that probiotics should not replace conventional antifungal medications but may be used as a complementary therapy.
| Probiotics Benefits | Yogurt for Gut Health |
|---|---|
| – May promote gut health by improving the balance of beneficial bacteria | – Contains Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains that support gut health |
| – Potential immune system modulation | – May help maintain a healthy gut microbiota |
| – May aid in the prevention of yeast overgrowth | – May improve digestion and nutrient absorption |
Tea Tree Oil and Garlic
Tea tree oil and garlic have been investigated for their potential as alternative therapies in the management of yeast infections.
Tea tree oil, derived from the leaves of the Melaleuca alternifolia tree, has demonstrated antifungal properties due to its active component, terpinen-4-ol. Studies have shown that tea tree oil exhibits inhibitory effects against various fungal species, including Candida albicans, the most common cause of yeast infections. Additionally, tea tree oil has been found to possess anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating properties, which may contribute to its efficacy in treating yeast infections.
Garlic, known for its antimicrobial properties, has also been explored as a potential remedy. Allicin, a compound found in garlic, has shown antifungal activity against Candida species. However, further research is needed to fully understand the benefits of tea tree oil and the effectiveness of garlic in treating yeast infections.
Prevention Tips for Yeast Infections
This section will discuss prevention tips for yeast infections, focusing on two key points: maintaining good hygiene and wearing breathable fabrics.
Good hygiene practices, such as regularly washing the genital area with mild soap and water, can help prevent the overgrowth of yeast.
Additionally, wearing breathable fabrics, such as cotton underwear, can help keep the genital area dry and prevent the buildup of moisture, which can contribute to yeast infections.
Maintaining Good Hygiene
Maintaining good hygiene is crucial in preventing and managing yeast infections, as it helps to minimize the accumulation of bacteria and fungi in the affected area. By following preventive measures and incorporating certain daily routines, individuals can reduce their risk of developing yeast infections. Some key practices to consider include:
| Preventive Measures | Daily Routines |
|---|---|
| Wearing breathable underwear and avoiding tight clothing | Regularly washing and drying the affected area |
| Using mild, unscented soaps and avoiding irritating products | Changing out of damp clothes, such as sweaty workout gear, promptly |
| Avoiding douching and using scented feminine hygiene products | Maintaining proper oral hygiene and avoiding excessive sugar intake |
By incorporating these practices into their daily routines, individuals can promote good hygiene and reduce the likelihood of yeast infections. It is important to note that while good hygiene plays a significant role, it may not completely eliminate the risk of yeast infections, especially in individuals with underlying medical conditions or weakened immune systems.
Wearing Breathable Fabrics
By choosing to wear breathable fabrics, individuals can create an environment that minimizes moisture and promotes airflow, which can help reduce the risk of developing yeast infections. Here are some benefits of wearing breathable fabrics and the best breathable fabric choices:
- Absorbency: Breathable fabrics such as cotton and linen have high absorbency, allowing them to absorb moisture from the body and keep the skin dry.
- Moisture-wicking: Fabrics like bamboo and microfiber have moisture-wicking properties, which means they can pull moisture away from the skin and evaporate it quickly.
- Ventilation: Natural fabrics like silk and wool have natural ventilation properties that allow air to circulate, preventing the build-up of moisture and heat.
- Hypoallergenic: Breathable fabrics like organic cotton and hemp are hypoallergenic and less likely to cause skin irritation or allergies.
By choosing the right breathable fabrics, individuals can maintain a dry and well-ventilated environment, reducing the chances of yeast infections.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seeking medical attention is crucial when experiencing persistent symptoms of a yeast infection, as prompt treatment with antifungal medications is necessary to alleviate discomfort and prevent potential complications.
While mild yeast infections can sometimes resolve on their own or with the use of home remedies, it is important to consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen.
Common signs and symptoms of a yeast infection include itching, burning, redness, and a thick white discharge. These symptoms can cause significant discomfort and impact daily activities.
Antifungal medications work by targeting the yeast cells and inhibiting their growth, thus eliminating the infection. These medications can be prescribed in various forms, such as creams, suppositories, or oral tablets, and are generally effective in providing relief from symptoms within a few days.
Seeking medical attention ensures appropriate diagnosis and treatment, leading to a quicker resolution of the infection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can yeast infections be passed on to sexual partners?
Yeast infections can be transmitted to sexual partners through sexual contact. While they generally do not affect fertility, they can cause complications during pregnancy, such as premature birth or passing the infection to the newborn.
Are there any over-the-counter antifungal medications available?
Over-the-counter antifungal medications are available for treating yeast infections. The effectiveness of these OTC options may vary, and they should be used according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer or healthcare professional.
What are the common side effects of oral antifungal medications?
Common side effects of oral antifungal medications include gastrointestinal disturbances, such as nausea and diarrhea, as well as potential liver toxicity. Effectiveness comparison reveals varying success rates among different antifungals.
Are there any natural remedies that can effectively treat yeast infections?
Natural remedies and alternative treatments may offer some relief for yeast infections. Examples include probiotics, tea tree oil, garlic, and yogurt. However, more research is needed to determine their effectiveness and safety compared to antifungal medications.
Can yeast infections be prevented by following a specific diet?
Preventing yeast infections through diet is possible by maintaining a healthy gut. A balanced diet rich in probiotics, fiber, and low in sugar can promote gut health and reduce the risk of yeast overgrowth.