What is colon – Definition, Problems, Treatments
The human colon, also known as the large intestine, is a part of the digestive system that is responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes from digested food, and storing feces before elimination. It is a long, muscular tube that begins at the end of the small intestine and ends at the rectum.
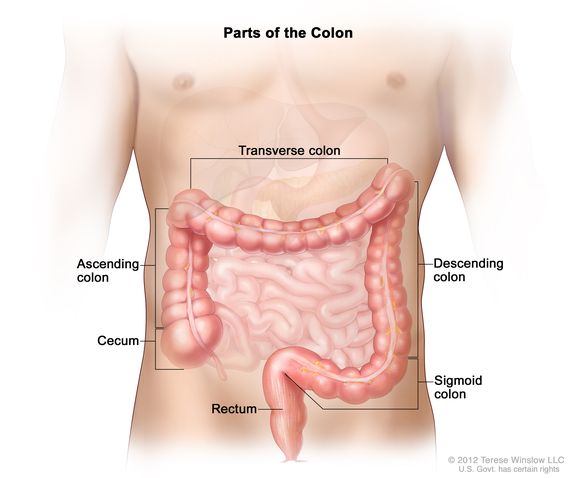
The colon is divided into four sections: the ascending colon, the transverse colon, the descending colon, and the sigmoid colon. The colon also contains a large population of beneficial bacteria that aid in the digestion and absorption of food. Some common conditions that can affect the colon include diverticulitis, irritable bowel syndrome, and colon cancer.
Functions: what colon does
The main function of the colon is to reabsorb water and electrolytes from the remaining semi-solid waste material after it leaves the small intestine, forming the feces. The feces are then stored in the rectum before elimination from the body. The colon also plays a role in the absorption of certain vitamins and minerals such as vitamin K and some B vitamins, and electrolytes like sodium and chloride.
The colon also contains a large population of beneficial bacteria known as gut microbiome, which aid in the digestion of food and support the immune system. Another important function is to eliminate toxins and waste material from the body. The colon also plays a role in regulating bowel movements, and helps to prevent constipation by contracting and relaxing the muscles in its walls.
How to find colon
The colon is located in the abdominal cavity of the body. It begins at the end of the small intestine, specifically at the cecum which is located at the right lower quadrant of the abdomen, and extends to the rectum.
The colon then continues to the anus, where feces are eliminated from the body. The colon is divided into four sections: the ascending colon, the transverse colon, the descending colon, and the sigmoid colon.
The ascending colon runs upward along the right side of the abdomen, the transverse colon runs horizontally across the abdomen, the descending colon runs downward along the left side of the abdomen, and the sigmoid colon is the lowermost section of the colon that connects to the rectum.
What causes colon problems
The most popular factors that can cause problems with the colon, including:
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, which cause inflammation and ulceration of the colon and rectum.
- Diverticulitis, which is a condition in which small pockets or pouches in the colon walls become inflamed or infected.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), a disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
- Colorectal cancer, which is a type of cancer that develops in the colon or rectum. It is typically caused by the abnormal growth of cells in the lining of the colon or rectum.
- Polyps, which are small growths on the lining of the colon or rectum that can become cancerous if left untreated.
- Constipation, which is a common problem that can be caused by a lack of fiber in the diet, lack of physical activity, or certain medications.
- Hemorrhoids, which are swollen veins in the anus and lower rectum that can cause discomfort and bleeding.
- Infections, such as bacterial infections of the colon, like Clostridium difficile (C. diff)
- Lifestyle factors such as diet low in fiber, high in processed food, alcohol and tobacco use, and lack of physical activity can also contribute to colon problems
What does colon pain feel like
Colon pain can feel differently for different people, but some common descriptions include:
- Cramping or aching: The pain may feel like a dull ache or a sharp, intense cramp that comes and goes.
- Constant or intermittent: The pain can be constant or intermittent, and it can vary in intensity.
- Localized or diffuse: The pain can be localized to a specific area of the colon or be diffuse and spread throughout the abdomen.
- Tenderness: The area of the colon that is affected may be tender to the touch.
- Accompanied by other symptoms: The pain may be accompanied by other symptoms such as bloating, constipation, diarrhea, gas, nausea, vomiting, or rectal bleeding.
These symptoms can be caused by a variety of conditions and not all of them are related to the colon specifically. Consult with a doctor or gastroenterologist if you have any symptoms or concerns about your colon health, and they can help to determine the cause of your pain and recommend appropriate treatment.
TOP 10 colon diseases
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) – Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are types of IBD that cause inflammation and ulceration of the colon and rectum. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, and weight loss.
- Diverticulitis – This is a condition in which small pockets or pouches in the colon walls become inflamed or infected. Symptoms include abdominal pain, fever, constipation, and diarrhea.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) – This is a disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. The cause of IBS is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to a dysfunction of the muscles in the colon.
- Colorectal Cancer – This is a type of cancer that develops in the colon or rectum. Symptoms include blood in the stool, abdominal pain, and weight loss.
- Polyps – These are small growths on the lining of the colon or rectum that can become cancerous if left untreated. Symptoms include rectal bleeding and a change in bowel habits.
- Constipation – This is a common problem that can be caused by a lack of fiber in the diet, lack of physical activity, or certain medications. Symptoms include infrequent bowel movements and difficulty passing stools.
- Hemorrhoids – These are swollen veins in the anus and lower rectum that can cause discomfort and bleeding. Symptoms include pain and itching around the anus, and bright red blood in the stool.
- Infections – Bacterial infections of the colon such as Clostridium difficile (C. diff) can cause symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever.
- Ulcerative proctitis- is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that affects only the rectum, causing inflammation and ulcers. Symptoms can include rectal bleeding, diarrhea, and pain or discomfort in the rectum.
- Pseudomembranous colitis – is a serious complication of antibiotic use caused by an overgrowth of Clostridium difficile bacteria. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever.

Doctors who specializes in colon problems
A gastroenterologist is a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of conditions and diseases of the digestive system, including the colon. They have completed advanced training in the management of conditions that affect the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), pancreas, gallbladder, and biliary system.
Gastroenterologist
A Gastroenterologist can perform a variety of tests to diagnose colon problems, including colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, and stool analysis, and provide treatments such as medication, diet and lifestyle modifications, and in some cases, surgery.
Colorectal surgeon
A colorectal surgeon is a specialist surgeon who treats diseases of the colon, rectum, and anus. They have completed advanced training in the surgical management of colon and rectal diseases. They can perform a variety of surgeries, including colon resection, colectomy, and proctectomy.
There are other specialists who may also be involved in the treatment of colon problems, such as a general surgeon, an oncologist, and a radiation oncologist.
In case of colon cancer, a multidisciplinary team of specialists may work together to provide the best care, which may include a gastroenterologist, a colorectal surgeon, a medical oncologist, and a radiation oncologist.