What Is The Cardiovascular System? Hypertension And Heart Disease
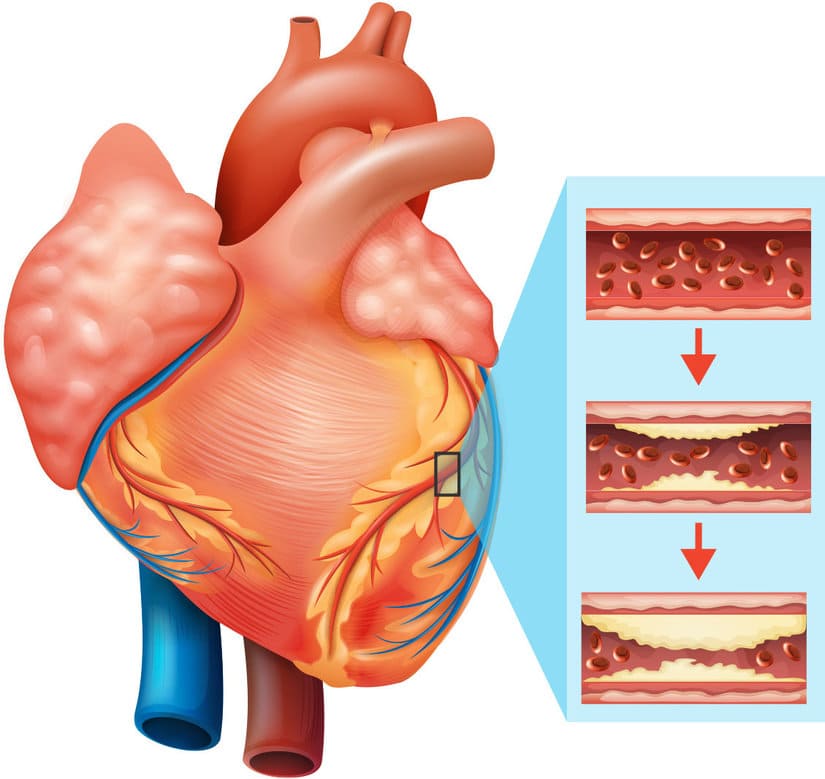
The cardiovascular system is one of the most vital systems in the human body, responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to all organs and tissues. It is made up of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, which work together to maintain circulation throughout the body.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels. It is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications.
Heart disease, on the other hand, refers to a range of conditions that affect the heart, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Both hypertension and heart disease can have serious consequences on a person’s health, highlighting the importance of understanding the cardiovascular system and how it functions.
Key Takeaways
- The cardiovascular system delivers oxygen and nutrients to all organs and tissues, regulates body temperature, pH balance, and fluid balance.
- Hypertension is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels and is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications.
- Heart disease refers to a range of conditions that affect the heart and can be caused by lifestyle factors such as smoking, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle.
- Lifestyle modifications such as eating a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques can help prevent and manage hypertension and heart disease. Early detection and prevention are crucial, and treatment options should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Anatomy of the Cardiovascular System
The anatomy of the cardiovascular system encompasses the heart, blood vessels, and blood, which work in unison to circulate oxygen and nutrients throughout the body.
The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest cavity, and it is responsible for pumping blood to all parts of the body.
The blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries, serve as the highways and byways of the cardiovascular system, transporting blood to and from the heart.
The arteries carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the body’s tissues and organs, while veins return deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Capillaries are tiny, thin-walled vessels that connect the arteries and veins, enabling the exchange of nutrients, gases, and waste products between the blood and tissues.
The blood consists of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Plasma is the liquid component of blood, which carries nutrients, hormones, and waste products.
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds and transports oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues.
White blood cells play a critical role in the immune system, defending the body against infections, viruses, and other foreign invaders.
Platelets are small cell fragments that help in blood clotting, preventing excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is damaged.
The cardiovascular system is an essential component of the human body, enabling the delivery of vital nutrients and oxygen to all organs and tissues, and helping to maintain homeostasis and overall health.
Functions of the Cardiovascular System
One of the primary roles of the circulatory system is to transport oxygen and nutrients to all the cells of the body. This is accomplished through the actions of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart, a muscular organ, pumps blood throughout the body, while the blood vessels act as conduits to transport the blood to all the cells. The blood, composed of red and white blood cells, plasma, and platelets, carries oxygen and nutrients to the cells and removes waste products.
In addition to providing oxygen and nutrients to the cells, the cardiovascular system also plays a critical role in regulating body temperature, pH balance, and fluid balance. The blood vessels can constrict or dilate to regulate blood flow, which helps to control body temperature. The blood also helps to maintain a proper balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body, which is essential for proper cellular function.
Any dysfunction in the cardiovascular system, such as hypertension or heart disease, can have severe consequences on overall health and wellbeing.
Causes of Hypertension
An elevated blood pressure reading is often caused by a combination of lifestyle and genetic factors. The lifestyle factors that contribute to hypertension include a diet high in sodium, lack of physical activity, obesity, and excessive alcohol consumption. Genetic factors can also play a role in the development of hypertension, particularly if there is a family history of high blood pressure.
In addition, certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease and sleep apnea, can also cause hypertension. One of the main mechanisms involved in the development of hypertension is the narrowing of the blood vessels, which increases the resistance to blood flow and raises blood pressure.
This narrowing can be caused by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, a process known as atherosclerosis. Other factors that can increase the risk of atherosclerosis and hypertension include smoking, high cholesterol levels, and diabetes. Managing these risk factors through lifestyle changes and medication can help to prevent hypertension and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Symptoms of Hypertension
Identifying symptoms of high blood pressure is crucial in promoting early intervention and preventing potential health complications. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, often exhibits no symptoms in its early stages and is often referred to as the ‘silent killer.’
However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, and vision changes. These symptoms may be indicative of more severe complications, such as heart attack, stroke, or kidney damage. It is important for individuals who experience these symptoms to seek immediate medical attention as this can reduce the risk of serious health complications.
In addition to physical symptoms, high blood pressure can also have psychological effects on individuals. It has been associated with anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline. Elevated blood pressure levels have been shown to contribute to the development of cognitive impairment and dementia in older adults.
Therefore, regular blood pressure monitoring and early intervention can not only prevent physical complications but also maintain cognitive function in later life. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, can also help manage blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of hypertension-related complications.
Effects of Hypertension on the Body
The impact of high blood pressure on the body can lead to various health complications, including damage to vital organs such as the brain and kidneys. Hypertension can cause the walls of blood vessels to thicken and stiffen, restricting blood flow to the organs. Over time, this can lead to damage and scarring of the organs, affecting their function and leading to serious health problems.
The table below outlines some of the effects of hypertension on different organs in the body:
| Organ | Effect of Hypertension |
|---|---|
| Brain | Increased risk of stroke, dementia, and cognitive impairment |
| Heart | Increased risk of heart attack, heart failure, and arrhythmias |
| Kidneys | Decreased kidney function and increased risk of kidney disease |
| Eyes | Increased risk of vision loss and eye damage |
| Arteries | Increased risk of atherosclerosis, aneurysm, and peripheral artery disease |
It is important to manage hypertension through lifestyle changes and medication, as it can have serious and long-term effects on the body. Regular monitoring and management of blood pressure can help prevent these complications and maintain overall health.
Causes of Heart Disease
One of the primary culprits behind the development of cardiac ailments is the accumulation of plaque in the arteries. This buildup leads to the hardening and narrowing of the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. As a result, the heart must work harder to pump blood through the constricted vessels, leading to high blood pressure and potential damage to the heart muscle.
There are several factors that contribute to the development of heart disease, aside from plaque buildup. These include smoking, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. While some of these risk factors are controllable, such as quitting smoking and adopting a healthier diet and exercise routine, others such as genetics and age cannot be changed.
It is important for individuals to be aware of their risk factors and take steps to manage them in order to prevent the development of heart disease.
- Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States, with approximately 655,000 deaths per year.
- Women are more likely to die from heart disease than from breast cancer.
- The risk of heart disease increases with age, with men over the age of 45 and women over the age of 55 being at higher risk.
- Heart disease is often preventable through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions.
Symptoms of Heart Disease
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of cardiac ailments is crucial for early detection and treatment. Some common symptoms of heart disease include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and cold sweats.
Chest pain, also known as angina, is one of the most common symptoms and is often described as a feeling of pressure or tightness in the chest.
Shortness of breath can occur during physical activity or even at rest and is often a sign of congestive heart failure. Fatigue is another common symptom and can be caused by a reduced blood flow to the muscles and organs.
Additionally, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and cold sweats are also symptoms that may indicate heart disease. Dizziness can be caused by a drop in blood pressure, while nausea and vomiting may occur due to a lack of blood flow to the digestive tract. Cold sweats can be a sign of a heart attack and should be taken seriously.
It is important to note that some people may not experience any symptoms at all, especially in the early stages of heart disease. Therefore, regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for early detection and prevention of heart disease.
Treatment Options for Hypertension and Heart Disease
Treatment options for managing high blood pressure and related ailments involve implementing lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques, as well as medication and surgical procedures in severe cases.
One of the first steps in managing hypertension is making lifestyle changes. This includes eating a diet that is low in sodium and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Regular exercise is also important for maintaining a healthy weight, reducing stress, and improving cardiovascular health. Additionally, stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can also be helpful.
In cases where lifestyle modifications are not enough, medication may be prescribed to help lower blood pressure. There are several types of medications available, including diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium channel blockers. These medications work in different ways to lower blood pressure and may be used in combination with each other.
In severe cases, surgical procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery may be necessary to improve blood flow to the heart. Ultimately, the best course of treatment will depend on the individual’s specific circumstances and should be determined in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cardiovascular system is a complex network of organs and vessels that work together to circulate blood throughout the body. It plays a critical role in maintaining overall health and well-being, and any disruption in its function can lead to serious health problems.
Hypertension and heart disease are two of the most common cardiovascular disorders, and they can have devastating effects on the body if left untreated. It is essential to recognize the causes and symptoms of these conditions and seek medical attention promptly.
Lifestyle changes, medication, and surgery are some of the treatment options available for hypertension and heart disease. With proper care and management, individuals with these conditions can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. However, prevention is always better than cure, and adopting a healthy lifestyle and regular medical check-ups can go a long way in preventing cardiovascular diseases.