What Is The Function Of Bronchodilators In Managing Respiratory Conditions?
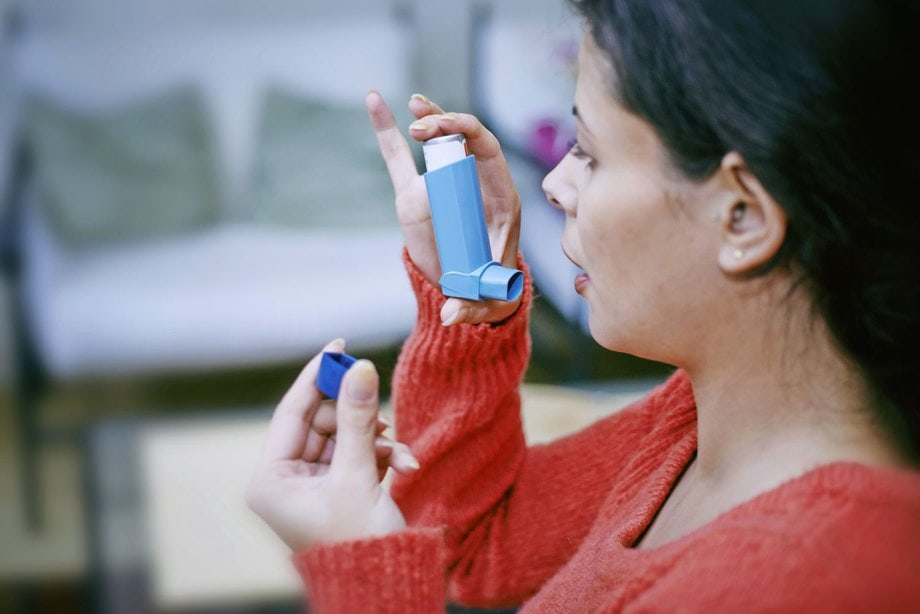

Bronchodilators play a crucial role in the management of respiratory conditions by alleviating symptoms such as bronchoconstriction and airway obstruction. These medications work by relaxing the smooth muscles lining the airways, leading to bronchodilation and improved airflow.
The use of bronchodilators is particularly beneficial in conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and bronchiolitis. This article aims to provide an overview of respiratory conditions commonly treated with bronchodilators, the mechanisms of action of these medications, the different types of bronchodilators available, and the benefits and potential side effects associated with their use.
Additionally, the article will discuss commonly used combination therapies and provide guidance on the proper usage and administration of bronchodilators. Understanding the function and appropriate use of bronchodilators is of utmost importance in the effective management of respiratory conditions.
Key Takeaways
- Bronchodilators relax smooth muscles in the airways, improving airflow and reducing symptoms.
- Combination therapies with bronchodilators enhance efficacy and provide additional benefits.
- Inhalation is the preferred route of administration for targeted delivery to the lungs.
- Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals is recommended for monitoring treatment response.
Overview of Respiratory Conditions
Respiratory conditions encompass a wide range of disorders affecting the lungs and airways, ranging from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to asthma and bronchiectasis. These respiratory diseases are characterized by various symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing, and chest tightness.
COPD is a progressive lung disease that includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, often caused by smoking or exposure to pollutants.
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition that results in airway constriction and increased mucus production, leading to recurrent episodes of wheezing and breathlessness.
Bronchiectasis is a condition characterized by irreversible widening and thickening of the airways, leading to excess mucus production and recurrent infections.
The management of these respiratory conditions often involves the use of bronchodilators, which are medications that help relax and widen the airways, improving airflow and reducing symptoms. Bronchodilators can be delivered through inhalers, nebulizers, or orally, and they work by targeting specific receptors in the airways, causing smooth muscle relaxation and bronchial dilation.
By alleviating airway constriction, bronchodilators effectively relieve symptoms and improve lung function in individuals with respiratory conditions.
How Bronchodilators Work
Bronchodilators are medications that are commonly used in the management of respiratory conditions. They work by causing relaxation of the muscles in the airways, which leads to improved airflow to the lungs.
This relaxation of the airway muscles allows for easier breathing and can help alleviate symptoms such as wheezing and shortness of breath.
Relaxation of Airway Muscles
The relaxation of airway muscles plays a crucial role in the management of respiratory conditions. Bronchodilators, a class of medications used to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), work by promoting the relaxation of these muscles. Here are four key aspects of airway muscle relaxation:
- Reduction of bronchoconstriction:
- Bronchodilators help to counteract the constriction of the airways, which is a common feature of respiratory conditions.
- By relaxing the smooth muscles surrounding the airways, bronchodilators allow for improved airflow.
- Increased bronchial diameter:
- By promoting airway muscle relaxation, bronchodilators help to widen the bronchial tubes.
- This allows for easier breathing and reduces the resistance to airflow.
- Prevention of airway inflammation:
- Bronchodilators can also help to reduce the inflammatory response in the airways, which can contribute to the narrowing of the air passages.
- By reducing inflammation, these medications further promote airway muscle relaxation.
- Improved mucus clearance:
- In addition to relaxing the airway muscles, bronchodilators can enhance the clearance of mucus from the airways.
- This helps to prevent mucus buildup, which can obstruct airflow and exacerbate respiratory symptoms.
Overall, the relaxation of airway muscles achieved through the use of bronchodilators is essential in managing respiratory conditions by improving airflow, reducing inflammation, and facilitating mucus clearance.
Improved Airflow to the Lungs
Improved airflow to the lungs is crucial for optimizing respiratory function and enhancing overall pulmonary health.
Bronchodilators play a significant role in achieving this goal by dilating the airways and allowing for improved lung function. These medications work by relaxing the smooth muscles surrounding the airways, thereby reducing airway constriction and facilitating easier airflow.
By widening the air passages, bronchodilators enable more efficient exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs, leading to improved respiratory health. The increased airflow not only helps alleviate symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, and coughing but also enhances the oxygenation of tissues and organs, promoting overall well-being.
In managing respiratory conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and bronchitis, bronchodilators are essential in maintaining optimal lung function and improving the quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.
Types of Bronchodilators
This paragraph will discuss the types of bronchodilators, specifically short-acting and long-acting bronchodilators.
Short-acting bronchodilators are medications that provide immediate relief of symptoms by relaxing the muscles in the airways, allowing for easier breathing.
On the other hand, long-acting bronchodilators are medications that provide a sustained effect over a longer period of time, typically lasting for 12 hours or more.
These two types of bronchodilators are commonly used in the management of respiratory conditions to improve breathing and alleviate symptoms.
Short-Acting Bronchodilators
Short-acting bronchodilators, such as albuterol, provide rapid relief by relaxing the smooth muscles surrounding the airways, allowing increased airflow and alleviating symptoms of respiratory conditions. These bronchodilators are commonly referred to as quick relief medications.
Short-acting bronchodilators work by activating beta-2 adrenergic receptors in the smooth muscles of the airways, leading to their relaxation. This relaxation allows the airways to widen, reducing airway resistance and improving airflow.
The effects of short-acting bronchodilators are usually felt within minutes and can last for a few hours. These medications are commonly used in the treatment of acute episodes of bronchoconstriction, such as in asthma attacks or exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). They are also used as a rescue medication for individuals experiencing sudden shortness of breath or wheezing.
Long-Acting Bronchodilators
Long-acting bronchodilators, such as salmeterol and formoterol, exert their effects by maintaining bronchial smooth muscle relaxation for an extended period of time, providing sustained relief from bronchoconstriction. These medications are commonly used as maintenance therapy for respiratory conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
The main advantages of long-acting bronchodilators include their ability to provide continuous bronchodilation over a prolonged period, reducing the frequency of symptoms and improving lung function. They are usually prescribed in combination with inhaled corticosteroids to achieve better control of respiratory symptoms and prevent exacerbations.
Key benefits of long-acting bronchodilators include:
- Improved lung function and exercise tolerance
- Reduced symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath
- Decreased frequency of exacerbations and hospitalizations
- Better quality of life for individuals with respiratory conditions
Overall, long-acting bronchodilators play a crucial role in the management of respiratory conditions by providing sustained relief and improving overall respiratory function. They are an important component of maintenance therapy in individuals with chronic respiratory diseases.
Commonly Used Combination Therapies
Commonly used combination therapies involving bronchodilators play a crucial role in the management of respiratory conditions. These therapies involve the use of multiple drugs to achieve better control of symptoms and improve lung function. One of the main advantages of combination therapies is the ability to target different aspects of the underlying disease process. By combining bronchodilators with other medications, such as corticosteroids, the anti-inflammatory effects can be enhanced, leading to improved symptom control and reduced exacerbations.
However, it is important to consider potential drug interactions when using combination therapies. Some medications may interact with each other, leading to reduced effectiveness or increased side effects. Healthcare professionals must carefully evaluate the patient’s individual needs and medical history to determine the most appropriate combination therapy.
Overall, commonly used combination therapies involving bronchodilators offer a comprehensive approach to managing respiratory conditions, providing better symptom control and improved quality of life for patients.
| Medication | Mechanism of Action | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Bronchodilators | Relax smooth muscles in airways | Tremors, increased heart rate |
| Corticosteroids | Reduce inflammation in airways | Oral thrush, hoarseness |
| Anticholinergics | Inhibit bronchoconstriction | Dry mouth, constipation |
| Beta-agonists | Relax bronchial smooth muscles | Nervousness, palpitations |
| Leukotriene modifiers | Block inflammatory response | Headache, nausea |
Benefits and Potential Side Effects
One of the key advantages of combination therapies involving bronchodilators is their ability to provide a comprehensive approach to the treatment of respiratory conditions, offering both symptom control and improved quality of life for patients. When used in combination with other medications, bronchodilators can enhance their efficacy and provide additional benefits.
Here are some potential benefits of combination therapies with bronchodilators:
- Enhanced bronchodilation: Combining different types of bronchodilators can result in a more significant and sustained bronchodilatory effect, leading to improved airflow and reduced symptoms.
- Reduced inflammation: Some combination therapies include corticosteroids, which can help decrease airway inflammation and prevent exacerbations.
- Simplified treatment regimen: By combining multiple medications into a single inhaler or nebulizer, combination therapies can simplify the treatment regimen, making it easier for patients to adhere to their medication schedule.
- Improved patient outcomes: Combination therapies have been associated with improved lung function, reduced hospitalizations, and enhanced overall quality of life for patients with respiratory conditions.
While combination therapies with bronchodilators offer many benefits, it is important to consider potential risks and alternative treatments. Some individuals may experience side effects such as palpitations, tremors, or throat irritation. Additionally, alternative treatments such as pulmonary rehabilitation or surgical interventions may be considered in certain cases. Ultimately, the selection of the most appropriate treatment approach should be based on individual patient characteristics and preferences, as well as the guidance of healthcare professionals.
Proper Usage and Administration
Proper usage and administration of combination therapies with bronchodilators play a crucial role in optimizing treatment outcomes and ensuring effective management of respiratory health.
Bronchodilators are medications that relax the smooth muscles in the airways, thereby widening them and making it easier for air to flow in and out of the lungs. To achieve the desired therapeutic effects, it is important to follow the prescribed dosage and frequency of administration.
Inhalation is the preferred route of administration for bronchodilators, as it allows for targeted delivery to the lungs and minimizes systemic side effects. It is essential to use the appropriate inhaler device and technique, as incorrect usage can lead to inadequate drug delivery.
Patients should be educated on proper inhaler technique and advised to rinse their mouth after inhalation to prevent local side effects such as oral candidiasis. Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals is recommended to monitor treatment response and adjust the medication regimen as needed.
By adhering to proper usage and administration guidelines, individuals can optimize the benefits of bronchodilator therapy and effectively manage their respiratory conditions.
Conclusion and Importance of Bronchodilators in Respiratory Management
The significance of bronchodilators in respiratory management cannot be overstated, as they play a pivotal role in improving the quality of life for individuals with respiratory conditions. These medications work by relaxing the smooth muscles in the airways, thereby widening the bronchi and allowing for easier breathing. By reducing airway constriction, bronchodilators help to alleviate symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. They are commonly used in the management of conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and bronchiectasis. Bronchodilators are available in different forms, including inhalers, nebulizers, and oral tablets. The choice of delivery method depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s preference. Overall, bronchodilators are an essential component of respiratory management, providing relief and improving lung function for individuals with respiratory conditions.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Rapid onset of action | Potential side effects such as tremors and increased heart rate |
| Effective in relieving symptoms | Some individuals may develop tolerance over time |
| Can be used as rescue medication | May interact with other medications |
| Convenient and easy to use | Different types of bronchodilators may require different administration techniques |
| Can be used in combination therapy | Some individuals may not respond adequately to bronchodilators |
Frequently Asked Questions
Are bronchodilators only used for managing respiratory conditions?
Bronchodilators are primarily used for managing respiratory conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. However, they can also have alternative uses in other medical conditions. It is important to note that bronchodilators may have potential side effects.
Can bronchodilators be used as a long-term treatment for respiratory conditions?
Bronchodilators can be used as a long-term treatment for respiratory conditions. They have shown long-term effectiveness in improving airflow and reducing symptoms. However, they may also have potential side effects, such as tremors and increased heart rate.
Are there any alternative treatments to bronchodilators for managing respiratory conditions?
Alternative therapies and natural remedies can be considered as options for managing respiratory conditions. These treatments may include breathing exercises, herbal remedies, acupuncture, and dietary changes. However, their effectiveness varies and should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Are there any age restrictions or limitations for using bronchodilators?
Bronchodilators are commonly used to manage respiratory conditions, and there are no age restrictions or limitations for their use. They work by relaxing the muscles in the airways, allowing for easier breathing.
Can bronchodilators be used as a standalone treatment or are they always combined with other medications?
Bronchodilators can be used as a standalone treatment or in combination with other medications. The decision depends on the severity and type of respiratory condition. Standalone use may be sufficient for mild cases, while combination therapy is often necessary for more severe conditions.