What Is The Immune System? Defenses Against Pathogens And Diseases
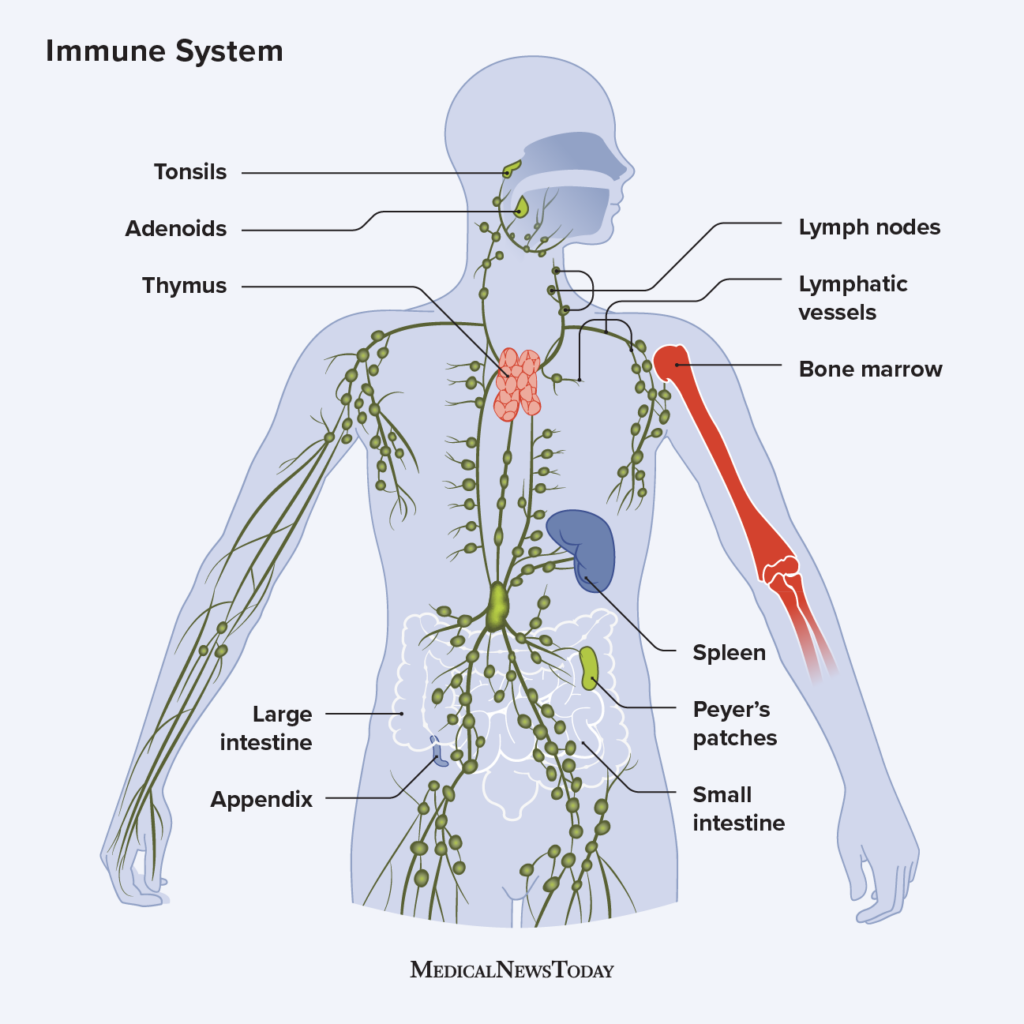
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful pathogens and diseases. This intricate defense mechanism is essential for maintaining good health and preventing infections.
The immune system is designed to recognize and destroy any foreign invaders that may enter the body, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. The immune system is made up of several different components, including white blood cells, antibodies, and lymphocytes. These components work together to identify and destroy harmful pathogens, while also providing immunity against future infections.
While the immune system is generally very effective at protecting the body, it can sometimes become weakened or compromised, leaving individuals vulnerable to infections and diseases. Understanding how the immune system works and how to support its function can help individuals maintain good health and prevent the spread of illness.
Key Takeaways
- The immune system defends against harmful pathogens and diseases by recognizing and destroying foreign invaders.
- Components of the immune system include white blood cells, antibodies, and lymphocytes, which play critical roles in protecting the body from infections.
- Pathogens can invade the body through inhalation, ingestion, or direct contact, and the immune system responds through the innate and adaptive immune systems.
- Healthy lifestyle habits, such as consuming a balanced diet, regular physical exercise, and getting enough sleep, can enhance the body’s natural ability to combat harmful invaders.
Components of the Immune System
The immune system is composed of various components, including white blood cells, antibodies, lymphatic vessels, and organs such as the thymus and spleen, which work together to protect the body from pathogens and diseases.
White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are the primary cells involved in the immune response. They can be further classified into two types: phagocytes and lymphocytes. Phagocytes are responsible for engulfing and destroying invading pathogens, while lymphocytes are responsible for recognizing and responding to specific antigens.
Antibodies, on the other hand, are proteins produced by specific types of lymphocytes called B cells. These proteins recognize and bind to specific antigens, marking them for destruction by other components of the immune system.
The lymphatic vessels and organs are also essential components of the immune system, as they aid in the production and distribution of lymphocytes throughout the body. The thymus is responsible for the development and maturation of T cells, while the spleen filters blood and removes old or damaged red blood cells.
Together, these components form a complex and sophisticated system that plays a crucial role in protecting the body from harm.
White Blood Cells: The Frontline Defenders
White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, play a crucial role in detecting and eliminating foreign invaders in the body. They are part of the immune system and come in various types, each with a specific function. The most common types of white blood cells are neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.
Neutrophils are the most abundant type of white blood cells and are the first to arrive at the site of infection. They engulf and destroy bacteria and other foreign substances.
Lymphocytes are responsible for identifying and eliminating viruses, bacteria, and abnormal cells, such as cancer cells.
Monocytes act as a cleanup crew, engulfing and removing dead cells and debris.
Eosinophils and basophils are involved in allergic reactions and parasitic infections.
The coordination between these different types of white blood cells is crucial in the immune response and the prevention of infections and diseases.
White blood cells are the frontline defenders of the immune system, constantly patrolling the body and eliminating foreign invaders. Their importance cannot be overstated, as they are essential in maintaining the bodys health and preventing infections and diseases.
Understanding the different types of white blood cells and their functions is crucial in understanding the immune system and the bodys defense mechanisms.
The Role of Antibodies in Immunity
Antibodies are proteins produced by B cells that play a crucial role in recognizing and neutralizing foreign substances in the body. These foreign substances, or antigens, can include bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
Antibodies work by binding to the antigens and marking them for destruction by other immune system cells. Antibodies are highly specialized and can recognize a wide range of antigens. This is due to the fact that they are made up of different regions that can bind to different parts of an antigen.
Thus, the immune system is able to recognize and respond to a diverse array of pathogens. Additionally, antibodies can also provide immunity against future infections by the same pathogen. This is because once the body has been exposed to a particular antigen, it can produce a more rapid and effective immune response upon subsequent exposures.
Lymphocytes: The Immune System’s Elite Fighters
Lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, are integral to the body’s ability to mount a successful defense against invading pathogens. They are produced in the bone marrow and mature in either the thymus gland (T cells) or the bone marrow (B cells). Lymphocytes have a unique ability to recognize and respond to specific antigens, which are molecules on the surface of pathogens that trigger an immune response.
There are two main types of lymphocytes: T cells and B cells. T cells are responsible for cell-mediated immunity, which involves directly attacking infected cells. B cells are responsible for humoral immunity, which involves producing antibodies that bind to and neutralize pathogens. Both types of lymphocytes play critical roles in protecting the body from infections. The table below summarizes the key characteristics of T cells and B cells.
| T Cells | B Cells | |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Mature in the thymus gland | Mature in the bone marrow |
| Function | Cell-mediated immunity | Humoral immunity |
| Response to antigens | Recognize antigens presented by infected cells | Recognize free-floating antigens |
Overall, lymphocytes are essential components of the immune system. They have the ability to recognize and respond to specific pathogens, and they play key roles in both cell-mediated and humoral immunity. By understanding how lymphocytes work, researchers can develop better strategies for preventing and treating infectious diseases.
How Pathogens Invade the Body
In order for infectious agents to cause harm, they must first penetrate the body’s natural barriers. These barriers include the skin and mucous membranes, which act as physical barriers to prevent pathogens from entering the body. However, if a pathogen does manage to enter the body, it can infect cells and cause damage.
There are several ways in which pathogens can invade the body. These include:
- Inhalation: When a person breathes in air containing viruses or bacteria.
- Ingestion: When a person eats or drinks contaminated food or water.
- Direct contact: When a person touches an infected surface or an infected person.
Once a pathogen has entered the body, it can then attach to host cells and enter them. The pathogen can then replicate itself and spread throughout the body, causing damage and potentially leading to illness or disease.
It is the job of the immune system to identify and eliminate these pathogens before they can cause harm.
The Immune Response: Fighting Back Against Infection
After discussing how pathogens invade the body, it is now important to understand how the immune system responds to these invaders. The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi. The immune system is divided into two main categories: the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system.
The innate immune system is the first line of defense against pathogens, and it provides a rapid response to invading pathogens. The innate immune system includes physical and chemical barriers such as the skin, mucous membranes, and stomach acid, as well as immune cells such as neutrophils and macrophages. These cells recognize and destroy invaders through a process known as phagocytosis. The adaptive immune system, on the other hand, provides a more specific response to pathogens. This system includes immune cells such as T and B lymphocytes that are able to recognize and remember specific pathogens, allowing for a quicker and more effective response in the future. The following table provides a summary of the differences between the innate and adaptive immune systems:
| Innate Immune System | Adaptive Immune System | |
|---|---|---|
| Response time | Rapid, within minutes to hours | Slower, takes days to weeks |
| Specificity | Broad, responds to a wide range of pathogens | Specific, recognizes and remembers specific pathogens |
| Memory | No memory, response is not improved with repeated exposure | Memory cells allow for a quicker and more effective response with repeated exposure |
| Components | Physical and chemical barriers, immune cells such as neutrophils and macrophages | Immune cells such as T and B lymphocytes |
| Activation | Activated by the presence of pathogens | Activated by the presence of specific antigens |
Overall, the immune response is a complex process that involves both the innate and adaptive immune systems working together to defend the body against harmful pathogens. By understanding how these systems work, we can better appreciate the incredible complexity and sophistication of the human body’s defense mechanisms.
Strengthening Your Immune System Naturally
One way to enhance the body’s natural ability to combat harmful invaders is by adopting healthy lifestyle habits. These habits are not only essential for overall well-being, but also help in boosting the immune system.
Here are some ways to strengthen the immune system naturally:
- Consuming a balanced diet that is rich in nutrients is crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system. The diet should include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Additionally, incorporating foods that are high in antioxidants, such as berries, nuts, and leafy greens, can help in reducing inflammation and boosting the immune system.
- Regular physical exercise is another way to improve the immune system. Exercise helps in increasing blood flow, reducing stress, and improving overall health. Engaging in moderate-intensity activities such as brisk walking or biking for at least 30 minutes a day can help in strengthening the immune system.
- Getting enough sleep is essential for the body to function properly. Lack of sleep can weaken the immune system, making it more susceptible to infections. Adults should aim for at least 7-8 hours of sleep each night.
- Stress can have a negative impact on the immune system. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help in reducing stress and improving the immune system.
Incorporating these healthy habits into daily routine can help in strengthening the immune system naturally and improving overall health.
Medical Interventions for Immune Support
Medical interventions for enhancing the body’s natural ability to combat harmful invaders have been developed to help individuals with compromised immune function. These interventions include immunotherapy, which uses the body’s own immune system to fight cancer, and immunosuppressive drugs, which reduce the activity of the immune system to prevent rejection of transplanted organs.
Immunotherapy can involve the use of vaccines, which stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells, or monoclonal antibodies, which are designed to target specific proteins on cancer cells. Immunosuppressive drugs are used to prevent the immune system from attacking transplanted organs, but can also be used to treat autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
Another medical intervention for immune support is the use of antibiotics to treat bacterial infections. Antibiotics work by killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria, which can cause a range of illnesses from strep throat to pneumonia. However, overuse of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic resistance, where bacteria evolve to become resistant to the drugs.
Other medical interventions include antiviral drugs, which are used to treat viral infections such as HIV and hepatitis, and immunoglobulin therapy, which involves the use of antibodies to treat immune deficiencies and autoimmune diseases. While medical interventions can be effective in enhancing immune function, it is important to use them responsibly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid potential side effects and complications.
Conclusion
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful pathogens and diseases.
White blood cells act as the frontline defenders by recognizing and destroying foreign invaders.
Antibodies play a crucial role in immunity by binding to pathogens and marking them for destruction.
Lymphocytes are the immune system’s elite fighters that target specific pathogens and provide long-term protection.
Pathogens invade the body through different routes, such as inhalation, ingestion, or direct contact.
The immune response involves a series of coordinated events that aim to eliminate the invading pathogens.
The immune system can be strengthened naturally through a healthy lifestyle, including diet, exercise, and stress reduction.
Medical interventions, such as vaccines and immunotherapy, can also provide additional support to the immune system.
In conclusion, understanding the immune system’s components, functions, and mechanisms is essential for maintaining good health and preventing infections.
By supporting our immune system through healthy lifestyle habits and medical interventions, we can enhance our body’s natural defenses against pathogens and diseases.