What Is The Impact Of Sleep Apnea On Daytime Fatigue And Performance?
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder characterized by repetitive pauses in breathing during sleep, resulting in disrupted sleep patterns and reduced oxygen levels in the body. This condition can have a significant impact on daytime fatigue and performance, affecting various aspects of an individual’s life.
Daytime fatigue is a prominent symptom of sleep apnea, often leading to decreased alertness, concentration difficulties, and excessive daytime sleepiness. These symptoms can have a detrimental effect on cognitive performance, including memory, attention, and decision-making abilities.
Furthermore, untreated sleep apnea has been associated with an increased risk of various health conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, and diabetes.
Diagnosis and treatment options for sleep apnea are available, ranging from lifestyle modifications to continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy. By effectively managing sleep apnea, individuals can improve their quality of life and mitigate the impact of daytime fatigue and performance deficits.
This article explores the relationship between sleep apnea, daytime fatigue, and performance, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle changes in managing this condition.
Key Takeaways
- Sleep apnea causes disrupted sleep patterns, leading to increased daytime fatigue.
- Daytime fatigue from sleep apnea can result in decreased alertness, concentration difficulties, and excessive daytime sleepiness.
- Sleep apnea can have a detrimental effect on cognitive performance, affecting memory, attention, and decision-making abilities.
- Untreated sleep apnea is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, and diabetes.
Understanding Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, often resulting in fragmented sleep patterns and persistent daytime fatigue.
It is estimated that approximately 15 million adults in the United States have moderate to severe sleep apnea.
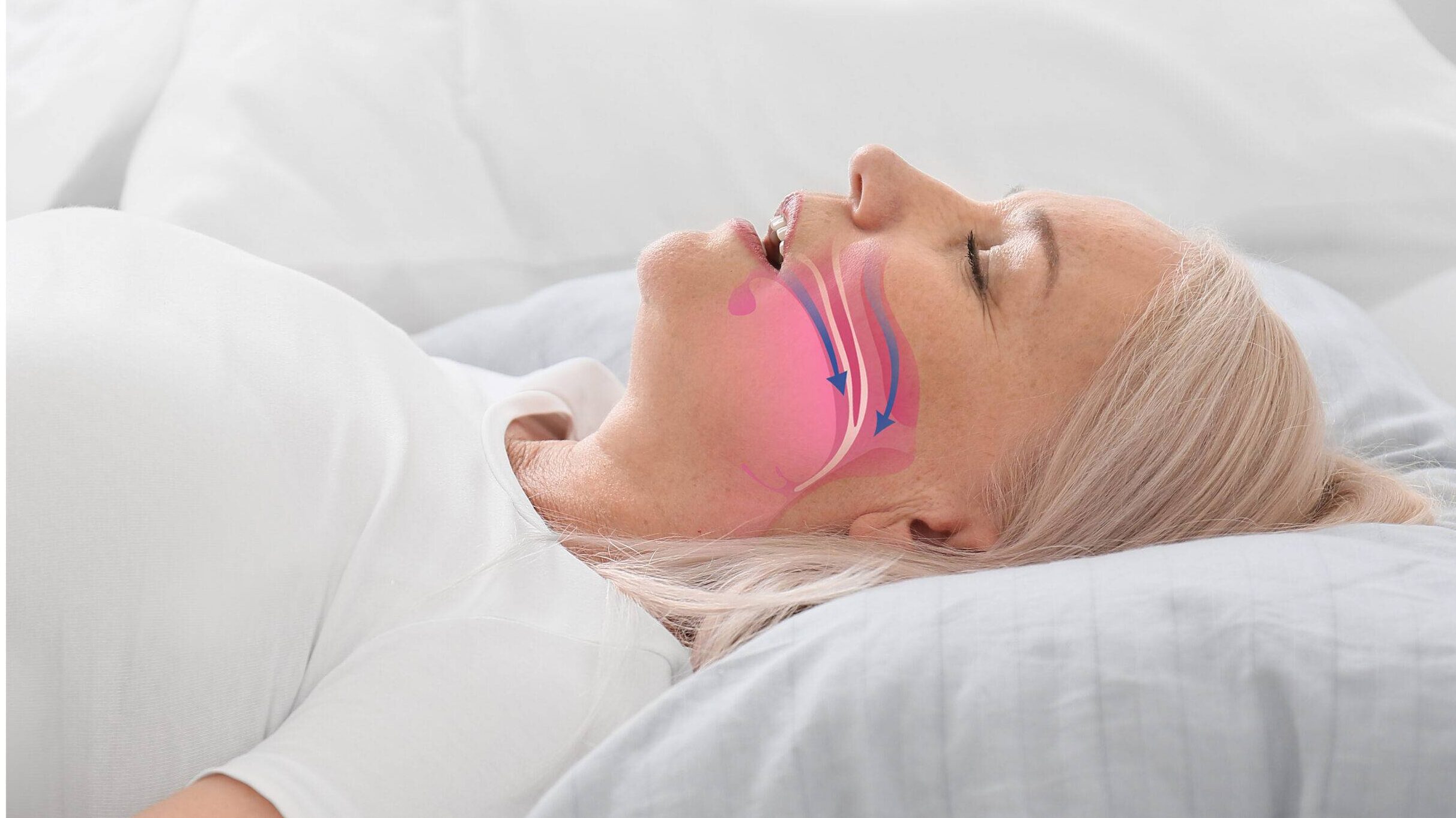
The most common type of sleep apnea is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), where the airway becomes partially or completely blocked during sleep. This leads to a decrease in oxygen levels in the blood, causing the individual to wake up briefly to restore normal breathing.
These frequent awakenings disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to daytime fatigue and sleepiness. In addition to fatigue, sleep apnea has been associated with a decline in cognitive function, impaired concentration, and decreased performance in daily activities, including work and driving.
Effective treatment options for sleep apnea, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, can help alleviate these symptoms and improve daytime functioning.
The Relationship Between Sleep Apnea and Daytime Fatigue
This paragraph will discuss the relationship between sleep apnea and daytime fatigue, focusing on the key points of disrupted sleep patterns and oxygen deprivation.
Sleep apnea is characterized by intermittent pauses in breathing during sleep, leading to disrupted sleep patterns and a decrease in the quality of sleep. This disruption can result in excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue, making it difficult for individuals with sleep apnea to maintain optimal energy levels throughout the day.
Additionally, sleep apnea can also cause oxygen deprivation, which further contributes to feelings of fatigue and reduced daytime performance.
Disrupted Sleep Patterns
Disrupted sleep patterns caused by sleep apnea have been associated with increased daytime fatigue and impaired cognitive performance. Sleep apnea is characterized by periods of interrupted breathing during sleep, leading to frequent awakenings and poor sleep quality. As a result, individuals with sleep apnea often experience excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty concentrating, and decreased alertness. This can significantly impact their ability to perform daily tasks, such as driving or operating machinery, increasing the risk of accidents.
Moreover, disrupted sleep patterns can also have emotional consequences, including irritability, mood swings, and decreased motivation. Individuals with sleep apnea may also have difficulty maintaining relationships or participating in social activities due to their constant fatigue.
Overall, the negative impact of sleep apnea on daytime fatigue and performance highlights the importance of diagnosis and treatment for this sleep disorder.
- Constant exhaustion
- Frustration and irritability
- Feelings of depression and anxiety
- Impaired memory and concentration
- Decreased productivity and performance
Oxygen Deprivation and its Effects on Energy Levels
Oxygen deprivation during sleep, caused by sleep apnea, can lead to a significant decrease in energy levels. Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repetitive pauses in breathing during sleep, resulting in intermittent hypoxia. These periods of reduced oxygen supply can have detrimental effects on daytime functioning.
The body relies on oxygen to produce energy through various metabolic processes, including cellular respiration. When oxygen levels are compromised, the body’s ability to generate energy is hindered. As a result, individuals with sleep apnea often experience excessive daytime fatigue and reduced alertness. This can have a profound impact on their performance, both in occupational and daily activities.
In addition to the immediate consequences of decreased energy levels, chronic sleep apnea has also been associated with long-term health risks, such as cardiovascular disease and cognitive impairment. Therefore, addressing sleep apnea and ensuring adequate oxygen supply during sleep is crucial for maintaining optimal energy levels and overall well-being.
Cognitive Performance and Sleep Apnea
Impaired cognitive performance is a prevalent consequence of sleep apnea, significantly affecting an individual’s ability to think, learn, and remember. Research has consistently shown that individuals with sleep apnea experience deficits in various cognitive domains, including attention, memory, executive function, and processing speed.
These cognitive impairments can manifest as difficulties in concentrating, forgetfulness, decreased mental alertness, and reduced information processing abilities. The severity of cognitive dysfunction is often related to the severity of sleep apnea, with more severe cases showing greater cognitive deficits.
Additionally, untreated sleep apnea has been associated with an increased risk of developing cognitive decline and dementia. The underlying mechanisms linking sleep apnea and cognitive impairment are not fully understood, but likely involve a combination of intermittent hypoxemia, sleep fragmentation, and chronic sleep deprivation.
Effective treatment of sleep apnea, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, has been shown to improve cognitive performance and mitigate the cognitive deficits associated with the condition.
Health Risks Associated with Untreated Sleep Apnea
Untreated sleep apnea poses significant health risks that extend beyond cognitive impairment and can lead to serious medical conditions.
One of the most common health risks associated with untreated sleep apnea is cardiovascular disease. The repeated episodes of breathing cessation during sleep can lead to high blood pressure, heart rhythm abnormalities, and an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Additionally, untreated sleep apnea is strongly linked to metabolic disorders such as diabetes. The disrupted sleep patterns and oxygen deprivation caused by sleep apnea can affect the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of developing diabetes.
Moreover, untreated sleep apnea has been associated with an increased risk of obesity, as it disrupts the hormones that regulate appetite and energy expenditure.
Overall, addressing and treating sleep apnea is crucial to prevent the development of these serious health conditions.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
One effective way to address the diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea is through a comprehensive evaluation by a sleep specialist. A sleep specialist will typically conduct a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and may order additional diagnostic tests such as a sleep study. Treatment options for sleep apnea vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may be managed through lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, avoiding alcohol and sedatives, and sleeping on one’s side. For moderate to severe cases, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy is often recommended. This involves wearing a mask over the nose or mouth during sleep, which delivers a constant flow of air to keep the airway open. Other treatment options may include oral appliances, positional therapy, and in some cases, surgery. It is important for individuals with sleep apnea to seek proper diagnosis and treatment to alleviate symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
| Treatment Options | Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle changes | Weight loss, avoiding alcohol and sedatives, sleeping on one’s side | |||
| CPAP therapy | Wearing a mask that delivers a constant flow of air to keep the airway open | |||
| Oral appliances | Devices that help keep the airway open during sleep | |||
| Positional therapy | Encouraging sleeping in certain positions to prevent airway obstruction | |||
| Surgery | Various surgical procedures to physically modify the airway and improve breathing | Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) | A common treatment that involves wearing a mask over the nose or mouth during sleep to deliver a steady flow of air pressure, keeping the airway open and preventing obstruction. |
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Sleep Apnea
This discussion will focus on two key lifestyle changes that can help manage sleep apnea: weight loss and exercise, and avoiding alcohol and sedatives.
Weight loss and regular exercise have been shown to improve sleep apnea symptoms by reducing excess weight and improving overall cardiovascular health.
Additionally, avoiding alcohol and sedatives can help prevent the relaxation of the muscles in the throat, which can contribute to the obstruction of airflow during sleep.
Weight Loss and Exercise
Weight loss and exercise have been shown to have a positive impact on reducing daytime fatigue and improving performance in individuals with sleep apnea.
Excess weight and obesity are major risk factors for sleep apnea, and losing weight can help alleviate symptoms. Studies have demonstrated that even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can lead to significant improvements in sleep apnea severity and daytime sleepiness.
Furthermore, exercise has been found to improve sleep quality and reduce the frequency of apnea events during sleep. Regular physical activity can also enhance cardiovascular health and increase overall energy levels, leading to reduced fatigue and improved performance during the day.
Therefore, incorporating weight loss strategies and exercise into the management of sleep apnea can greatly contribute to enhancing daytime functioning and overall quality of life for individuals with this condition.
Avoiding Alcohol and Sedatives
Avoiding alcohol and sedatives can significantly enhance the overall effectiveness of sleep apnea management and contribute to improved daytime functioning and quality of life.
1) Alcohol acts as a muscle relaxant, which can worsen the collapse of the upper airway during sleep, leading to more frequent apnea events. By abstaining from alcohol, individuals with sleep apnea can reduce the severity and frequency of these events, resulting in better sleep quality.
2) Sedatives, such as sleeping pills or tranquilizers, can depress the central nervous system and reduce muscle tone, further obstructing the airway. Avoiding sedatives can help maintain normal muscle tone and prevent the worsening of sleep apnea symptoms.
3) Both alcohol and sedatives can disrupt the sleep cycle, leading to fragmented sleep and excessive daytime sleepiness. By avoiding these substances, individuals can improve their daytime alertness and cognitive performance.
Support and Resources for Sleep Apnea Patients
Support and resources play a crucial role in helping sleep apnea patients manage their condition effectively.
One important form of support is through support groups and online communities, where individuals can connect with others who are facing similar challenges and share their experiences. These platforms provide a sense of community and a space for individuals to seek advice, share tips, and receive emotional support.
Additionally, professional assistance and guidance are essential for sleep apnea patients, as healthcare professionals can provide personalized treatment plans, offer education about the condition, and monitor progress to ensure optimal management of symptoms.
Support Groups and Online Communities
Online communities dedicated to sleep apnea provide a platform for individuals to connect and exchange valuable information regarding the impact of the condition on daytime fatigue and performance. These communities offer support and resources for individuals diagnosed with sleep apnea, allowing them to share experiences, seek advice, and find solutions to common challenges.
Through these online platforms, individuals can connect with others who may be going through similar struggles, fostering a sense of belonging and understanding. Moreover, these communities often provide access to educational resources, such as articles and videos, that offer information about the relationship between sleep apnea and daytime fatigue and performance.
By participating in these communities, individuals can gain knowledge, support, and strategies to manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Professional Assistance and Guidance
Seeking professional assistance and guidance can provide individuals with valuable resources and strategies to effectively manage their condition and improve their overall well-being. By consulting with healthcare professionals specializing in sleep medicine, individuals with sleep apnea can receive accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans tailored to their specific needs.
These professionals can offer guidance on various treatment options, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, oral appliances, or surgery. Additionally, they can provide information on lifestyle modifications, including weight loss, regular exercise, and sleep hygiene practices, which can significantly reduce the severity of sleep apnea symptoms.
Moreover, seeking professional help allows individuals to access ongoing support and monitoring to ensure treatment efficacy and address any concerns that may arise. Taking advantage of these resources can empower individuals to effectively manage their sleep apnea, minimize daytime fatigue, and enhance their overall quality of life.
- Access to accurate diagnoses
- Personalized treatment plans
- Information on various treatment options
- Ongoing support and monitoring
Improving Quality of Life with Sleep Apnea
Implementing effective strategies to improve quality of life for individuals with sleep apnea can lead to reduced daytime fatigue and improved cognitive performance. Sleep apnea is a chronic condition characterized by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep, resulting in fragmented and poor-quality sleep. This can lead to excessive daytime sleepiness, decreased concentration, and impaired cognitive function.
To address these issues, lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime can be beneficial. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy is considered the gold standard treatment for sleep apnea, as it helps maintain an open airway during sleep.
Additionally, cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBTi) can address the psychological and behavioral aspects of sleep apnea, improving sleep quality and overall well-being. By implementing these strategies, individuals with sleep apnea can experience a significant improvement in their quality of life, leading to decreased daytime fatigue and enhanced cognitive performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How common is sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. It affects approximately 10-20% of adults worldwide, with higher prevalence rates among older individuals and those who are obese.
What are the symptoms of sleep apnea?
The symptoms of sleep apnea include loud snoring, interrupted breathing during sleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, morning headache, difficulty concentrating, and irritability. It is a common sleep disorder that affects a significant portion of the population.
Can sleep apnea be cured?
Sleep apnea cannot be fully cured, but it can be effectively managed through lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and avoiding alcohol and sedatives, as well as the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy or other treatments.
Does sleep apnea only affect adults?
Sleep apnea can affect individuals of all ages, not just adults. It is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, resulting in disturbed sleep patterns and potential daytime fatigue and impaired performance.
Is sleep apnea hereditary?
Sleep apnea has a hereditary component, with genetic factors playing a role in its development. Studies have found that certain genes are associated with an increased risk of sleep apnea, suggesting a genetic influence on the condition.