What Is The Integumentary System? Skin, Hair, And Nails
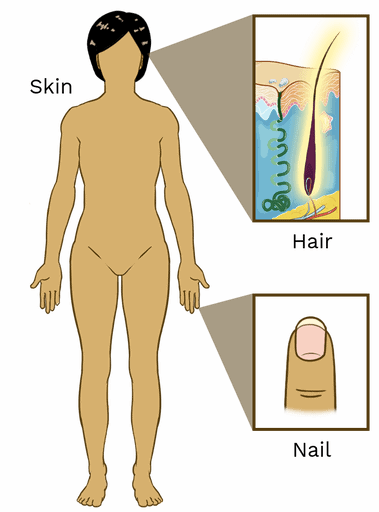
The integumentary system is an essential component of the human body, comprising the skin, hair, and nails. It is the largest organ system in the body, providing critical protective and sensory functions.
The skin, hair, and nails play vital roles in regulating body temperature, protecting against environmental factors, and providing sensory feedback to the brain.
The integumentary system is a complex network of structures that work together to provide a range of functions. The skin is the largest organ in the system, covering the entire body and acting as a barrier against harmful external agents.
The hair and nails are also important components, providing additional protection and sensory feedback. Understanding the structure and function of the integumentary system is crucial for maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails, and for diagnosing and treating various disorders that affect these structures.
Key Takeaways
- The integumentary system includes skin, hair, and nails and is the largest organ system in the body.
- The skin acts as a barrier that protects the body from harmful substances and regulates temperature.
- Hair provides an additional layer of protection and helps regulate body temperature, and there are three types of hair.
- Nails protect the fingertips and toes and are made up of tough, protective protein called keratin. Nail disorders can indicate underlying health conditions and should be examined by a medical professional.
The Importance of the Integumentary System
The integumentary system plays a critical role in protecting the body from external environmental factors such as physical trauma, microbial invasion, and ultraviolet radiation.
The skin, which is the largest organ of the body, acts as a barrier that prevents the entry of harmful substances into the body. It also helps to regulate body temperature and acts as a sensory organ, allowing us to feel sensations such as touch, pressure, and pain.
In addition to the skin, the integumentary system also includes hair and nails. Hair provides an additional layer of protection for the skin and helps to regulate body temperature. Nails, on the other hand, protect the fingertips and toes and provide support for the tips of the digits.
Overall, the integumentary system is crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of the body, and any damage to this system can have significant consequences for our overall health.
The Structure of the Skin
Composed of various layers, the outermost layer of the integumentary structure contains dead cells that provide a barrier to protect the body against external factors. This layer is known as the epidermis, and it is the thinnest layer of the skin.
Below the epidermis is the dermis, which is responsible for providing strength, elasticity, and flexibility to the skin. Within the dermis, there are two layers: the papillary and reticular layers.
The papillary layer contains blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerve endings that are responsible for the sensation of touch. The reticular layer contains collagen and elastin fibers that provide the skin with strength, as well as hair follicles and sweat glands.
Overall, the structure of the skin is complex and essential in protecting the body from external factors, regulating temperature, and providing sensory information.
The Function of the Skin
One of the crucial roles of the outermost layer of the human body is to provide a protective barrier against various external factors. This layer is called the epidermis, and it is responsible for protecting the body from harmful substances such as bacteria, viruses, and chemicals. Additionally, the skin also protects the body from physical injury by acting as a shock absorber.
Another function of the skin is to regulate body temperature. The skin is equipped with sweat glands, which produce sweat to cool down the body when it gets too hot. When the body is too cold, the skin helps to conserve heat by constricting blood vessels and reducing blood flow to the skin’s surface.
The skin also plays a role in vitamin D synthesis, which is essential for the body’s calcium absorption and bone health. Overall, the skin’s complex functions make it an integral part of the body’s overall health and well-being.
Types of Hair and Their Functions
Various types of hair on the human body serve different functions, contributing to the overall health and well-being of the individual. There are three types of hair on the human body: vellus hair, terminal hair, and intermediate hair.
Vellus hair is short, thin, and lightly pigmented. It covers most parts of the body and serves to regulate body temperature by trapping heat near the skin.
Terminal hair is thick, long, and darkly pigmented. It is found on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, pubic area, and armpits. Terminal hair provides protection and insulation to these areas.
Intermediate hair is longer than vellus hair but shorter than terminal hair. It is found on the arms, legs, and torso, and serves to provide protection and insulation to these areas.
In addition to their protective and insulating functions, hair also serves a sensory role. Hair follicles contain nerve endings that enable the detection of changes in the environment, such as touch and temperature. This sensory function is particularly important in the scalp, where hair follicles are densely packed and highly sensitive to touch.
Hair also plays a role in social communication, with styles and colors often used to convey cultural and personal identity.
Overall, the various types of hair on the human body serve important functions that contribute to the individual’s physical and social well-being.
The Structure and Function of Nails
The human body possesses a unique structure that allows for the protection and support of the fingertips through a specific type of appendage known as nails. Nails are made up of a tough, protective protein called keratin and are located at the end of each finger and toe. They play a significant role in performing everyday tasks such as picking up objects, scratching, and gripping.
The structure of nails consists of several layers, including the nail plate, nail bed, and nail matrix. The nail plate is the visible part of the nail that we see and touch, while the nail bed is the skin underneath the nail plate. The nail matrix is the area where new cells are produced, and it determines the shape and thickness of the nail. The function of nails extends beyond just protection and support as they also provide clues about a person’s overall health. For instance, nail discoloration, texture, and thickness can indicate underlying health conditions such as anemia, liver disease, or diabetes.
| Nail Structure | Description |
|---|---|
| Nail Plate | The visible part of the nail that we see and touch |
| Nail Bed | The skin underneath the nail plate |
| Nail Matrix | The area where new cells are produced, determining the shape and thickness of the nail |
Overall, nails are a crucial component of the integumentary system, and their structure and function are essential for the everyday functioning of the human body. Through the use of a nail table, the audience can better visualize the different parts of the nail and their respective functions.
Common Skin Disorders
Common skin disorders can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and often require medical attention. Skin disorders can cause discomfort, pain, embarrassment, and even lead to social isolation.
Here are some of the most common skin disorders that affect people worldwide:
- Acne: This is a common skin condition that affects most people at some point in their lives. Acne is caused by clogged pores, which can lead to pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. Acne can have a significant impact on a person’s self-esteem, especially during adolescence.
- Eczema: This is a chronic skin condition that causes inflammation, redness, and itching. Eczema can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, allergies, and environmental irritants. People with eczema often have to manage their symptoms with medication and lifestyle changes.
- Psoriasis: This is a chronic autoimmune skin disorder that causes the rapid growth of skin cells. Psoriasis can cause patches of red, scaly skin that can be itchy and painful. Psoriasis can also affect the joints, causing a condition known as psoriatic arthritis.
- Rosacea: This is a chronic skin condition that causes redness and swelling on the face. Rosacea can also cause small, red, pus-filled bumps on the face. People with rosacea often have to manage their symptoms with medication and lifestyle changes.
Overall, skin disorders can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing any symptoms of a skin disorder to receive proper diagnosis and treatment.
Common Hair Disorders
Hair disorders can cause significant discomfort and affect a person’s physical appearance and confidence. One of the most common hair disorders is alopecia, which is characterized by hair loss. Alopecia can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormonal imbalances, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications. In some cases, alopecia can be temporary and the hair may grow back on its own, while in other cases it may be permanent and require medical treatment.
Another common hair disorder is dandruff, which is characterized by white flakes on the scalp and hair. Dandruff can be caused by a variety of factors, including dry scalp, oily scalp, or an overgrowth of yeast on the scalp. While dandruff is not a serious medical condition, it can be embarrassing and uncomfortable. Treatment options for dandruff include over-the-counter shampoos containing ingredients such as salicylic acid, coal tar, or ketoconazole, as well as prescription shampoos and medication.
Regular hair care and good hygiene practices can also help prevent and manage dandruff.
Common Nail Disorders
Nail disorders can cause discomfort and affect a person’s physical appearance, making it important to understand their causes and treatment options.
Some common nail disorders include fungal infections, ingrown nails, and psoriasis. Fungal infections can cause the nail to become discolored, thickened, and brittle, and may require antifungal medication to treat.
Ingrown nails occur when the nail grows into the surrounding skin, causing pain and inflammation. Treatment options for ingrown nails include soaking the affected area in warm water, wearing proper footwear, and in severe cases, surgical removal of the affected portion of the nail.
Psoriasis can affect both the skin and nails, causing the nails to become thickened, ridged, and discolored. Treatment for psoriatic nail changes may include medications such as topical corticosteroids or injections of biologic medications.
Proper nail care, such as keeping nails trimmed and avoiding trauma to the nails, can also help prevent nail disorders from occurring.
It is important to seek medical attention if you notice any changes or abnormalities in your nails, as some nail disorders may be indicators of underlying health conditions.
Conclusion
The integumentary system is an essential part of the human body, consisting of the skin, hair, and nails. Its primary function is to protect the body from external factors such as pathogens, chemicals, and physical damage.
The skin, the largest organ of the human body, is composed of three layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. Each layer plays a vital role in protecting the body and regulating body temperature.
In addition to its protective function, the integumentary system also plays a significant role in maintaining homeostasis. It helps regulate body temperature by sweating and shivering, and it also helps the body produce vitamin D.
The hair and nails are also important components of the integumentary system. Hair protects the skin and helps regulate body temperature, while nails protect the fingertips and allow for fine motor skills.
Overall, the integumentary system is a complex and intricate system that plays a vital role in protecting and regulating the body. Understanding its structure and functions is essential for maintaining good health and preventing common disorders that can affect the skin, hair, and nails. By keeping the integumentary system healthy, individuals can maintain their overall well-being and quality of life.