What Is The Lymphatic System? Immunity And Disease Defense
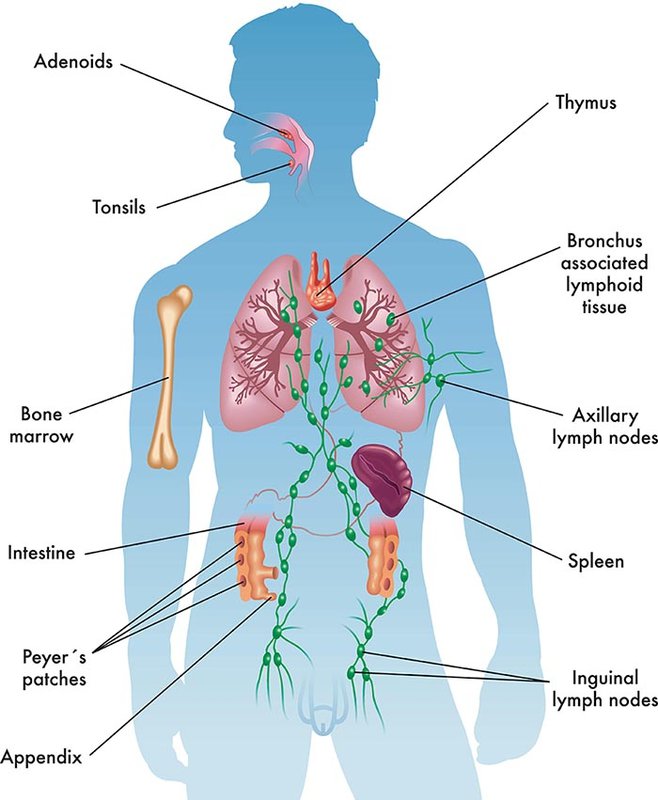
The lymphatic system is a complex network of tissues, vessels, and organs that plays a critical role in maintaining the body’s immune system and defending against diseases.
This system is comprised of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic organs like the spleen and thymus, and white blood cells. Its primary function is to transport lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells and waste products, from the tissues and organs back to the bloodstream.
The lymphatic system is an essential component of the body’s immune defense mechanism. It helps to identify and eliminate foreign substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells, that could potentially harm the body.
The system also plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance and preventing edema by returning excess fluid from the tissues back to the bloodstream. Despite its critical role in the body, the lymphatic system is often overlooked and not well understood by many people.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the lymphatic system, its functions, and its significance in disease prevention and immunity.
Key Takeaways
- The lymphatic system defends against diseases and maintains fluid balance in the body.
- It is comprised of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic organs, and white blood cells.
- The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in supporting the immune response.
- Disorders of the lymphatic system, such as lymphedema and lymphoma, can significantly impact overall health and require proper treatment and management.
Anatomy of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels, lymph nodes, and organs that work together to transport lymphatic fluid, filter it for pathogens, and return it to the bloodstream.
The lymphatic vessels are a one-way system that carries lymph from the tissues towards the heart. The lymphatic system is closely connected to the circulatory system, as the lymphatic vessels eventually empty into the veins near the heart.
The lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures located along the lymphatic vessels. They act as filters, trapping and destroying pathogens and other harmful substances that are carried in the lymphatic fluid.
The lymph nodes also contain immune cells, such as lymphocytes, which help to fight off infections. The lymphatic organs, such as the thymus, spleen, and tonsils, also play a role in the immune system by producing and storing immune cells.
Together, the lymphatic system works to defend the body against diseases and infections.
Functions of the Lymphatic System
One of the major roles of the lymphatic vessels is to transport excess fluid and proteins from the interstitial spaces back to the bloodstream. This process is essential for maintaining fluid balance in the body and preventing swelling or edema.
The lymphatic vessels also play an important role in the immune system by carrying lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, to sites of infection or inflammation.
The functions of the lymphatic system can be summarized as follows:
- Drainage of excess fluid and proteins from tissues
- Transportation of lymphocytes to sites of infection or inflammation
- Absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the digestive system
- Removal of cellular waste and debris from tissues
Overall, the lymphatic system is a crucial component of the body’s defense against disease and plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s fluid balance and overall health.
Lymphatic Vessels and Nodes
Transportation of lymphocytes and the removal of waste from tissues are facilitated by a network of vessels and nodes that make up a crucial part of the body’s fluid balance and overall health.
Lymphatic vessels are thin-walled tubes that originate in the interstitial fluid surrounding tissues and organs and converge into larger lymphatic trunks. These trunks ultimately lead to two main lymphatic ducts, which empty into the bloodstream. The lymphatic vessels are lined with endothelial cells and are equipped with one-way valves that prevent backflow of lymph and promote the movement of lymph towards the ducts.
Lymph nodes are small, round or bean-shaped structures that are distributed throughout the body and are critical components of the immune system. Lymph nodes act as filters that trap foreign substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells, while allowing the lymphocytes to mount an immune response to these invaders.
Lymph nodes are connected to the lymphatic vessels and are organized into clusters that are concentrated in areas such as the neck, armpits, groin, and abdomen. The lymphocytes that are produced in the bone marrow and thymus migrate to the lymph nodes, where they mature and multiply. The lymph nodes also contain specialized cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that help to eliminate pathogens and activate the immune response.
Lymphatic Organs: Spleen and Thymus
The spleen and thymus are two important organs that are involved in the maturation and activation of immune cells. The spleen is a large organ located in the upper left side of the abdomen, and it is responsible for filtering blood and removing old or damaged red blood cells, as well as producing and storing white blood cells. The spleen also plays a crucial role in the immune system by producing antibodies and activating immune cells to fight against infections. Additionally, the spleen can store blood in case of an emergency, such as a sudden loss of blood.
The thymus, on the other hand, is a small gland located in the chest behind the sternum. It is responsible for the development and maturation of T cells, a type of white blood cell that helps fight infections and cancer cells. The thymus is most active during childhood and adolescence, and it gradually decreases in size and function as we age. Despite this, it still plays an important role in the immune system throughout our lives.
The spleen and thymus work together to produce and activate immune cells, making them essential organs in the body’s ability to defend against disease.
White Blood Cells and Immune System Components
White blood cells and other components of the immune system play a crucial role in identifying and eliminating harmful pathogens in the body. These cells are produced in bone marrow and are transported throughout the body via the lymphatic vessels.
There are several types of white blood cells, including lymphocytes, neutrophils, and monocytes, each with specific functions in the immune system. Lymphocytes are responsible for recognizing and attacking specific pathogens, while neutrophils and monocytes are involved in the process of phagocytosis, where they engulf and digest harmful microorganisms.
In addition to white blood cells, the immune system also includes other components such as antibodies, cytokines, and complement proteins. Antibodies are proteins produced by lymphocytes that specifically target and neutralize pathogens. Cytokines are signaling molecules that regulate the immune response, while complement proteins help to destroy pathogens by breaking down their cell walls.
These components work together to mount an effective immune response against invading pathogens, ultimately protecting the body from disease.
Lymphatic System and Disease Prevention
Antibodies and complement proteins work in tandem to neutralize and destroy pathogens, preventing the spread of disease throughout the body. The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in supporting this process.
The lymphatic vessels and nodes act as a filtering system, capturing and removing harmful substances, including pathogens and cancer cells, from the body. The lymph nodes contain specialized immune cells, including B cells, T cells, and macrophages, which work together to identify and eliminate foreign invaders.
Furthermore, the lymphatic system is responsible for producing and transporting lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell that plays a vital role in the body’s immune response. These lymphocytes can recognize and remember specific pathogens, allowing the body to mount a quicker and more effective defense against future infections.
In addition, the lymphatic system also helps to regulate fluid balance in the body, preventing the buildup of excess fluids that can lead to swelling and inflammation. Overall, the lymphatic system plays a critical role in the body’s defense against disease, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy immune system.
Disorders of the Lymphatic System
Disorders of the lymphatic system can cause significant physical and emotional distress for individuals affected by them. One common disorder is lymphedema, which occurs when the lymphatic system is unable to properly drain excess fluid from the tissues, resulting in swelling and discomfort. This can happen due to a variety of reasons, including genetic factors, injury, or infection. Lymphedema can affect any part of the body, but is most commonly seen in the arms or legs. While there is currently no cure for lymphedema, treatments such as compression garments and massage therapy can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for those affected.
Another disorder of the lymphatic system is lymphoma, which is a type of cancer that affects the lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. Lymphoma can originate in the lymphatic system itself or can spread to the lymph nodes from other areas of the body. There are two main types of lymphoma: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Symptoms of lymphoma can include swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Treatment options may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of both, depending on the type and stage of the cancer. While lymphoma can be a serious and potentially life-threatening condition, early detection and treatment can greatly improve outcomes for patients.
| Lymphedema | Lymphoma |
|---|---|
| Swelling and discomfort | Swollen lymph nodes |
| Can affect any part of the body | Can originate in the lymphatic system or spread from other areas of the body |
| Compression garments and massage therapy can help manage symptoms | Treatment options may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of both |
Maintaining a Healthy Lymphatic System
Disorders of the lymphatic system can significantly impact the body’s overall health and ability to fight off disease. Therefore, maintaining a healthy lymphatic system is crucial for optimal immune function. In this section, we will explore some of the ways to keep the lymphatic system healthy and functioning optimally.
Firstly, maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help keep the lymphatic system healthy. Excess weight can put pressure on the lymphatic system, leading to lymphatic dysfunction and a weakened immune response.
Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water can help keep the lymphatic system functioning properly, as it relies on water to transport lymphatic fluid throughout the body.
Other ways to promote lymphatic health include getting enough rest, minimizing stress, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
By adopting these healthy habits, individuals can support their lymphatic system and overall immune function, leading to improved health and wellness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the lymphatic system is a crucial component of the body’s immune system. Its function is to remove waste and excess fluids from the body, as well as to fight off infections and diseases. The system is made up of lymphatic vessels, nodes, and organs, each playing a unique role in maintaining a healthy immune system.
White blood cells, such as lymphocytes, are also essential components of the lymphatic system, as they help to identify and destroy harmful pathogens.
While the lymphatic system is critical to our overall health, disorders of the system can occur, leading to various conditions such as lymphedema and lymphoma.
It is essential to maintain a healthy lymphatic system by eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding harmful toxins.
Overall, understanding the lymphatic system’s anatomy and functions can help individuals take the necessary steps to maintain a healthy immune system and prevent disease.