What Is The Lymphatic System? Immunity And Lymph Nodes
The lymphatic system is a crucial part of the human body’s immune system, responsible for filtering and removing waste products and pathogens from the body. It is a complex network of vessels and organs that work together to maintain the body’s fluid balance and protect it from infections and diseases.
Understanding the lymphatic system and its functions is important for maintaining overall health and preventing illnesses.
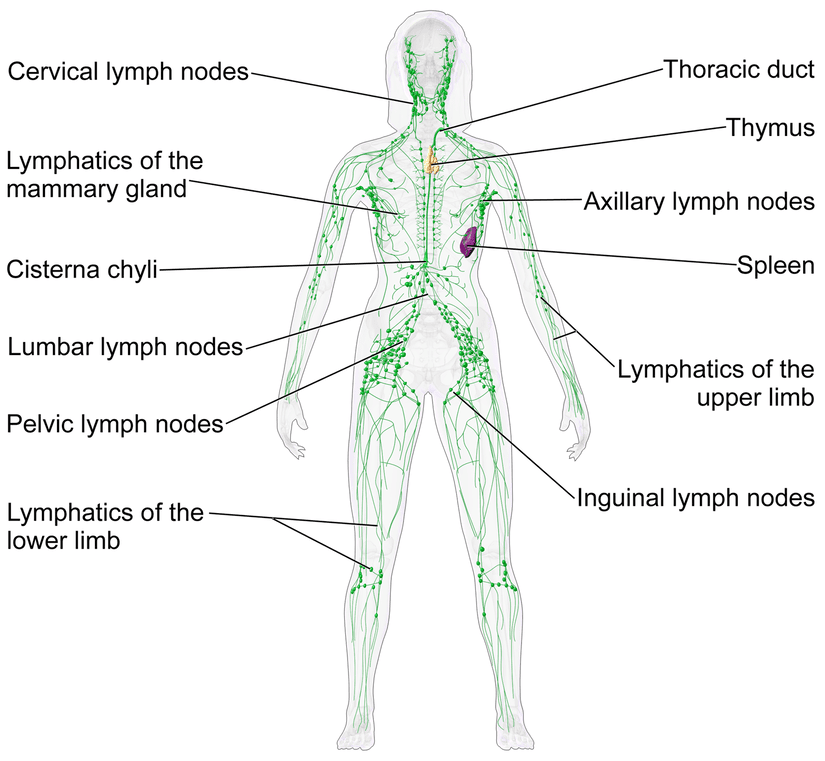
The lymphatic system consists of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and other lymphoid organs, including the spleen and thymus.
The lymphatic vessels are a network of thin tubes that run throughout the body, carrying lymphatic fluid, which is a clear, colorless fluid that contains immune cells and other substances.
The lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that act as filters, trapping and destroying harmful substances, such as bacteria and viruses.
Together, the lymphatic system plays a critical role in supporting the immune system and keeping the body healthy.
Key Takeaways
- The lymphatic system is a crucial part of the immune system that filters and removes waste products and pathogens from the body.
- It consists of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and other lymphoid organs that carry lymphatic fluid and activate immune response to help eliminate pathogens.
- A compromised lymphatic system can lead to infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancer, as well as malabsorption and nutrient deficiencies.
- Regular physical activity and a balanced diet that is rich in whole and nutrient-dense foods can help ensure optimal lymphatic function and reduce the risk of lymphedema.
What is the lymphatic system? An Overview
The lymphatic system is a network of vessels, tissues, and organs that plays a crucial role in immune function, fluid balance, and lipid absorption. Unlike the cardiovascular system, which has a central pump (the heart), the lymphatic system relies on the contraction of smooth muscles in the walls of lymphatic vessels to move lymph fluid throughout the body.
Lymph is a clear fluid that contains white blood cells, including lymphocytes, which are key players in the immune response, as well as proteins and waste products.
The lymphatic system is comprised of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic organs (such as the spleen, thymus, and tonsils), and lymphatic tissues (such as the adenoids and Peyer’s patches in the small intestine). Lymphatic vessels are similar to veins in structure, but have thinner walls and more valves to prevent backflow.
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph and trap foreign particles, such as bacteria and viruses, as well as cancer cells. When lymphatic vessels and nodes become infected or inflamed, they can cause swelling and tenderness, known as lymphedema.
Understanding the function and structure of the lymphatic system is key to understanding how the immune system works and how diseases can affect the body.
The Role of Lymph Nodes in the Immune System
Crucial components of our body’s defense mechanism, small structures found throughout our body selectively filter out harmful substances and alert our immune system to potential threats. These structures are called lymph nodes and are part of the lymphatic system.
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that are strategically located throughout the body. They act as filters for the lymph fluid that flows through them, trapping foreign substances such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells. Once trapped, these harmful substances are removed by immune cells, such as lymphocytes, that reside within the lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes also play a critical role in activating the immune response. When foreign substances are detected in the lymph fluid, the immune cells within the lymph nodes work together to mount an effective defense against the invading pathogen. This process involves the production and release of antibodies, which identify and neutralize the harmful substances, and the activation of other immune cells that help to destroy the pathogen.
Without lymph nodes, our immune system would not be able to effectively identify and eliminate foreign invaders, leaving us vulnerable to infection and disease. Lymph nodes are an essential component of the immune system. They act as a filter for harmful substances, remove them from the body, and activate the immune response to help eliminate pathogens.
Understanding the role of lymph nodes in the immune system is crucial for developing effective treatments for diseases that affect the lymphatic system, such as lymphoma and leukemia.
Lymphatic Fluid and Its Functions
An often-overlooked component of our body’s defense mechanism is the clear fluid that circulates throughout our tissues and organs, carrying essential nutrients and immune cells to where they are needed most. This fluid is called lymphatic fluid, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s immunity.
Lymphatic fluid is generated from the interstitial fluid that surrounds cells and tissues, and it is collected by the lymphatic vessels. The lymphatic vessels transport the fluid to the lymph nodes, where it is filtered and purified before being returned to the bloodstream.
The lymphatic system performs several functions that are essential for maintaining the body’s health and immunity. Here are three important roles that lymphatic fluid plays in the body:
- Lymphatic fluid carries immune cells: Lymphatic fluid contains white blood cells, which are the cells that play a crucial role in fighting infections and diseases. These cells circulate through the lymphatic system, and they are transported to the lymph nodes for filtering and purification. Once purified, the immune cells are returned to the bloodstream to help fight off infections and diseases.
- Lymphatic fluid removes waste: Lymphatic fluid also collects waste products and cellular debris that are produced by the body. These waste products are transported to the lymph nodes, where they are filtered out and eliminated from the body.
- Lymphatic fluid maintains fluid balance: Finally, lymphatic fluid helps to maintain the body’s fluid balance. By collecting excess fluid from tissues and organs, the lymphatic system prevents the buildup of fluid that can lead to swelling and edema. This function is particularly important in the legs, where the lymphatic system plays a crucial role in preventing fluid buildup and maintaining healthy circulation.
Lymphatic System Disorders and Treatment Options
Disorders of the lymphatic system can have a significant impact on an individual’s overall health and well-being, causing discomfort and limiting mobility. Some of the common lymphatic system disorders include lymphedema, lymphoma, and infectious diseases. Lymphedema is a condition where there is a blockage in the lymphatic vessels leading to the accumulation of lymphatic fluid in the tissues, causing swelling, pain, and stiffness. This condition can be congenital or acquired, and it is often associated with cancer treatment. Lymphoma is a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system and can spread to other parts of the body. It can cause symptoms such as swollen lymph nodes, fever, fatigue, and weight loss. Infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, HIV, and syphilis can also affect the lymphatic system and cause inflammation and damage to the lymph nodes.
The treatment options for lymphatic system disorders depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Lymphedema can be managed through a combination of therapies such as compression garments, exercises, and manual lymphatic drainage. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove the blockage or damaged tissue. Lymphoma is often treated with chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of both. Infectious diseases are typically treated with antibiotics or antiviral medications. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms associated with lymphatic system disorders, as early detection and treatment can improve the outcome and prevent complications.
| Disorder | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Lymphedema | Swelling, pain, stiffness | Compression garments, exercises, manual lymphatic drainage, surgery |
| Lymphoma | Swollen lymph nodes, fever, fatigue, weight loss | Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, combination therapy |
| Infectious diseases | Inflammation, damage to lymph nodes | Antibiotics, antiviral medications |
The table above shows some of the common lymphatic system disorders, their symptoms, and treatment options. It highlights the importance of seeking medical attention and the different approaches to managing these conditions. By understanding the different disorders that can affect the lymphatic system and the available treatment options, individuals can take steps to maintain their overall health and well-being.
How the Lymphatic System Affects Overall Health
The proper functioning of the lymphatic system is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing various health complications. This network of vessels and organs works together to remove excess fluids, waste products, and toxins from the body, while also playing a crucial role in the immune system.
Here are some ways in which the lymphatic system affects overall health:
- Immune response: The lymphatic system is closely connected to the immune system, which is responsible for defending the body against infections and diseases. Lymph nodes, for instance, contain immune cells that help identify and destroy pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses. When the lymphatic system is compromised, the body becomes more vulnerable to infections, autoimmune disorders, and even cancer.
- Fluid balance: The lymphatic system also plays a key role in regulating the fluid balance in the body. When the lymphatic system is functioning properly, it helps prevent the build-up of excess fluid, which can lead to swelling, edema, and other complications. However, when the lymphatic system is not functioning properly, this can result in lymphedema, a condition in which fluid accumulates in the tissues, causing swelling and discomfort.
- Nutrient absorption: The lymphatic system is involved in the absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the digestive system. These nutrients are transported through the lymphatic vessels and eventually enter the bloodstream, where they are used by the body for various functions. When the lymphatic system is compromised, this can lead to malabsorption and nutrient deficiencies.
- Waste removal: The lymphatic system also helps remove waste products and toxins from the body. This is particularly important for the proper functioning of the liver and kidneys, which rely on the lymphatic system to remove metabolic waste and other harmful substances. When the lymphatic system is compromised, this can lead to the accumulation of toxins in the body, which can cause a range of health problems.
Overall, the lymphatic system is a crucial component of the body’s overall health and well-being. Maintaining a healthy lymphatic system is essential for preventing various health complications and promoting optimal health.
The Importance of Exercise for Lymphatic Health
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining the flow of lymphatic fluid throughout the body and preventing lymphatic congestion.
The lymphatic system relies on muscle contractions to move lymphatic fluid, which contains immune cells and waste products, through the vessels and towards the lymph nodes.
Exercise helps to stimulate these contractions and increase the flow of lymphatic fluid, which can improve immune function and reduce inflammation.
In addition to promoting lymphatic flow, exercise can also help to reduce the risk of lymphedema, a condition characterized by swelling in the limbs due to lymphatic blockage.
Studies have shown that exercise can improve lymphatic function and reduce the severity of lymphedema symptoms in individuals with breast cancer-related lymphedema.
However, it is important to note that individuals with lymphedema should consult with their healthcare provider before starting an exercise program, as certain types of exercise may exacerbate their symptoms.
Overall, regular exercise is an important component of maintaining lymphatic health and supporting immune function.
Nutrition and the Lymphatic System
Regular exercise has been shown to benefit our lymphatic system by improving its function and reducing the risk of lymphatic-related diseases. However, exercise is only one aspect of maintaining a healthy lymphatic system.
Nutrition also plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal lymphatic function. The lymphatic system relies on a variety of nutrients, such as vitamins C, E, and A, as well as zinc and selenium, to function properly. These nutrients help to support lymphocyte production, which are a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in our immune system.
Additionally, a diet that is high in fiber and low in processed foods can also benefit our lymphatic system by reducing inflammation and promoting healthy digestion. On the other hand, a diet that is high in saturated and trans fats, as well as sugar and salt, can have negative effects on lymphatic function and overall health.
Therefore, it is important to maintain a balanced diet that is rich in whole and nutrient-dense foods to support our lymphatic system. Overall, nutrition plays a crucial role in the function of our lymphatic system, and a balanced diet that is rich in nutrients and low in processed foods can help to ensure optimal lymphatic function and reduce the risk of lymphatic-related diseases.
By combining regular exercise and proper nutrition, we can take steps to support our lymphatic system and improve our overall health and wellbeing.
Future Research and Developments in Lymphatic System Science
Advancements in understanding the molecular mechanisms of lymphatic vessel development and function may lead to new therapeutic targets for lymphatic-related diseases. Recent research has shown that the lymphatic system plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis, immune surveillance, and immune response. The lymphatic vessels are responsible for the transport of interstitial fluid, lipids, and immune cells, and their dysfunction is associated with a range of diseases, including lymphedema, inflammation, and cancer.
To improve our understanding of the lymphatic system, researchers are investigating the molecular pathways involved in lymphatic vessel formation, migration, and maintenance. This has led to the identification of several key molecules, including VEGF-C and VEGF-D, which are involved in lymphatic sprouting and growth. Targeting these molecules, as well as others involved in lymphatic development and function, may lead to new therapies for lymphatic-related diseases.
Additionally, the development of new imaging techniques, such as lymphoscintigraphy and near-infrared fluorescence lymphatic imaging, is allowing for better visualization of lymphatic vessels and their function, which may aid in the diagnosis and treatment of lymphatic-related disorders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the lymphatic system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s immune system and overall health. This complex network of vessels, nodes, and organs works to filter and remove harmful substances from the body, while also aiding in the circulation of fluids and nutrients. Lymphatic system disorders can have serious consequences, including lymphedema, infections, and cancer. Therefore, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, to support optimal lymphatic function.
Advancements in research and technology have led to new treatments and therapies for lymphatic system disorders, offering hope for those affected by these conditions. As scientists continue to uncover the mysteries of the lymphatic system, we can expect to see further breakthroughs in understanding and treating these complex disorders.
With proper care and attention, we can support the health of our lymphatic system and ensure its vital role in maintaining overall wellness.