What Is The Role Of Sleep Studies In Diagnosing Sleep Apnea?

Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep. It can lead to various health issues, including daytime sleepiness, high blood pressure, and heart problems.
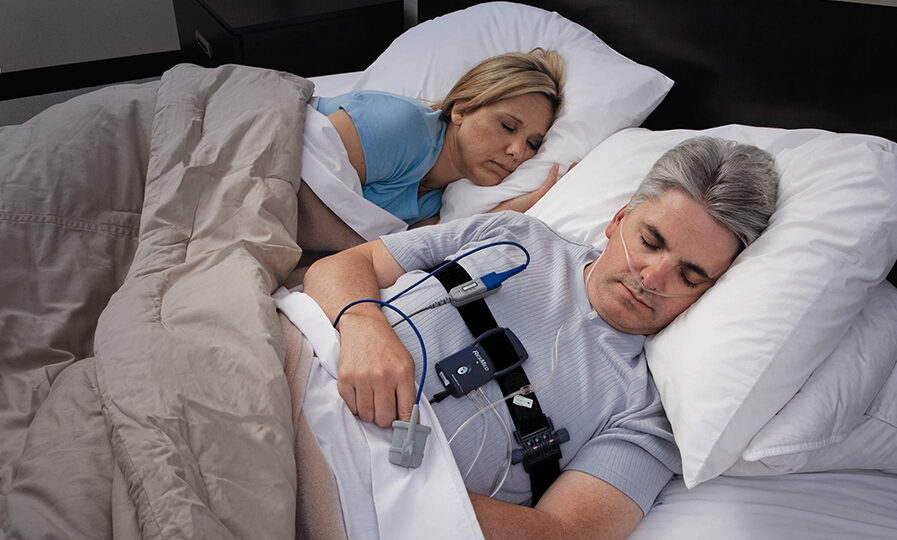
To diagnose sleep apnea accurately, sleep studies play a crucial role. Sleep studies, also known as polysomnography, involve monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep, such as brain waves, eye movements, heart rate, and oxygen levels. These studies help in identifying the presence and severity of sleep apnea.
There are different types of sleep studies, including in-lab studies and home sleep tests, each offering unique advantages and limitations. Interpreting the results of sleep studies requires expertise, and collaboration with healthcare professionals is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Sleep studies not only aid in the initial diagnosis but also play a significant role in the long-term management of sleep apnea by assessing treatment effectiveness. Understanding the role of sleep studies is vital for healthcare practitioners to provide appropriate care for individuals with sleep apnea.
Key Takeaways
- Sleep studies, also known as polysomnography, are crucial for accurately diagnosing sleep apnea.
- Sleep studies help in identifying the presence and severity of sleep apnea.
- Sleep studies provide objective measurements and data for accurate diagnosis and assessment of sleep apnea.
- Sleep studies assist in developing appropriate treatment plans tailored to each patient’s specific needs.
Understanding Sleep Apnea
The understanding of sleep apnea can be enhanced through the utilization of sleep studies, which provide objective measurements and data to accurately diagnose and assess the severity of the condition, ultimately leading to effective treatment interventions and improving the overall quality of life for individuals affected by this potentially life-threatening sleep disorder.
Sleep apnea is characterized by repeated episodes of partial or complete cessation of breathing during sleep, resulting in disrupted sleep patterns and decreased oxygen levels in the body.
Sleep studies, also known as polysomnography, involve monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep, including brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, and oxygen levels. These studies provide valuable information about the frequency and duration of apnea events, as well as the associated changes in oxygen levels and sleep architecture.
By analyzing the data obtained from sleep studies, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose sleep apnea, determine its severity, and tailor appropriate treatment strategies, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy or oral appliances, to alleviate symptoms and improve sleep quality.
Importance of Sleep Studies
Importantly, the use of specialized tests allows for a comprehensive evaluation of the breathing patterns during sleep, aiding in the accurate identification of potential respiratory disorders.
Sleep studies, also known as polysomnography, play a crucial role in diagnosing sleep apnea. These studies involve monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep, such as brain waves, eye movements, muscle activity, and breathing patterns.
Through the use of sensors and electrodes, sleep studies provide valuable information about the frequency and severity of apnea episodes, as well as other associated abnormalities like oxygen desaturation and disrupted sleep architecture.
Sleep studies help differentiate between obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea (CSA), and complex sleep apnea syndrome (combination of OSA and CSA).
The data obtained from sleep studies assist physicians in developing appropriate treatment plans tailored to each patient’s specific needs.
Overall, sleep studies are an essential tool in accurately diagnosing and managing sleep apnea.
Identifying Sleep Apnea Through Sleep Studies
Sleep studies, known as polysomnography, provide a comprehensive evaluation of breathing patterns during sleep, aiding in the accurate identification of potential respiratory disorders. These studies are essential in diagnosing sleep apnea, a common and potentially serious sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep.
By monitoring various physiological parameters such as brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, oxygen levels, and muscle activity, sleep studies can help identify the presence and severity of sleep apnea.
The information gathered from sleep studies allows healthcare professionals to determine the appropriate treatment options for individuals suffering from sleep apnea. Some of the key findings that sleep studies can reveal include the frequency and duration of breathing disruptions, the level of oxygen saturation in the blood, and the presence of abnormal sleep patterns.
Different Types of Sleep Studies
Polysomnography, also known as sleep studies, can be classified into different types, each focusing on specific aspects of sleep and respiratory patterns.
The most common type is the overnight polysomnography, which assesses various sleep parameters, including brain waves, eye movements, muscle activity, and heart rate. This type of study is considered the gold standard for diagnosing sleep apnea as it allows for the detection of apneas, hypopneas, and other abnormalities that occur during sleep.
Another type of sleep study is the split-night polysomnography, which combines diagnostic and titration components. This study is typically performed when an initial diagnosis of sleep apnea is suspected, allowing for the adjustment of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy during the same night.
Multiple sleep latency testing is another type of sleep study that evaluates daytime sleepiness and assesses the presence of other sleep disorders.
Overall, the different types of sleep studies play a crucial role in diagnosing sleep apnea by providing comprehensive information about sleep patterns and respiratory abnormalities.
Interpreting Sleep Study Results
The interpretation of sleep study results is crucial for understanding the severity and impact of sleep disorders on an individual’s overall health and well-being.
Sleep studies, which involve monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep, provide valuable information that can help diagnose and classify sleep apnea.
The results of these studies are typically analyzed by sleep specialists, who use standardized scoring systems to assess the frequency and severity of respiratory events, such as apneas and hypopneas.
They also evaluate other factors, such as sleep architecture, oxygen saturation levels, and arousals from sleep.
The interpretation of these results allows for the identification of the type of sleep apnea (obstructive, central, or mixed) and the determination of its severity.
This information is crucial for developing an appropriate treatment plan and monitoring the effectiveness of interventions aimed at improving sleep quality and reducing the associated health risks.
Collaborating with Healthcare Professionals
Consulting with a sleep specialist is crucial in the management of sleep apnea. They have specialized knowledge and expertise in diagnosing and treating sleep disorders. Collaborating with a sleep specialist allows for the development of a personalized treatment plan, tailored to the individual needs of the patient.
Regular monitoring of progress and adjusting treatment as necessary ensures optimal outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals with sleep apnea.
Importance of Consulting with a Sleep Specialist
To ensure accurate and thorough diagnosis of sleep apnea, it is crucial to seek guidance from a qualified sleep specialist. Sleep specialists are healthcare professionals who specialize in diagnosing and treating sleep disorders, including sleep apnea. They have extensive knowledge and experience in conducting sleep studies, which are essential in diagnosing sleep apnea.
Sleep studies, also known as polysomnography, involve monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep, such as brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, and breathing patterns. These studies are typically conducted in a sleep laboratory or sometimes even in the comfort of the patient’s home using portable monitoring devices. The data collected during sleep studies provides valuable insights into the quality and quantity of sleep, as well as any abnormalities or disruptions that may indicate the presence of sleep apnea.
Consulting with a sleep specialist is important because they can interpret the sleep study results accurately and determine the appropriate course of action for diagnosis and treatment. They can recommend further tests, such as a multiple sleep latency test or a maintenance of wakefulness test, to assess daytime sleepiness and evaluate the severity of sleep apnea. Additionally, sleep specialists can provide guidance on lifestyle modifications, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, oral appliances, or surgical interventions, depending on the severity of the condition.
Consulting with a sleep specialist is the key to ensuring a comprehensive and individualized approach to diagnosing and managing sleep apnea. Their expertise and specialized knowledge in sleep medicine enable them to provide the most effective and appropriate care for individuals with sleep apnea.
| Parameter | Description | Importance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain activity | Measures electrical activity of the brain during sleep | Helps identify sleep stages and detect abnormal patterns | ||||
| Eye movements | Tracks eye movements during sleep | Assists in identifying rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and sleep disorders | ||||
| Heart rate | Monitors heart rate and rhythm during sleep | Detects irregularities that may be related to sleep apnea | ||||
| Breathing patterns | Records respiratory effort and airflow during sleep | Allows identification of abnormal breathing patterns | ||||
| Oxygen saturation | Measures the level of oxygen in the blood during sleep | Helps determine if there are oxygen desaturation events | Heart rate variability | Measures the changes in time intervals between heartbeats during sleep | Provides information about the autonomic nervous system and overall cardiovascular health | |
| Snoring | Monitors the intensity and frequency of snoring sounds during sleep | Helps identify potential sleep apnea and other breathing disorders | ||||
| Body position | Tracks the body position changes during sleep | Helps determine if certain positions contribute to breathing difficulties | ||||
| Sleep stages | Records brain wave activity and eye movements during sleep | Allows assessment of sleep quality and identification of sleep disorders | ||||
| Sleep efficiency | Calculates the percentage of time spent asleep compared to total time in bed | Provides information on sleep fragmentation and overall sleep efficiency | ||||
| Sleep arousals | Detects brief awakenings or shifts in sleep during the night | Helps identify sleep disturbances and disruptions in sleep continuity | ||||
| Sleep latency | Measures the time it takes to fall asleep after lights out | Provides insight into sleep onset difficulties and potential sleep disorders | ||||
| REM sleep behavior disorder | Monitors muscle activity during REM sleep | Helps diagnose and manage REM sleep behavior disorder | ||||
| Respiratory effort-related arousal | Measures changes in breathing effort during sleep | Helps identify respiratory-related sleep disorders | ||||
| Nocturnal seizures | Records brain activity during sleep to detect epileptic activity | Helps diagnose and manage nocturnal seizures and epilepsy | ||||
| Periodic limb movements | Tracks leg movements during sleep | Allows identification and management of periodic limb movement disorder | ||||
| Sleep apnea | Monitors breathing effort and airflow to detect pauses in breathing during sleep | Helps diagnose and manage sleep apnea and other breathing disorders |
Developing a Treatment Plan
Developing an effective treatment plan for individuals with sleep apnea involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s sleep study results and personalized recommendations from a qualified sleep specialist. By analyzing the data obtained from sleep studies, such as polysomnography and home sleep apnea tests, sleep specialists can determine the severity and specific characteristics of a patient’s sleep apnea. This information is crucial for tailoring the treatment plan to the individual’s needs.
The treatment plan may include a combination of non-invasive therapies, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) or oral appliances, as well as lifestyle modifications. Additionally, sleep specialists may recommend weight loss programs, positional therapy, or surgery in severe cases.
Regular follow-up appointments with the sleep specialist are also essential to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment plan and make necessary adjustments.
- Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy
- Oral appliance therapy
- Lifestyle modifications
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Treatment
Monitoring progress and adjusting treatment is an integral part of managing sleep apnea, as it allows healthcare professionals to assess the effectiveness of the chosen therapy and make necessary modifications to optimize patient outcomes.
Regular follow-up appointments and objective measurements are crucial in tracking the progress of patients with sleep apnea.
One commonly used tool in monitoring treatment efficacy is the use of sleep studies. These studies, such as polysomnography or home sleep apnea testing, can provide objective data on the patient’s sleep patterns, respiratory events, and oxygen levels.
By analyzing these data, healthcare professionals can determine if the treatment is effectively reducing the frequency and severity of sleep apnea episodes. If necessary, adjustments can be made to the treatment plan, such as changing the type or pressure of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Overall, monitoring progress and adjusting treatment based on objective data obtained from sleep studies is essential in effectively managing sleep apnea.
Treatment Options for Sleep Apnea
This discussion will focus on the treatment options for sleep apnea.
The three main treatment options are Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy, oral appliances, and surgery.
CPAP therapy involves the use of a machine that delivers a steady stream of air pressure to keep the airway open during sleep.
Oral appliances are custom-made devices that help to reposition the jaw and tongue to improve airflow.
Surgery may be an option for individuals with severe sleep apnea. It can involve various procedures to remove or modify the tissues that are obstructing the airway.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy involves the use of a pressurized air machine to deliver a steady stream of air into the patient’s airway, thereby maintaining an open and unobstructed airway during sleep.
This therapy is considered the gold standard treatment for moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
The CPAP machine consists of a mask that covers the nose or both the nose and mouth, and a motor that generates the necessary air pressure.
The mask is secured over the patient’s face, creating a seal to prevent air leakage.
The pressurized air from the machine is delivered through the mask, keeping the airway open and preventing the collapse of the upper airway.
CPAP therapy has been shown to significantly improve symptoms of sleep apnea, such as excessive daytime sleepiness and snoring, and it also reduces the risk of associated health complications, including cardiovascular disease.
Compliance with CPAP therapy is essential for its effectiveness, and regular follow-up with healthcare professionals is recommended to ensure proper usage and adjustment of the machine settings.
Oral Appliances
Oral appliances are a non-invasive treatment option for moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea that can help maintain an open airway during sleep. These appliances, also known as mandibular advancement devices (MADs) or mandibular repositioning devices (MRDs), are custom-made and fitted by dentists. They work by positioning the lower jaw slightly forward, which helps to prevent the collapse of the soft tissues and maintain the patency of the upper airway.
The effectiveness of oral appliances in treating sleep apnea varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual patient’s response. While they may not be as effective as Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy, oral appliances offer a more comfortable alternative for some patients who cannot tolerate or refuse CPAP treatment.
Regular follow-up visits with the dentist are necessary to monitor the efficacy and fit of the appliance and make any necessary adjustments.
Surgery
Surgery is a potential treatment option for individuals with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea who do not respond well to other non-invasive interventions. It aims to alleviate the underlying anatomical factors contributing to the condition, such as excessive soft tissue or structural abnormalities in the upper airway.
There are several surgical procedures available, including:
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): This procedure involves removing excess tissue from the throat, such as the uvula and part of the soft palate, to widen the airway.
- Genioglossus advancement: This surgery advances the tongue muscles forward to prevent them from obstructing the airway during sleep.
- Maxillomandibular advancement: In this procedure, the upper and lower jawbones are surgically moved forward to enlarge the airway and improve breathing during sleep.
These procedures can help widen the airway, remove excess tissue, or reposition the jaw to improve airflow during sleep. However, it is important to note that surgery is typically considered a last resort due to its invasiveness and potential risks. It is usually recommended after a thorough evaluation of the individual’s specific condition and a lack of response to other treatment options.
Additionally, surgery may not completely cure sleep apnea and may require ongoing management and follow-up care.
Importance of Sleep Studies in Long-Term Management
Sleep studies play a vital role in the comprehensive and long-term management of sleep apnea by providing objective data on the severity of the condition and guiding the development of appropriate treatment plans.
These studies, also known as polysomnography, involve monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep, including brain activity, heart rate, breathing patterns, and oxygen levels. By collecting this data, sleep studies can accurately diagnose sleep apnea and determine its severity.
This information is crucial in tailoring individualized treatment plans, as different patients may require different interventions based on the severity of their sleep apnea.
Sleep studies also allow healthcare professionals to monitor the effectiveness of treatment interventions over time and make necessary adjustments as needed.
Overall, sleep studies are essential in the long-term management of sleep apnea, ensuring that patients receive the appropriate care and support to improve their sleep quality and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How common is sleep apnea among the general population?
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder among the general population. Its prevalence varies depending on the population studied, but it is estimated that around 20% of adults worldwide may have some form of sleep apnea.
Can sleep apnea be diagnosed without undergoing a sleep study?
Sleep apnea cannot be definitively diagnosed without undergoing a sleep study. Sleep studies are essential in assessing the severity of sleep apnea and determining the appropriate treatment options for individuals with this condition.
Are there any risks or side effects associated with undergoing a sleep study?
There may be some risks and side effects associated with undergoing a sleep study, such as discomfort from the equipment, difficulty falling asleep, or feeling tired the next day. However, these risks are generally minimal and temporary.
Can sleep apnea be cured or only managed through treatment options?
Sleep apnea can be managed through various treatment options such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, oral appliances, and lifestyle changes. However, there is currently no known cure for sleep apnea.
How long does it typically take to receive the results of a sleep study?
The typical timeframe for receiving results from a sleep study varies, but it generally takes around 1-2 weeks. However, the specific duration may depend on factors such as the type of sleep study conducted and the workload of the sleep study facility.