What Is The Sensory System? Exploring Vision, Hearing, And Touch
The sensory system is a complex network of organs and nerve pathways that enables us to perceive and interpret the world around us. It is responsible for relaying information about our environment to the brain, allowing us to see, hear, touch, taste, and smell. The sensory system is a critical component of our daily lives, allowing us to navigate our surroundings and interact with others.
Understanding the sensory system is essential for comprehending how we experience the world. This article will explore the basics of the sensory system, including its anatomy and function.
Specifically, we will delve into three of the most important senses – vision, hearing, and touch – and examine how they operate. We will also discuss the process of sensory integration, which describes how the brain processes and integrates information from multiple sensory systems.
Finally, we will examine common sensory disorders and impairments and explore ways to enhance our sensory experiences.
Key Takeaways
- The sensory system is responsible for relaying information about our environment to the brain through specialized organs and nerve pathways.
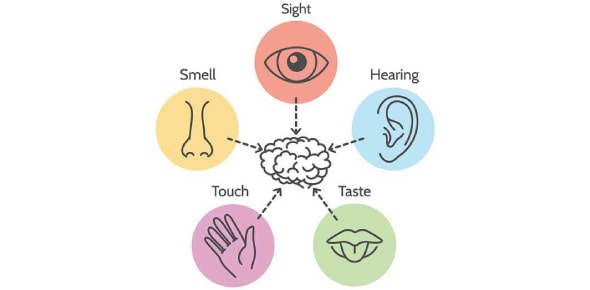
- It is composed of five senses: sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell, each specialized to detect specific types of stimuli.
- Sensory integration, selective attention, and perceptual grouping are important processes that contribute to our ability to interpret sensory input.
- Sensory disorders and impairments can significantly affect an individual’s ability to process and interpret sensory information, but enhancing sensory experiences can be achieved through various means such as sensory therapies and assistive devices.
The Basics of the Sensory System
An understanding of the basics of the sensory system is essential in comprehending how we perceive the world around us through our senses of vision, hearing, and touch.
The sensory system is a complex network of nerves, cells, and organs that work together to process external stimuli and transmit that information to the brain.
The system is comprised of five senses: sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell.
Each sense is specialized to detect specific types of stimuli.
Vision, for example, is our ability to detect light and process it into images.
Hearing, on the other hand, allows us to detect sound waves and interpret them as speech, music, or other auditory information.
Touch is our ability to detect pressure, temperature, and pain, and to perceive textures and shapes.
Understanding the basics of each sense will provide a foundation for comprehending how we experience the world through our senses.
The Anatomy of the Sensory System
The intricate structures and specialized cells that make up the pathways for receiving and processing sensory information are essential components of the human body. These structures and cells are distributed throughout the body, with some concentrated in specific sensory organs.
The sensory system is composed of the peripheral nervous system, which includes sensory receptors and neurons, and the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord.
The sensory system is responsible for receiving information from the environment and transmitting it to the brain for processing. The anatomy of the sensory system varies depending on the type of sensory information being processed.
For example, the anatomy of the visual system includes the eyes, optic nerves, and visual cortex, while the anatomy of the auditory system includes the ears, auditory nerves, and auditory cortex.
Despite these differences, however, there are some common features in the anatomy of the sensory system that contribute to its effectiveness, such as the ability to filter out irrelevant information and the ability to process multiple sensory inputs simultaneously.
Vision: How Our Eyes See the World
One of the most fascinating aspects of human perception is the way our eyes take in information from the world around us. Vision is the most important sense for humans, as it allows us to perceive our surroundings, recognize faces, read, and perform countless other tasks.
Our eyes are complex organs that work together with different structures to capture light, transform it into electrical impulses, and send them to the brain for interpretation. The human eye has several key components, including the cornea, iris, lens, retina, and optic nerve.
The cornea and lens work together to focus incoming light onto the retina, which contains specialized cells called photoreceptors that convert light into electrical signals. These signals are then transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve, which allows us to see.
Despite the complexity of the visual system, our brains are able to process visual information quickly and efficiently, allowing us to make sense of the world around us.
Hearing: How Our Ears Interpret Sound
Our perception of sound is a complex process that involves the outer, middle, and inner ear working together to translate sound waves into electrical signals that the brain can interpret. The outer ear, which includes the visible part of the ear and the ear canal, collects sound waves and directs them towards the eardrum. The middle ear, which consists of the eardrum and three small bones called the ossicles, amplifies the sound waves and transmits them to the inner ear. The inner ear is where the actual translation of sound waves into electrical signals occurs, through the use of hair cells in the cochlea. These hair cells are sensitive to different frequencies of sound waves and convert their vibrations into electrical signals that are then sent to the brain via the auditory nerve.
To better understand how sound is perceived, a table can be used to illustrate the different parts of the ear and their functions. The table below includes the three main parts of the ear, their components, and their roles in the process of hearing.
| Part of Ear | Components | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Ear | Pinna, Ear Canal | Collects sound waves and directs them towards the eardrum |
| Middle Ear | Eardrum, Ossicles (Malleus, Incus, Stapes) | Amplifies sound waves and transmits them to the inner ear |
| Inner Ear | Cochlea, Hair Cells, Auditory Nerve | Translates sound waves into electrical signals that are sent to the brain for interpretation |
By breaking down the process of hearing into its individual components, we can gain a deeper understanding of how sound is interpreted by the brain. This knowledge can be useful in fields such as audiology, speech therapy, and hearing aid design.
Touch: How We Feel Different Textures and Temperatures
Perceiving tactile sensations like textures and temperatures is a complex process that involves different types of sensory receptors located in the skin. These receptors are called mechanoreceptors and thermoreceptors, respectively.
Mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical stimuli, such as pressure, stretching, and vibration, while thermoreceptors respond to changes in temperature. Together, these receptors allow us to feel a wide range of tactile sensations that help us explore and interact with the environment.
Mechanoreceptors are further classified into four types: Merkel cells, Meissner’s corpuscles, Ruffini endings, and Pacinian corpuscles. Each type of mechanoreceptor responds to different types of mechanical stimuli and is located in different layers of the skin.
For example, Merkel cells are located in the upper layers of the skin and respond to light pressure, while Pacinian corpuscles are located deeper in the skin and respond to deep pressure and vibration. Through these receptors, we are able to distinguish between different textures, such as the roughness of sandpaper or the smoothness of silk.
Overall, the sense of touch is essential for our daily lives, allowing us to perceive and respond to the world around us.
Sensory Integration: How Our Brain Processes Information
The complexity of sensory integration in the brain evokes a sense of wonder and amazement at how seamlessly our minds process information from multiple sources.
Our sensory system includes an intricate network of neurons, receptors, and pathways that work together to create a cohesive perception of the world around us.
Sensory integration refers to the brain’s ability to combine and interpret information from multiple sensory modalities, such as vision, hearing, touch, and smell, to create a unified experience.
To achieve this integration, the brain relies on several mechanisms, including selective attention, perceptual grouping, and multisensory integration.
Selective attention allows us to focus on specific stimuli while filtering out irrelevant information.
Perceptual grouping refers to the brain’s ability to organize sensory input into meaningful patterns and objects, such as recognizing a face or a melody.
Multisensory integration involves combining information from different sensory modalities to create a more complete and accurate perception of the environment. For example, the brain can combine visual and auditory cues to determine the location of a sound or a moving object.
Overall, the process of sensory integration is essential for our ability to navigate the world and interact with our environment.
Common Sensory Disorders and Impairments
Various sensory disorders and impairments can significantly affect an individual’s ability to process and interpret sensory information. These conditions can arise due to various factors such as genetic predisposition, brain injury, or developmental issues.
Some common sensory disorders include Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD), and Dyslexia.
ASD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects an individual’s social communication and interaction skills. Individuals with ASD may also experience sensory sensitivities, such as an aversion to loud noises, bright lights, or certain textures.
ADHD, on the other hand, affects an individual’s ability to focus and sustain attention. Children with ADHD may have difficulty sitting still, following instructions, or completing tasks.
SPD is a condition where an individual’s brain has difficulty processing and interpreting sensory information. Individuals with SPD may be oversensitive or undersensitive to certain sensory stimuli, such as touch, sound, or taste.
Finally, Dyslexia is a reading disorder that affects an individual’s ability to decode and process written language. It is often associated with difficulty processing auditory information, such as phonemes or syllables.
Enhancing Your Sensory Experiences
Improving our sensory experiences can greatly enhance our overall well-being and quality of life. Here are three ways to enhance your sensory experiences:
- Mindful Observation: One of the most effective ways to enhance your sensory experiences is to be mindful of your surroundings. This involves paying attention to the details of your environment and engaging all five senses. For example, when taking a walk, focus on the colors of the leaves, the sound of the birds chirping, the feel of the sun on your skin, the smell of the flowers, and the taste of the fresh air. By doing so, you can fully immerse yourself in the moment and appreciate the beauty of your surroundings.
- Sensory Stimulation: Another way to enhance your sensory experiences is to engage in activities that stimulate your senses. This can include listening to music, going to an art gallery, trying new foods, or even taking a hot bath with scented candles. By exposing yourself to new and different sensory experiences, you can expand your horizons and gain a greater appreciation for the world around you.
- Self-Care: Finally, taking care of your physical and mental health can also enhance your sensory experiences. Eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, practicing stress-reducing techniques, and staying physically active can all help to improve your overall well-being and make you more receptive to sensory experiences. By prioritizing self-care, you can create a more positive and enjoyable sensory experience for yourself and those around you.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the sensory system plays a crucial role in our daily lives by allowing us to perceive and interpret information from our surroundings. It is comprised of various organs, nerves, and neurons that work together to process sensory data.
Vision, hearing, and touch are three primary senses that enable us to see, hear, and feel the world around us. The brain plays a vital role in processing this information, integrating it, and producing an appropriate response.
Despite the importance of the sensory system, various disorders and impairments can affect it, leading to difficulties in perceiving and processing sensory information. However, there are ways to enhance our sensory experiences, such as through sensory stimulation therapy, mindfulness, and physical exercise.
Overall, understanding the sensory system can help us appreciate its complexity and the role it plays in our lives.