What Is The Sensory System? Perception And Sensory Integration
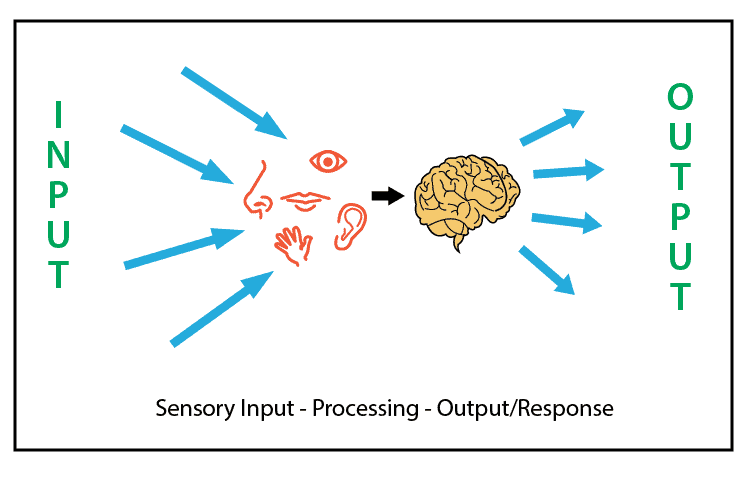
The sensory system is an essential aspect of our lives, responsible for how we perceive and interact with the world around us. It is a complex network of organs, nerves, and cells that work together to receive, process, and interpret sensory information from the environment. The sensory system is composed of five main senses, each with its unique set of receptors that allow us to experience the world in different ways.
Perception is the process by which we interpret sensory information, assigning meaning to the sensations we experience. Perception is a complex and multifaceted process that involves the integration of information from multiple sensory sources, as well as our prior knowledge and expectations.
Sensory processing disorders can disrupt this process, leading to challenges in perceiving and interpreting sensory information. Sensory integration is the process by which the brain brings together information from different senses to create a coherent picture of the world.
Understanding the sensory system and how it works can help us identify and address issues related to sensory processing and integration.
Key Takeaways
- The sensory system is responsible for how we perceive and interact with the world around us, and is composed of five main senses.
- Sensory integration is the process by which the brain combines information from different senses to create a coherent picture of the world, and can be enhanced through sensory integration therapy.
- Sensory processing disorders can disrupt the process of perceiving and interpreting sensory information, and seeking professional evaluation and support can often help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
- Dysfunction in sensory integration can lead to a range of developmental and behavioral problems, including sensory processing disorders, and difficulties with sensory processing can lead to developmental delays, learning difficulties, and behavioral issues.
An Overview of the Sensory System
The sensory system is a complex network of specialized cells and organs that work together to receive, process, and transmit sensory information from the environment to the brain.
The sensory system is responsible for detecting and responding to a wide range of stimuli such as light, sound, temperature, pressure, and chemicals.
The sensory system is composed of five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. Each sense has its own specialized organs and receptors that are designed to detect specific types of stimuli.
The sensory system is divided into two main parts: the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. The peripheral nervous system consists of all the sensory receptors and their associated nerves, while the central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord.
When a sensory receptor detects a stimulus, it sends a signal to the brain through the peripheral nervous system. The brain then processes the information and generates a response, which is sent back to the appropriate part of the body through the peripheral nervous system.
Sensory integration is the process by which the brain combines information from multiple senses to create a coherent picture of the world around us.
The Five Senses: How We Experience the World
When experiencing the world, humans rely on their five senses to gather information about their surroundings. These senses are sight, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. Each sense plays a unique role in how we experience the world around us.
Sight allows us to perceive light and color, and helps us navigate our environment.
Hearing allows us to detect sound and communicate with others.
Taste and smell work together to allow us to enjoy food and recognize different scents.
Touch helps us feel textures and temperatures, and is important for physical interactions with the world.
The five senses work together to provide us with a comprehensive understanding of our environment, and this process is known as sensory integration. This integration occurs in the brain, where information from each sense is processed and combined to create a cohesive experience.
For example, when eating food, taste and smell work together to create a sensory experience that allows us to fully appreciate the flavors of the food.
Sensory integration is an important aspect of how we interact with the world, and disruptions in this process can lead to sensory processing disorders.
Perception: Interpreting Sensory Information
Interpreting sensory information is a complex process that involves the brain’s ability to synthesize and make sense of various stimuli from the environment. This process is essential in enabling us to perceive and understand the world around us.
Perception is the brain’s interpretation of the sensory information it receives, and it involves multiple stages of processing.
The first stage in sensory processing is the detection of physical stimuli through the various sensory receptors in the body.
The second stage involves the transmission of this information to the brain, where it is processed and integrated with other sensory inputs.
The final stage is the interpretation of the sensory information, which allows us to make sense of the world around us.
This process of sensory integration is crucial in enabling us to perceive and respond to our environment appropriately. It also allows us to filter out irrelevant or distracting stimuli and focus on what is most important.
Sensory Processing Disorders: Common Challenges and Symptoms
Individuals with sensory processing disorders may experience difficulties in daily activities, such as processing sensory information, responding appropriately to stimuli, and interacting with others. These disorders are characterized by atypical responses to sensory stimuli, which can lead to difficulties in daily life. Some common challenges and symptoms of sensory processing disorders include hyper- or hypo-sensitivity to sensory input, difficulty with coordination and balance, and a tendency towards sensory overload or avoidance.
To better understand the different challenges and symptoms associated with sensory processing disorders, the following table outlines some common examples:
| Sensory Processing Disorder | Common Challenges and Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Auditory Processing Disorder | Difficulty hearing in noisy environments, difficulty distinguishing sounds, sensitivity to loud noises |
| Visual Processing Disorder | Difficulty with visual tracking, difficulty distinguishing colors or shapes, sensitivity to bright lights |
| Tactile Processing Disorder | Discomfort with certain textures or clothing, oversensitivity or undersensitivity to touch, difficulty with fine motor skills |
| Vestibular Processing Disorder | Difficulty with balance and coordination, dizziness or vertigo, sensitivity to movement |
| Proprioceptive Processing Disorder | Difficulty with body awareness, clumsiness, oversensitivity or undersensitivity to pressure or gravity |
It’s important to note that individuals with sensory processing disorders may experience a combination of these challenges and symptoms, and the severity can vary from person to person. Seeking professional evaluation and support from occupational therapists or other healthcare professionals can often help individuals with sensory processing disorders manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Sensory Integration: Bringing Together Multiple Senses
By combining information from multiple sensory modalities, the brain can create a more complete representation of the environment and facilitate adaptive behavior. Sensory integration refers to the process of combining and organizing sensory information from various sources, such as vision, hearing, touch, taste, and smell. This process enables us to form a coherent and accurate perception of the world around us. Sensory integration is a fundamental aspect of human development and is essential for learning, socialization, and daily living activities.
Sensory integration occurs automatically and unconsciously. The brain integrates sensory information from different modalities to create a unified perceptual experience. For example, when we watch a movie, we not only see the images on the screen but also hear the sounds and feel the vibrations of the speakers. Our brain combines these different sources of sensory information to create a single experience of watching the movie.
Sensory integration is crucial for our ability to interact with the world and respond appropriately to different stimuli. Dysfunction in sensory integration can lead to a range of developmental and behavioral problems, including sensory processing disorders. Understanding how sensory information is integrated can help us better understand how the brain processes information and how we can support individuals with sensory processing challenges.
The Role of the Brain in Sensory Perception
The brain is responsible for processing and organizing information from different sensory modalities to create a coherent and comprehensive understanding of the environment.
When sensory information is received by the brain, it is first processed in the primary sensory cortex, which is responsible for processing sensory information from a specific modality, such as vision or touch.
From there, the information is sent to higher-order sensory cortices, which integrate information from different sensory modalities. This integration allows for the brain to create a unified perception of the environment that incorporates information from multiple senses.
The role of the brain in sensory perception is complex and involves a variety of processes, including attention, memory, and decision-making.
Attention plays a crucial role in sensory perception, as it allows the brain to focus on important sensory information while ignoring irrelevant information.
Memory is also important in sensory perception, as it allows the brain to compare current sensory information to previous experiences and make predictions about future events.
Finally, decision-making is necessary in sensory perception, as it allows the brain to choose the most appropriate response to the sensory information it receives.
Overall, the brain plays a crucial role in sensory perception, allowing us to navigate and interact with the world around us.
Techniques for Improving Sensory Integration
One effective approach to enhance the brain’s ability to process and combine information from multiple modalities involves the use of sensory integration therapy.
This approach is based on the idea that sensory input is essential for normal development and that difficulties with sensory processing can lead to a range of problems, including developmental delays, learning difficulties, and behavioral issues.
Sensory integration therapy aims to help individuals improve their ability to process and integrate sensory information by providing them with a structured program of activities that target different sensory systems.
The activities used in sensory integration therapy are designed to stimulate different sensory systems, such as the vestibular, proprioceptive, and tactile systems, and to help individuals learn how to process and combine information from these systems.
Examples of activities used in sensory integration therapy include swinging, bouncing on a therapy ball, playing with textured materials, and engaging in gross motor activities such as climbing and jumping.
By providing individuals with a more comprehensive understanding of their environment and improving their ability to process and integrate sensory information, sensory integration therapy can have a positive impact on their overall quality of life.
Seeking Help: When to Consult a Professional
One way to improve sensory integration is by using various techniques, such as sensory diets, sensory rooms, and sensory toys. These techniques can help individuals with sensory processing issues become more regulated and better able to cope with sensory input.
However, there may be times when these techniques are not enough, and seeking professional help may be necessary.
When to consult a professional for sensory processing issues can vary depending on the individual and their specific needs. Here are four signs that may indicate it’s time to seek help from a professional:
- Sensory issues are interfering with daily activities and routines.
- Sensory issues are causing significant distress or anxiety.
- Sensory issues are impacting social interactions and relationships.
- Sensory issues are causing significant academic or occupational difficulties.
Consulting with a professional, such as an occupational therapist or sensory integration specialist, can provide individuals with a more comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment plan to address their sensory processing issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the sensory system is a complex network of organs, nerves, and brain structures that work together to allow us to experience and interpret the world around us.
Each of the five senses plays a unique and important role in this process, and the brain is responsible for processing and integrating the information received from these senses.
While most people are able to effectively process and integrate sensory information, some individuals may experience challenges related to sensory processing.
Sensory integration techniques, such as those used in occupational therapy, can be helpful in improving sensory processing abilities and reducing symptoms of sensory processing disorders.
If you or someone you know is experiencing difficulties related to sensory processing, it may be beneficial to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in this area.
With the right support and interventions, individuals can learn to effectively navigate the sensory world and improve their overall quality of life.