Why Hypertension Is Linked To Stroke Risk?
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a prevalent medical condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels. It is a significant risk factor for various cardiovascular diseases, including stroke.
Stroke, a leading cause of mortality and disability worldwide, occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, resulting in cell death and neurological impairments. The relationship between hypertension and stroke is well-established, with hypertension being a major contributor to stroke risk.
Understanding the mechanisms by which hypertension increases the likelihood of stroke is crucial for effective prevention and management strategies. This article aims to explore the connection between hypertension and stroke, focusing on the increased pressure on blood vessels, weakening of blood vessel walls, reduced blood flow to the brain, and impact on other risk factors.
By comprehending the underlying mechanisms, healthcare professionals can better manage hypertension and reduce the associated risk of stroke.
Key Takeaways
- Hypertension is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including stroke.
- Hypertension increases the risk of stroke by weakening blood vessel walls and promoting the formation of blood clots.
- Managing hypertension through lifestyle modifications and medication is crucial in preventing stroke occurrence.
- Hypertension interacts with other risk factors such as age, obesity, smoking, and diabetes, amplifying the risk of stroke.
The Mechanics of Hypertension
The pathophysiology of hypertension involves sustained elevated blood pressure levels, which can damage the blood vessels in the brain and increase the risk of stroke.
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a chronic condition characterized by increased force against the arterial walls. The mechanisms of hypertension include increased sympathetic nervous system activity, abnormal kidney function, and alterations in blood vessel structure.
These mechanisms contribute to the sustained elevation of blood pressure, leading to endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation. The impact of hypertension on cardiovascular health is significant as it promotes atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries, and increases the likelihood of blood clot formation.
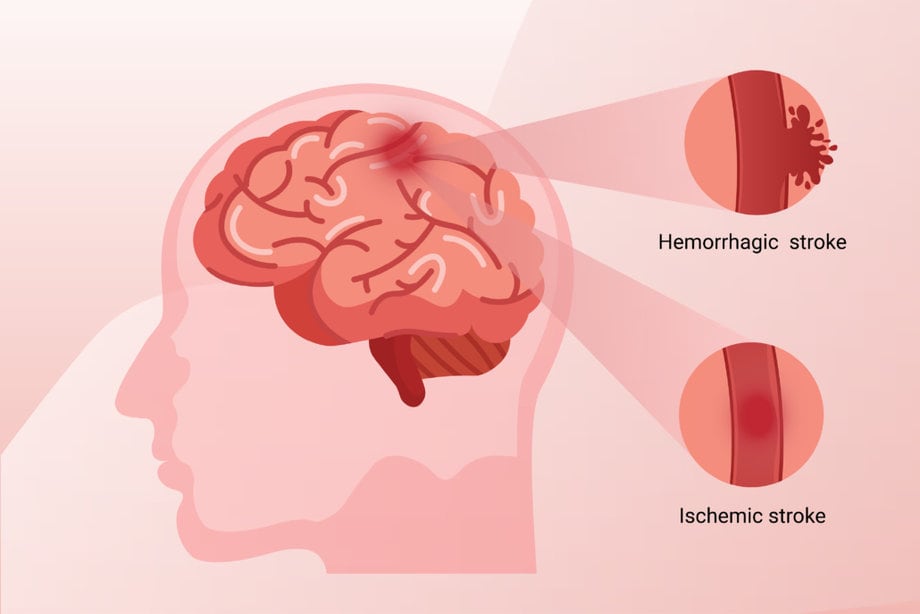
Both atherosclerosis and blood clots can disrupt blood flow to the brain, causing ischemic strokes. Additionally, hypertension can weaken blood vessel walls, making them more prone to rupture and causing hemorrhagic strokes.
Therefore, understanding the mechanisms of hypertension is crucial in comprehending its link to stroke risk.
Understanding Stroke
Understanding stroke is crucial in understanding why hypertension is linked to stroke risk. A stroke occurs when there is a disruption in the blood supply to the brain, resulting in brain cell damage or death. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a major risk factor for stroke.
The constant high pressure in the blood vessels can cause damage to the arteries, leading to the formation of blood clots or the weakening of blood vessel walls. These clots or weakened vessels can then block or rupture, resulting in a stroke.
Understanding prevention is essential in reducing stroke risk. Managing hypertension through lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, can significantly reduce the chances of having a stroke.
Recognizing the symptoms of stroke, such as sudden weakness or numbness, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, and severe headache, is also crucial in seeking immediate medical attention and minimizing the long-term effects of a stroke.
The Connection Between Hypertension and Stroke
This paragraph discusses the statistics, commonalities in risk factors, and mechanisms that link hypertension to stroke.
In terms of statistics, it is well-established that hypertension is a major risk factor for stroke, with studies consistently showing a strong positive association between the two conditions.
In addition to hypertension, there are several common risk factors for both conditions, including age, obesity, smoking, and diabetes.
Mechanistically, hypertension contributes to stroke risk by causing damage to the blood vessels and increasing the likelihood of blood clots, both of which can lead to blockages in the brain and subsequent stroke.
Statistics on the relationship between the two conditions
Statistics reveal a clear correlation between hypertension and an increased risk of stroke. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, affects a significant portion of the population, with statistics showing that around 1 in 3 adults in the United States have this condition.
Furthermore, studies have consistently demonstrated that individuals with hypertension are more likely to experience severe strokes. The relationship between hypertension and stroke severity can be attributed to the damaging effects of high blood pressure on blood vessels.
When blood pressure is consistently high, it puts strain on the arteries, causing them to become narrower and less elastic. This increases the risk of blood clots forming, which can then block blood flow to the brain, leading to a stroke.
Therefore, managing hypertension is crucial in reducing the risk of stroke.
- Hypertension affects approximately 1 in 3 adults in the United States.
- Individuals with hypertension are more likely to experience severe strokes.
- High blood pressure damages blood vessels, increasing the risk of blood clots and stroke.
Commonalities in risk factors
Commonalities can be observed in the factors that contribute to the development of both hypertension and an increased susceptibility to stroke. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a major risk factor for stroke. The mechanisms of hypertension involve increased pressure on the arterial walls, which can lead to damage and narrowing of the blood vessels.
This, in turn, can disrupt the normal flow of blood to the brain, increasing the risk of a stroke. Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing both conditions. Adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing stress are recommended strategies for reducing the risk of both hypertension and stroke.
These lifestyle modifications can help control blood pressure levels and maintain optimal cardiovascular health.
Mechanisms that link hypertension to stroke
The interplay between elevated blood pressure and the delicate network of blood vessels within the brain creates a precarious situation that can potentially result in devastating neurological consequences. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a significant risk factor for stroke, and understanding the mechanisms behind this link is crucial.
There are several ways in which hypertension can lead to strokes. Firstly, the long-term effects of hypertension on the brain can cause damage to the blood vessels, leading to their narrowing or blockage. This can result in reduced blood flow to the brain, leading to ischemic strokes.
Additionally, hypertension can weaken the blood vessel walls, making them more prone to rupture and causing hemorrhagic strokes. Other mechanisms include the promotion of atherosclerosis, formation of blood clots, and inflammation.
Recognizing and managing hypertension is essential in preventing stroke occurrence and reducing its impact on individuals.
- Narrowing or blockage of blood vessels
- Weakening of blood vessel walls
- Promotion of atherosclerosis
- Formation of blood clots
- Inflammation
Increased Pressure on Blood Vessels
This paragraph discusses the effects of high blood pressure on blood vessels, particularly in relation to the brain. High blood pressure can cause damage to blood vessels, leading to various complications.
In the case of the brain, the damage to blood vessels can increase the risk of stroke as well as the formation of blood clots.
Effects of high blood pressure on blood vessels
Effects of high blood pressure on blood vessels can lead to structural changes such as endothelial dysfunction, increased arterial stiffness, and formation of atherosclerotic plaques. The increased pressure on blood vessel walls can cause damage to the endothelium, the inner lining of the vessels, impairing its ability to dilate and constrict properly.
This dysfunction can lead to reduced blood flow and oxygen delivery to vital organs, including the brain. Moreover, high blood pressure increases the risk of blood clot formation. As the blood moves through narrowed and damaged blood vessels, it can cause turbulent flow, promoting the formation of clots. These clots can then block blood flow to the brain, leading to a stroke.
Additionally, atherosclerotic plaques can develop within the blood vessels, further narrowing them and increasing the risk of stroke. Therefore, the effects of high blood pressure on blood vessels play a significant role in the increased stroke risk associated with hypertension.
Damage to blood vessels in the brain
Damage to blood vessels in the brain is a significant consequence of high blood pressure, which further increases the risk of stroke. Hypertension causes the blood vessels in the brain to become narrow, stiff, and weak. This condition, known as cerebral small vessel disease, can lead to the formation of blood clots and the rupture of blood vessels. As a result, the brain may not receive an adequate blood supply, leading to tissue damage and potentially a stroke.
To prevent damage to blood vessels in the brain and reduce the risk of stroke, it is crucial to effectively manage hypertension. Lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, play a crucial role in blood pressure control. Additionally, medication options, such as antihypertensive drugs, may be prescribed to effectively lower blood pressure and minimize the risk of stroke.
To summarize the current subtopic, damage prevention and treatment options are essential in managing high blood pressure and reducing the risk of stroke.
| Damage Prevention | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Healthy diet | Antihypertensive drugs |
| Regular exercise | Lifestyle modifications |
| Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption |
Formation of blood clots
The formation of blood clots is a critical consequence of high blood pressure and can have severe implications for overall health. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a known risk factor for stroke, and the formation of blood clots plays a significant role in this link.
When blood pressure is consistently elevated, it can damage the lining of blood vessels, leading to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. These plaques can rupture and trigger the clotting cascade, resulting in the formation of a blood clot. If this clot travels to the brain and obstructs blood flow, it can cause a stroke.
Additionally, hypertension can cause abnormal blood clotting by altering the balance between procoagulant and anticoagulant factors in the blood. Therefore, managing hypertension is crucial in reducing the risk of stroke by preventing the formation of blood clots.
Weakening of Blood Vessel Walls
The impact of hypertension on the structure of blood vessels is a crucial aspect to consider when examining the link between hypertension and stroke risk.
Prolonged high blood pressure can lead to the weakening of blood vessel walls, making them more susceptible to damage.
This can result in the formation of aneurysms, which are abnormal bulges in blood vessels that can rupture and cause a stroke.
Impact of hypertension on the structure of blood vessels
Hypertension leads to alterations in the structure of blood vessels, resulting in diminished elasticity and increased stiffness. These changes have significant implications for the cardiovascular system.
Firstly, the effects on the heart are noteworthy. Hypertension causes the heart to work harder to pump blood against the increased resistance in the blood vessels. This leads to the thickening of the heart muscle, known as left ventricular hypertrophy, which can impair the heart’s ability to function efficiently.
Additionally, the increased stiffness of blood vessels increases the pressure on the vessel walls, making them more susceptible to damage. This can lead to the weakening of blood vessel walls and the formation of aneurysms or ruptures, which are risk factors for stroke.
In summary, the impact of hypertension on the structure of blood vessels contributes to the increased risk of stroke.
- Effects on the heart:
- Hypertension causes the heart to work harder, leading to left ventricular hypertrophy.
- Weakening of blood vessel walls:
- Increased stiffness of blood vessels makes them more prone to damage, increasing the risk of stroke.
Aneurysms and their association with stroke
Aneurysms, a consequence of the structural changes in blood vessels caused by hypertension, are characterized by the weakening of vessel walls and pose a significant threat to the integrity of the circulatory system. Aneurysm formation is closely associated with an increased risk of stroke.
When an aneurysm ruptures, it leads to bleeding in the brain, resulting in a stroke. The risk of rupture depends on the size and location of the aneurysm. Larger aneurysms have a higher likelihood of rupturing, while those located in critical areas of the brain are more likely to cause severe damage.
Treatment options for aneurysms include surgical intervention, endovascular coiling, and flow diversion techniques. These procedures aim to prevent rupture and minimize the risk of stroke, thereby addressing the link between hypertension and stroke risk.
Rupture of weakened blood vessels
Rupture of weakened blood vessels can lead to potentially life-threatening complications within the circulatory system. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a major risk factor for stroke due to its detrimental effects on blood vessels.
Prolonged and uncontrolled hypertension can result in the weakening of blood vessel walls, making them more susceptible to rupture. When blood vessels rupture, it can lead to bleeding in the brain, causing a hemorrhagic stroke. The weakened blood vessels may also form aneurysms, which are small balloon-like bulges that can burst and cause bleeding.
A ruptured blood vessel in the brain can disrupt the normal flow of blood, depriving brain cells of oxygen and nutrients, leading to permanent damage or death. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals with hypertension to manage their blood pressure effectively to minimize the risk of blood vessel damage and subsequent stroke.
Reduced Blood Flow to the Brain
Impaired cerebral circulation, resulting from elevated blood pressure, has been identified as a significant factor contributing to the increased risk of stroke associated with hypertension. Reduced blood flow to the brain, caused by elevated blood pressure, can lead to various detrimental effects on brain health. This occurs due to the damaging impact of high blood pressure on the delicate blood vessels supplying the brain. The reduced blood flow deprives the brain cells of oxygen and essential nutrients, impairing their normal functioning.
Consequently, the brain tissue becomes more vulnerable to ischemic injury, increasing the likelihood of stroke occurrence.
Unordered bullet list:
- Impaired cerebral circulation disrupts the delicate balance required for optimal brain function.
- The reduced blood flow hampers the brain’s ability to perform essential tasks, such as memory, attention, and decision-making.
- Prolonged reduction in blood flow can lead to irreversible brain damage, impacting overall cognitive abilities.
- In severe cases, reduced blood flow can result in a complete blockage of blood vessels, leading to a potentially fatal stroke.
Impact on Other Risk Factors
The impact of hypertension on other risk factors includes its influence on cholesterol levels. Hypertension has been found to increase cholesterol levels, which further contributes to the development of atherosclerosis and increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Hypertension also interacts with diabetes and obesity, creating a synergistic effect that amplifies the risk of stroke.
Understanding these connections is crucial for developing effective prevention and management strategies for individuals with hypertension.
Influence of hypertension on cholesterol levels
Influence of hypertension on cholesterol levels can significantly contribute to the increased risk of stroke.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a well-established risk factor for stroke, and its impact on cholesterol levels further exacerbates this risk.
Hypertension can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This plaque deposition can cause the arteries to narrow, reducing blood flow to the brain and increasing the likelihood of a stroke.
Moreover, hypertension can disrupt the balance of different types of cholesterol in the body, specifically increasing levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, which is commonly referred to as ‘bad’ cholesterol.
Elevated LDL cholesterol levels can promote the formation of plaque and further contribute to the risk of stroke.
Therefore, managing hypertension and maintaining healthy cholesterol levels are essential in reducing the incidence of stroke.
Interaction with diabetes and obesity
Hypertension, a major risk factor for stroke, has been found to have a significant influence on cholesterol levels. However, its interaction with other risk factors such as diabetes and obesity further exacerbates the risk.
Diabetes management plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of stroke in hypertensive individuals. Controlling blood glucose levels through medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring can help prevent complications associated with diabetes and reduce the risk of stroke.
Obesity prevention is also vital in reducing the risk of stroke in hypertensive individuals. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help control blood pressure and improve overall cardiovascular health.
To illustrate the importance of diabetes management and obesity prevention in stroke prevention, a table comparing different strategies and their effectiveness can be included:
| Strategies | Effectiveness in Stroke Prevention |
|---|---|
| Diabetes management | Reduces the risk of stroke in hypertensive individuals |
| Obesity prevention | Improves overall cardiovascular health and reduces stroke risk |
By incorporating these strategies, individuals with hypertension can effectively reduce their risk of stroke and improve their overall health.
Combined effects on stroke risk
Combining risk factors such as diabetes and obesity significantly increases the likelihood of experiencing a stroke. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common risk factor for stroke, and when it coexists with diabetes and obesity, the risk becomes even more pronounced. The mechanisms through which hypertension contributes to stroke risk are multifactorial.
Hypertension can damage blood vessels, causing them to become narrow and prone to rupture. Additionally, it can lead to the formation of blood clots, which can block blood flow to the brain. To mitigate the combined effects of these risk factors, prevention strategies should focus on managing blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and body weight.
Regular physical activity helps in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
A balanced diet low in sodium and saturated fats reduces the risk of developing hypertension.
Medication adherence is crucial for individuals with hypertension and diabetes to control their blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
Weight management through a healthy lifestyle and weight loss programs can significantly reduce the risk of stroke.
Regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar levels enables early detection and intervention.
Managing Hypertension to Reduce Stroke Risk
To effectively reduce the risk of stroke, it is crucial to adopt strategies for managing hypertension.
The management of hypertension involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medication.
Lifestyle modifications include maintaining a healthy body weight, engaging in regular physical activity, following a balanced diet low in sodium and high in fruits and vegetables, limiting alcohol intake, and quitting smoking.
These changes can help lower blood pressure and subsequently reduce the risk of stroke.
In addition to lifestyle modifications, medication may be prescribed to control hypertension.
Antihypertensive drugs, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, and calcium channel blockers, are commonly used to manage high blood pressure.
It is important for individuals with hypertension to work closely with their healthcare providers to ensure that medication is taken as prescribed and to monitor blood pressure regularly.
By effectively managing hypertension through a combination of lifestyle changes and medication, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of stroke.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of hypertension?
Symptoms of hypertension include headaches, shortness of breath, nosebleeds, and flushing. Other signs may include chest pain, dizziness, and vision problems. It is important to monitor and manage high blood pressure to prevent complications.
How can hypertension be diagnosed?
Diagnosis methods for hypertension include measuring blood pressure using a sphygmomanometer, conducting routine screenings, and evaluating medical history. Treatment options involve lifestyle modifications, such as exercise and diet changes, and medication management to control blood pressure levels effectively.
Are there any lifestyle factors that contribute to hypertension?
Diet and exercise play a crucial role in the development of hypertension. Unhealthy eating habits and a sedentary lifestyle contribute to high blood pressure. Stress management is also important as chronic stress can elevate blood pressure levels.
What are the potential complications of hypertension?
Potential complications of hypertension include heart disease, kidney damage, and vision problems. Treatment options for hypertension include lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise, as well as medication. Genetic factors also play a role in the development of hypertension.
Can hypertension be cured or only managed?
Hypertension can be managed through various treatment options, including lifestyle modifications, medication, and natural remedies. While there is no known cure for hypertension, these interventions aim to control blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of associated complications.







